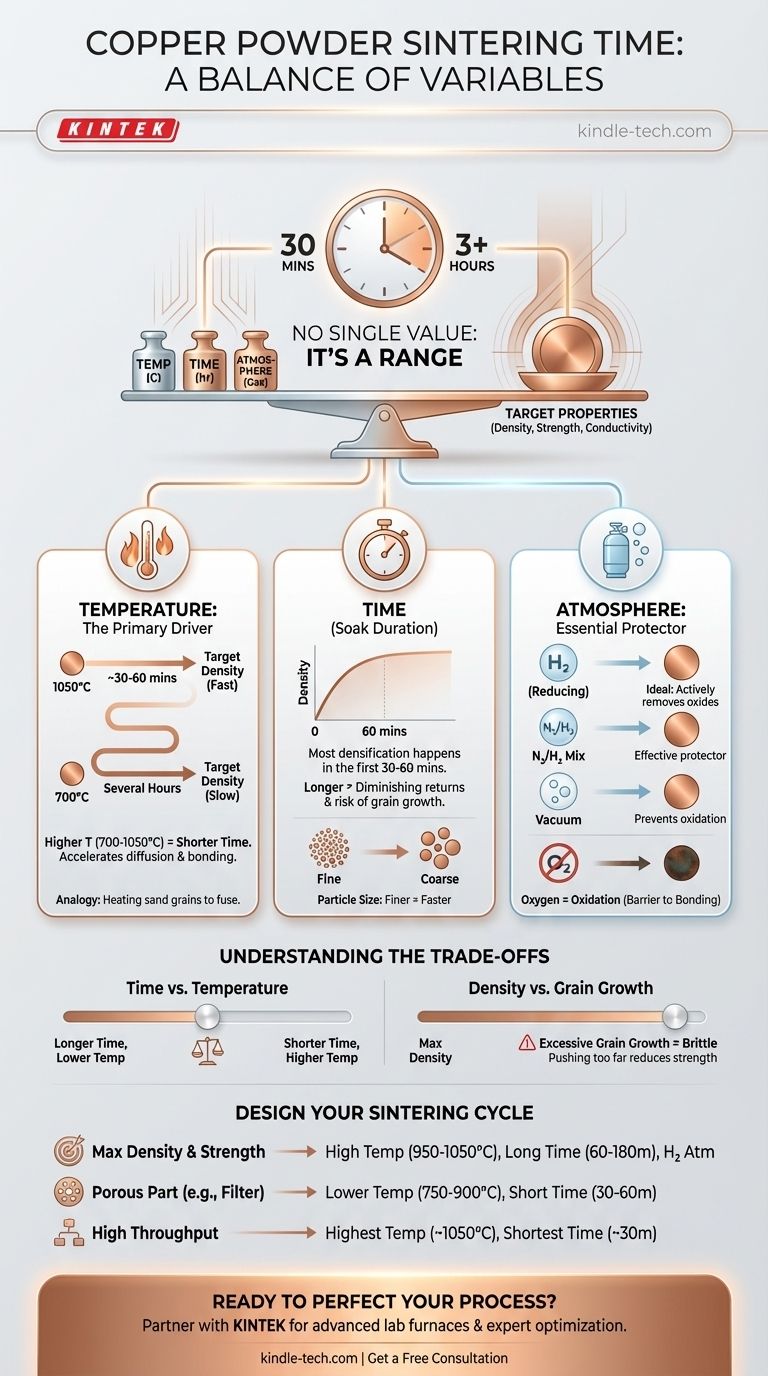
The time required to sinter copper powder is not a single value but a range, typically from 30 minutes to several hours at the peak temperature. This duration is critically dependent on the sintering temperature, the protective atmosphere used, and the final density you need to achieve. For example, a higher temperature drastically reduces the required time.
Sintering is a process controlled by a balance of time, temperature, and atmosphere. The central challenge isn't just about how long to heat the copper, but how to manipulate these variables to achieve the specific density, strength, and electrical conductivity your final component requires.
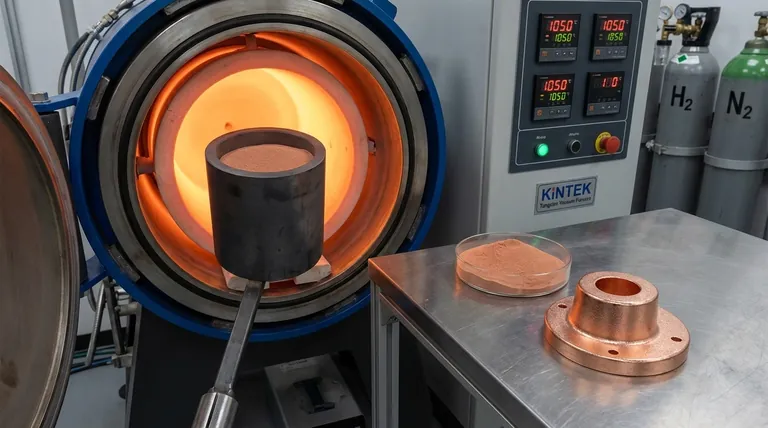

Understanding the Sintering Process
Sintering is a thermal treatment that bonds powder particles into a solid, coherent mass at a temperature below the material's melting point. For copper, which melts at 1085°C (1984°F), this process typically occurs between 700°C and 1050°C.
Imagine individual grains of sand in a sandbox. Sintering is like heating that box just enough for the surfaces of the grains to become sticky and fuse together at their contact points, eventually turning the loose sand into a single, solid sandstone block without ever melting it completely.
The Critical Variables That Control Sintering Time
The answer to "how long?" depends entirely on your specific process parameters. Understanding these variables gives you control over the final outcome.
Temperature: The Primary Driver
Temperature is the most influential factor. Higher temperatures provide more thermal energy, accelerating the atomic diffusion that bonds particles together.
As a rule, increasing the sintering temperature allows you to significantly decrease the sintering time needed to reach a target density. Sintering at 950°C might take hours, while sintering at 1050°C could achieve a similar or better result in under an hour.
Time: The Duration at Temperature
This is the "soak time" at your peak temperature. Longer times allow for more complete diffusion, reducing porosity and increasing the density and strength of the part.
However, the benefits of time have diminishing returns. The most significant densification often occurs in the first 30 to 60 minutes. Extending the time for hours primarily serves to eliminate the last few percentages of porosity and homogenize the microstructure.
Atmosphere: The Essential Protector
Copper readily oxidizes when heated in the presence of oxygen. A layer of copper oxide on the powder particles will act as a barrier, completely preventing them from bonding together.
Therefore, sintering copper must be done in a controlled atmosphere.
- Reducing Atmospheres: A mix of nitrogen and hydrogen (e.g., 95% N₂ / 5% H₂) or pure hydrogen is ideal. The hydrogen actively removes any surface oxides, promoting clean particle-to-particle contact.
- Inert Atmospheres: Argon or a pure nitrogen atmosphere can prevent further oxidation but will not clean existing oxides from the powder.
- Vacuum: Sintering in a vacuum is also highly effective at preventing oxidation.
Particle Size and Shape
The characteristics of your starting powder play a significant role. Finer powders, with their higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, have more energy driving the sintering process.
Smaller, more irregular particles will begin to bond and densify much faster than larger, spherical particles under the same conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a sintering cycle is an exercise in balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" method, only the one that is best for your specific application and constraints.
Time vs. Temperature
You can often achieve a similar final density by using a lower temperature for a longer time or a higher temperature for a shorter time. The high-temperature, short-time approach is often preferred in industrial settings to increase throughput and reduce energy costs per part.
Density vs. Grain Growth
Pushing for maximum density with very high temperatures or extremely long times can lead to a negative side effect: grain growth. As smaller grains are consumed by larger ones, the material's average grain size increases.
Excessive grain growth can reduce the mechanical strength and toughness of the final copper component, making it more brittle. This is a critical trade-off to manage.
Cost vs. Performance
The choice of atmosphere involves a trade-off between cost and effectiveness. Pure hydrogen is the most effective reducing agent but is more expensive and requires more stringent safety protocols than a nitrogen/hydrogen mix. A simple vacuum furnace may be cheaper to operate but slower to cycle.
Designing Your Sintering Cycle
To determine the right sintering time, you must first define your goal. Use these guidelines as a starting point for developing your specific process.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and strength: Plan for higher temperatures (950°C to 1050°C) and longer hold times (60 to 180 minutes) in a highly reducing atmosphere like hydrogen.
- If your primary focus is creating a porous part (e.g., a filter or wick): Use lower temperatures (750°C to 900°C) and shorter times (30 to 60 minutes) to encourage particle "necking" without full densification.
- If your primary focus is minimizing cycle time for high throughput: Use the highest temperature your furnace and component can safely tolerate (approaching 1050°C) to reduce the required hold time, potentially to as little as 30 minutes.
By consciously controlling these variables, you move from guessing at a time to engineering the precise properties of your final copper component.
Summary Table:
| Sintering Variable | Typical Range for Copper | Impact on Time & Result |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | 700°C - 1050°C | Higher temperature drastically reduces required time for a given density. |
| Time (at peak temperature) | 30 minutes - 3+ hours | Longer times increase density and strength, but with diminishing returns. |
| Atmosphere | H₂, N₂/H₂ Mix, Vacuum | Essential to prevent oxidation; a reducing atmosphere (H₂) promotes bonding. |
| Particle Size | Fine to Coarse | Finer powders sinter faster due to higher surface area. |
Ready to Perfect Your Copper Sintering Process?
Mastering the balance of time, temperature, and atmosphere is key to producing copper components with the exact density, strength, and conductivity you need. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab furnaces and consumables required for precise and repeatable sintering.
Our experts can help you select the right equipment and optimize your sintering cycle for maximum efficiency and performance. Contact us today to discuss your specific application and discover how KINTEK can be your partner in materials processing.
Get a Free Consultation & Optimize Your Sintering Cycle
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why is sintering easier in the presence of a liquid phase? Unlock Faster, Lower-Temperature Densification
- What is the sintering process of powder metallurgy? Transform Powder into Durable Metal Parts
- What is vacuum sintering? Achieve Unmatched Purity and Performance for Advanced Materials
- Why is environmental control within a vacuum furnace important for diffusion bonding? Master Titanium Alloy Laminates
- What are the defects in sintered parts? Avoid Warping, Cracking, and Porosity Issues



















