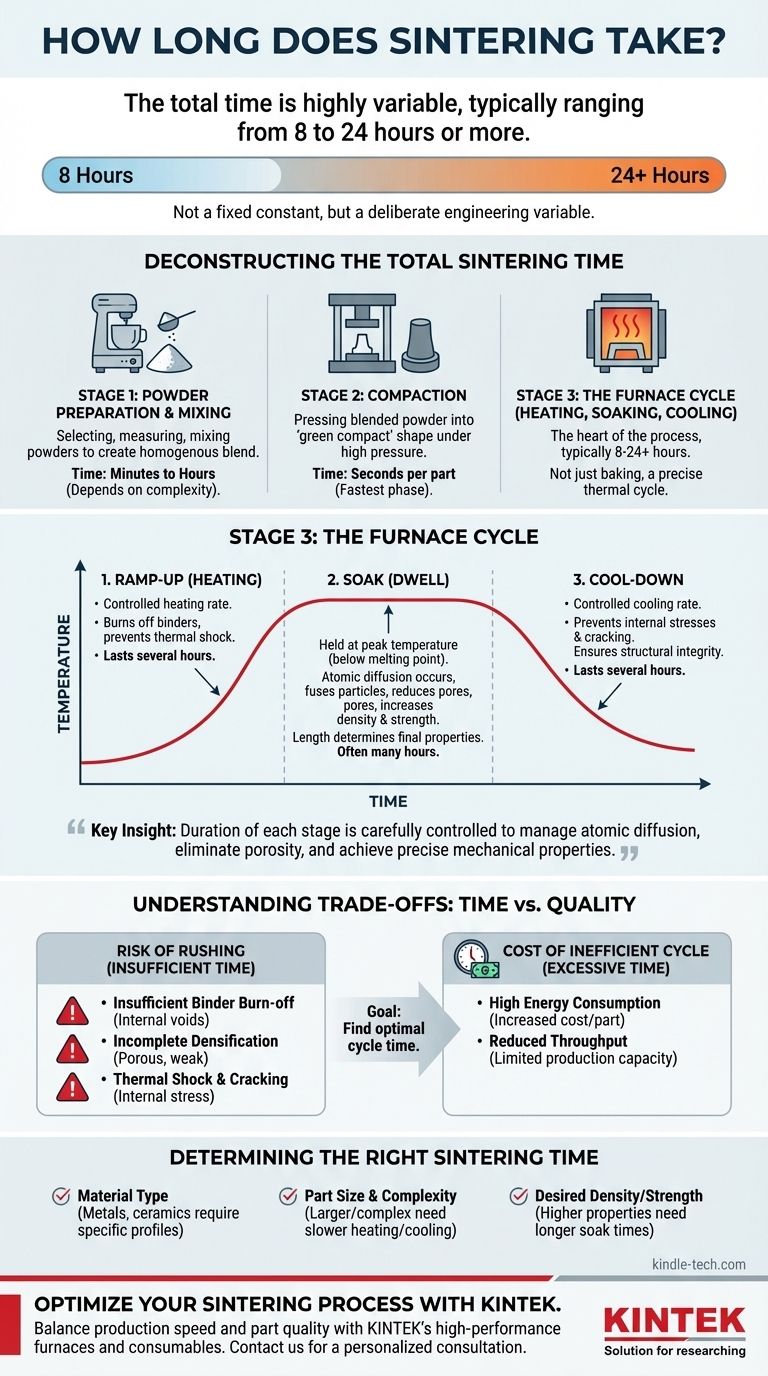
The total time for sintering is highly variable, typically ranging from 8 to 24 hours or more. This duration is not just the time spent at peak temperature but encompasses the entire furnace cycle, including controlled heating and cooling. The specific material, the size and complexity of the part, and the final desired properties like density and strength are the primary factors that dictate the exact length of the process.
The critical insight is that sintering time is not a fixed constant but a deliberate engineering variable. The duration of each stage is carefully controlled to manage atomic diffusion, eliminate porosity, and achieve the precise mechanical and physical properties required for the final component.
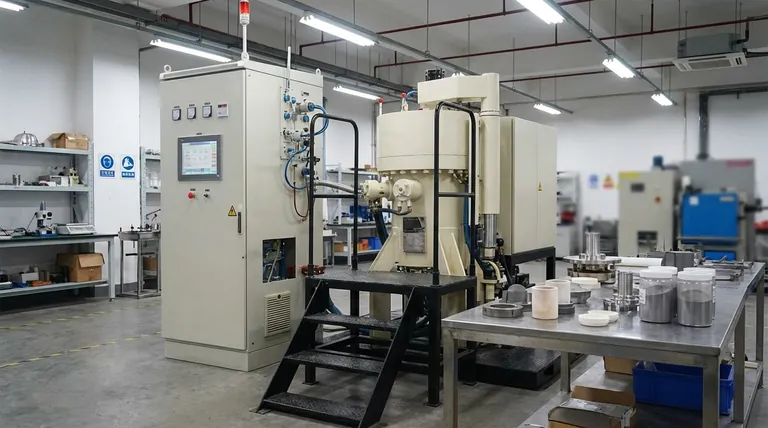

Deconstructing the Total Sintering Time
The "sintering time" people often ask about usually refers to the furnace cycle. However, the complete manufacturing process involves three distinct stages, each contributing to the overall production timeline.
Stage 1: Powder Preparation and Mixing
Before any heating occurs, the raw material must be prepared. This involves selecting, measuring, and mixing metal or ceramic powders to create a homogenous blend with the desired chemical composition.
This stage can range from minutes for a small, simple batch to several hours for large, complex industrial blends requiring strict quality control.
Stage 2: Compaction
Next, the blended powder is pressed into the desired shape, often called a "green compact." This is typically done in a rigid die under high pressure.
While the pressing action itself may only take seconds per part, this stage's overall time depends on the production volume. For the purpose of calculating a single part's journey, this is the fastest phase.
Stage 3: The Furnace Cycle (Heating, Soaking, and Cooling)
This is the heart of the sintering process and accounts for the vast majority of the time. It is not simply "baking" the part; it is a precisely controlled thermal process with three critical phases.
1. Ramp-Up (Heating): The furnace temperature is increased at a controlled rate. This slow ramp-up is crucial for burning off any residual binders from the compaction stage and preventing thermal shock, which could crack the part. This phase can last several hours.
2. Soak (Dwell): The parts are held at the peak sintering temperature, which is below the material's melting point. During this phase, atomic diffusion occurs, fusing the powder particles together, reducing pores, and increasing the part's density and strength. The length of the soak, often many hours, directly determines the final properties.
3. Cool-Down: Finally, the parts are cooled at a controlled rate. Just like the ramp-up, a slow and controlled cool-down is essential to prevent internal stresses and cracking, ensuring the part's structural integrity. This cooling period can also last for several hours.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Time vs. Quality
The duration of the sintering cycle is a direct trade-off between production speed and component quality. Understanding these compromises is key to successful manufacturing.
The Risk of Rushing the Process
Attempting to shorten the cycle to increase throughput can lead to significant defects.
- Insufficient Binder Burn-off: Ramping the temperature too quickly can trap binders, leading to internal voids and compromising the part's integrity.
- Incomplete Densification: A soak time that is too short will not allow for sufficient atomic diffusion, resulting in a porous, weaker final product that fails to meet specifications.
- Thermal Shock and Cracking: Rapid heating or cooling introduces temperature gradients that create internal stress, often causing microscopic or even visible cracks in the finished part.
The Cost of an Inefficient Cycle
While a longer cycle generally yields better properties, an unnecessarily long cycle has its own costs.
Every hour the furnace runs consumes significant energy, directly increasing the cost per part. Furthermore, longer cycles reduce the overall throughput of the equipment, limiting production capacity. The goal is always to find the optimal cycle time that reliably meets quality standards without wasting time and energy.
Determining the Right Sintering Time for Your Application
There is no single "correct" time for sintering. The ideal duration is dictated entirely by your project's goals and material constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Be prepared for longer soak times and slower ramp/cool cycles, pushing the total process time toward the upper end of the range (16-24+ hours).
- If your primary focus is high-volume production and cost-efficiency: You will need to optimize for the shortest possible cycle that still meets minimum quality specifications, which often requires extensive testing and process validation.
- If you are working with large, thick, or complex parts: Expect significantly longer cycles, as slow, controlled heating and cooling are paramount to prevent destructive thermal stresses across the part's geometry.
Ultimately, sintering time is not a fixed number but a critical engineering parameter you control to achieve your desired outcome.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Sintering Time |
|---|---|
| Material Type | Different powders (metals, ceramics) require specific temperature profiles. |
| Part Size & Complexity | Larger, thicker, or complex parts need slower heating/cooling to prevent cracking. |
| Desired Density/Strength | Higher final properties require longer "soak" times at peak temperature. |
| Furnace Cycle (Ramp, Soak, Cool) | The entire controlled thermal process, typically 8-24+ hours. |
Optimize your sintering process with KINTEK.
Struggling to balance production speed with part quality? The right lab equipment is the key. KINTEK specializes in high-performance furnaces and consumables designed for precise thermal control, helping you achieve the perfect density and strength for your components while maximizing efficiency.
Our experts can help you determine the ideal sintering cycle for your specific materials and application. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your laboratory's capabilities and throughput.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
People Also Ask
- What conditions does a vacuum hot press provide for Al2O3/ZrO2 sintering? Achieve 1550°C and 30 MPa Densification
- What is the impact factor of powder metallurgy progress? A 2022 Analysis & Context
- What are the advantages of a vacuum hot pressing furnace? Achieve high-density NTC ceramics with superior stability.
- What are the advantages of using a vacuum hot pressing sintering furnace? Superior Density for Nanocrystalline Fe3Al
- What are the advantages of vacuum sintering? Achieve Superior Purity, Strength, and Performance



















