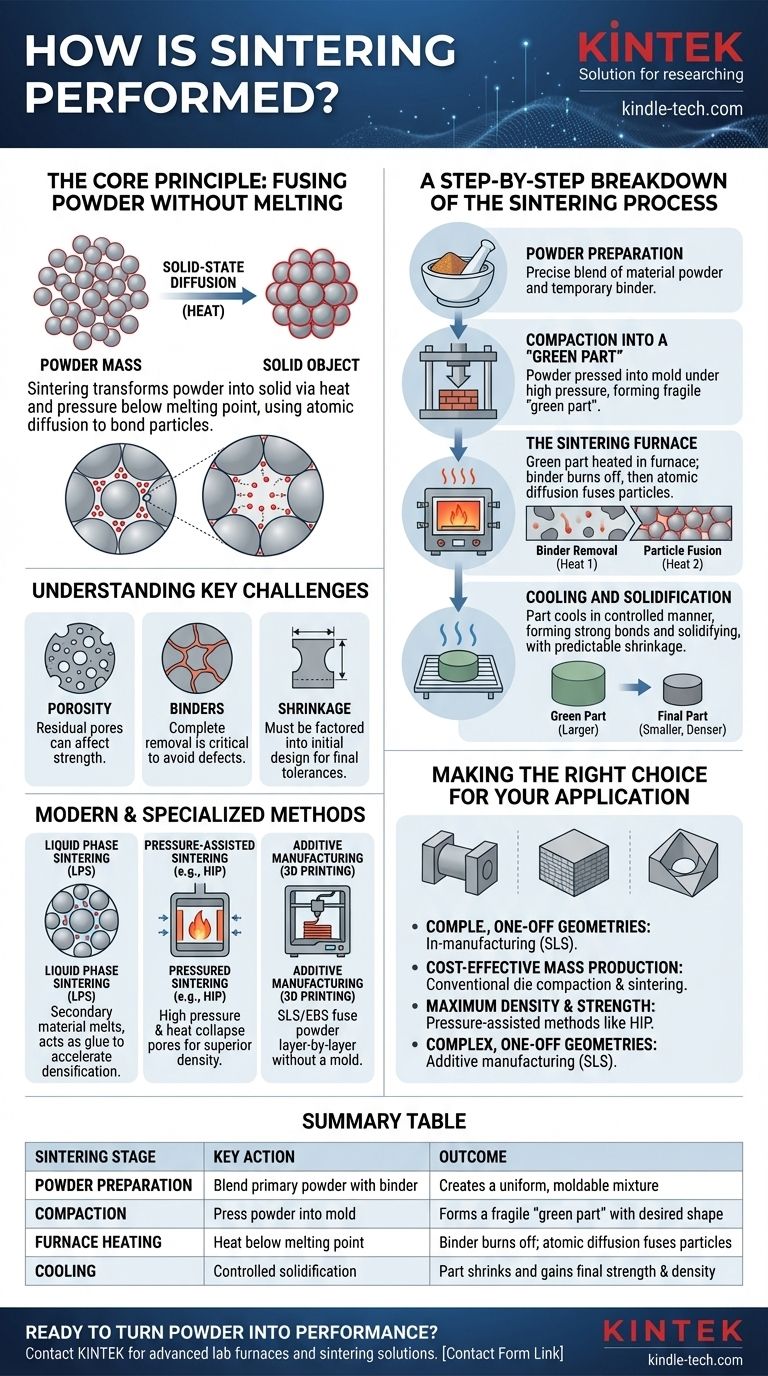
In essence, sintering is a manufacturing process that transforms a mass of powder into a solid object using heat and pressure. It consists of three primary stages: preparing and shaping the powdered material, heating it in a controlled furnace to a temperature below its melting point, and cooling it to form a densified, unified part. This method allows particles to fuse together on an atomic level without ever becoming a liquid.
The core principle of sintering is not melting, but solid-state diffusion. By applying heat energy, atoms are encouraged to migrate across the boundaries of individual powder particles, effectively bonding them into a single, dense mass. This makes it an invaluable technique for working with materials that have extremely high melting points.

The Core Principle: Fusing Powder Without Melting
What is Sintering?
Sintering, also known as frittage, is a thermal treatment for compacting and forming a solid material from powder. It is the go-to process for materials like tungsten, molybdenum, and certain ceramics, whose melting points are so high that casting them is impractical or prohibitively expensive.
The process reduces the porosity between the starting particles, increasing the density of the final object.
The Science of Atomic Diffusion
The magic of sintering happens at a microscopic level. When heated, the atoms within the powder particles gain kinetic energy. This energy allows them to move and rearrange themselves.
At the points where particles touch, atoms "jump" from one particle to another, gradually eliminating the empty space (pores) between them. This diffusion creates strong metallic or ceramic bonds, fusing the particles into a solid and coherent piece.
A Step-by-Step Breakdown of the Sintering Process
Stage 1: Powder Preparation
The process begins by creating a precise blend of materials. This often includes the primary metal or ceramic powder mixed with a temporary bonding agent.
These binders, such as wax, polymers, or even water, serve to hold the powder together in a preliminary shape during the next stage.
Stage 2: Compaction into a "Green Part"
The prepared powder is then compacted into its desired shape. This is typically done by pressing it into a mold or die under high pressure.
The resulting object is known as a "green part." It has the correct geometry but is mechanically fragile, similar in consistency to a piece of chalk, and requires the final heating stage to gain its strength.
Stage 3: The Sintering Furnace
The green part is placed into a controlled-atmosphere furnace. The heating cycle is carefully managed and occurs in two phases.
First, the temperature is raised to burn off or evaporate the binder material. Second, the temperature is increased further to just below the primary material's melting point. This is where atomic diffusion and particle fusion occur.
Stage 4: Cooling and Solidification
After being held at the sintering temperature for a specific duration, the component is cooled in a controlled manner. As it cools, the newly formed bonds strengthen, and the part solidifies into its final, dense state.
During this stage, the part shrinks as a result of the densification. This shrinkage is predictable and must be factored into the initial design of the mold and the green part.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Key Considerations
The Challenge of Porosity
While sintering significantly increases density, achieving a completely pore-free part is difficult. Residual porosity can remain, which may act as a stress concentration point and affect the mechanical properties of the final component.
The Critical Role of Binders
The binder is essential for forming the green part, but its complete removal is critical. If any binder is trapped during sintering, it can lead to internal defects, cracks, or weaknesses in the final product.
Managing Shrinkage
All sintered parts shrink. The amount of shrinkage depends on the material, initial powder density, and sintering parameters. Accurately predicting and compensating for this change in dimension is fundamental to achieving a part with the correct final tolerances.
Modern and Specialized Sintering Methods
Liquid Phase Sintering (LPS)
This variation involves adding a secondary material with a lower melting point to the powder mix. During heating, this additive melts and flows into the pores between the solid primary particles, acting like a glue. This liquid phase accelerates densification and can result in stronger parts.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering
Techniques like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) apply high pressure simultaneously with heat. The external pressure helps collapse pores more effectively, leading to significantly higher densities and improved mechanical performance compared to conventional sintering.
Additive Manufacturing (3D Printing)
Modern 3D printing technologies rely heavily on sintering. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Electron Beam Sintering (EBS) use a high-energy beam to fuse powdered material together layer by layer, building a complex part from the ground up without the need for a mold.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is cost-effective mass production of simple shapes: Conventional die compaction followed by furnace sintering is the standard, reliable method.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and superior mechanical strength: Pressure-assisted methods like Hot Isostatic Pressing (HIP) are the superior choice.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, one-off geometries or prototypes: Additive manufacturing techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) offer unmatched design freedom.
Understanding the principles behind sintering empowers you to select the precise method required to turn simple powders into high-performance components.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Stage | Key Action | Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Powder Preparation | Blend primary powder with binder | Creates a uniform, moldable mixture |
| Compaction | Press powder into a mold under high pressure | Forms a fragile 'green part' with the desired shape |
| Furnace Heating | Heat below melting point in controlled atmosphere | Binder burns off; atomic diffusion fuses particles |
| Cooling | Controlled solidification | Part shrinks and gains final strength and density |
Ready to turn your powder materials into high-performance components? The right sintering equipment is critical for achieving precise density, strength, and dimensional accuracy. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and consumables designed for reliable thermal processing of metals and ceramics. Whether you're engaged in conventional sintering, HIP, or additive manufacturing, our solutions ensure consistent results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's sintering needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is deposition in environmental chemistry? Understanding How Air Pollution Harms Ecosystems
- How thick is sputter coating SEM? Optimize Image Quality with 2-20 nm Coatings
- At what temperature will quartz melt? Unlocking Its Complex High-Temperature Journey
- What role do thermostatic shakers and Erlenmeyer flasks play in bioconversion? Optimize Your Xylose to Xylitol Process
- Why use high-precision weighing and homogenization for boride shielding? Achieve Superior Lead-Free Radiation Protection
- What is rotary extraction? Master the Art of Gentle Solvent Removal for Pure Concentrates
- What are 3 disadvantages of using biomass as a fuel? Key Challenges for Your Energy Strategy
- Why use gold for sputtering? Unlock Unmatched Conductivity and Corrosion Resistance



















