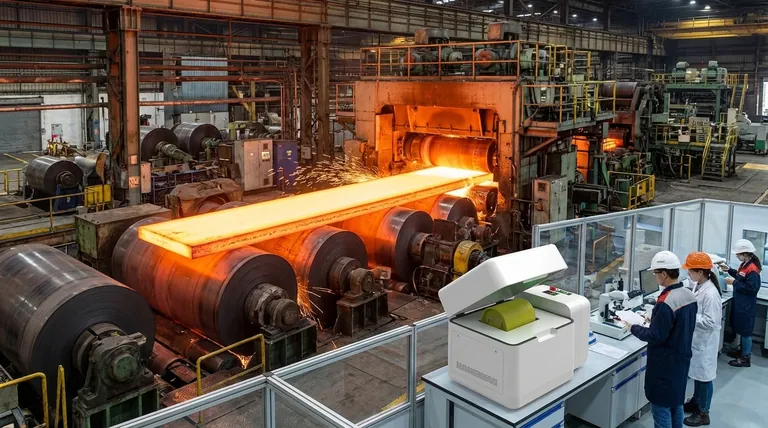
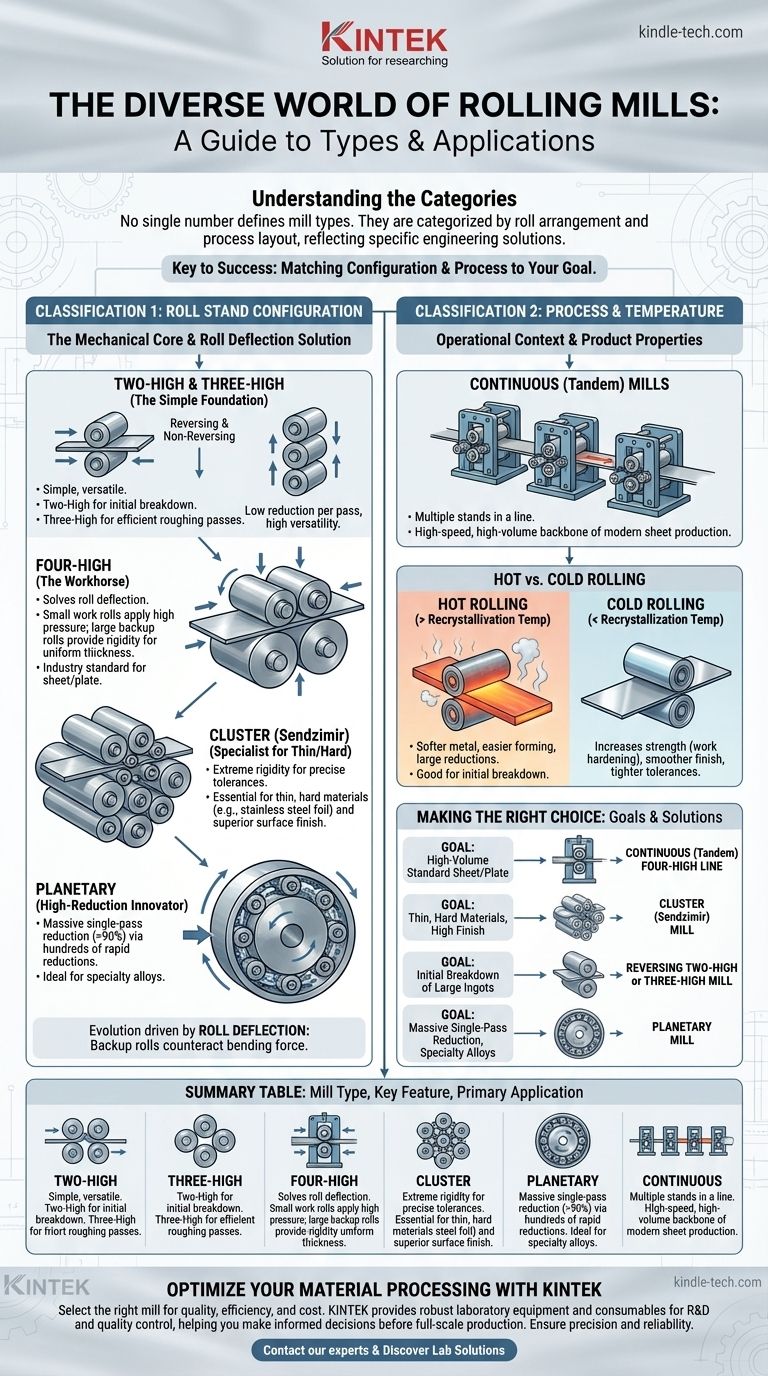
There is no single definitive number for the types of rolling mills, as they are classified based on different criteria, such as their mechanical configuration, the temperature of the metal, or their operational layout. The most common way to categorize them is by the arrangement of their rolls, which leads to primary types like the Two-High, Three-High, Four-High, Cluster, and Planetary mills.
The "type" of a rolling mill is not a simple label but a reflection of the specific engineering problem it was designed to solve. The key is to understand how a mill's roll configuration (e.g., Two-High vs. Cluster) and its process flow (e.g., Single Stand vs. Continuous) determine its capabilities, cost, and application.

Two Fundamental Ways to Classify Rolling Mills
To truly understand the landscape, you must recognize that mills are categorized along two primary axes: their physical roll arrangement and their overall process layout.
Classification 1: By Roll Stand Configuration
The arrangement of the rolls in a single "stand" is the most fundamental classification. This design directly dictates the mill's ability to apply pressure, reduce thickness, and control the final product's quality.
The Simple Foundation: Two-High & Three-High Mills
A Two-High mill is the simplest form, consisting of two opposing rolls. It may be "reversing," where the material passes back and forth, or "non-reversing."
A Three-High mill uses three rolls to allow the material to be passed in both directions without reversing the roll rotation, increasing efficiency over a basic Two-High setup. These are often used for initial roughing passes.
The Workhorse: Four-High Mills
The Four-High mill is a critical advancement and a workhorse of the industry. It uses two small-diameter work rolls that contact the metal, supported by two much larger backup rolls.
This design brilliantly solves the problem of roll deflection. The small work rolls apply higher specific pressure for better reduction, while the massive backup rolls provide rigidity to prevent the work rolls from bending, ensuring a uniform thickness across the product width.
The Specialist for Thin & Hard Materials: Cluster Mills
A Cluster mill, also known as a Sendzimir mill, takes the Four-High concept to its extreme. It uses very small work rolls supported by multiple layers of backup rolls in a cluster arrangement.
This configuration provides immense rigidity, making it essential for cold rolling very hard or thin materials, such as stainless steel or foils, to precise tolerances with a superior surface finish.
The High-Reduction Innovator: Planetary Mills
A Planetary mill is a highly specialized design. It features one large backup roll surrounded by numerous small "planetary" work rolls held in a cage.
As the main backup roll rotates, the planetary rolls rotate in the opposite direction while revolving around the main roll, delivering hundreds of small, rapid reductions. This allows for massive thickness reduction—over 90%—in a single pass, which is ideal for certain specialty alloys.
Classification 2: By Process and Temperature
Beyond the individual stand, mills are also defined by how they fit into the larger production line and the temperature at which they operate.
Continuous (or Tandem) Mills
A Continuous mill consists of multiple stands (e.g., several Four-High stands) arranged in a single line. The metal passes continuously from one stand to the next, with its thickness progressively reduced at each stage.
This high-speed, high-volume configuration is the backbone of modern steel and aluminum sheet production.
Hot vs. Cold Rolling Mills
This is a process distinction, not a mechanical one. Any mill configuration can be used for either process.
Hot rolling occurs above the metal's recrystallization temperature. This makes the metal softer and easier to form, allowing for large reductions in size.
Cold rolling occurs below the recrystallization temperature. This process increases the metal's strength and hardness (work hardening) and produces a smoother, more refined surface finish with tighter dimensional tolerances.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Complexity vs. Capability
Choosing a mill type involves balancing cost, capability, and the specific requirements of the final product.
Cost and Maintenance
Simple Two-High mills are relatively inexpensive and easy to maintain. In contrast, complex Cluster and Planetary mills are extremely expensive to build and operate, requiring specialized maintenance and highly skilled personnel.
The Problem of Roll Deflection
The evolution from Two-High to Four-High and then Cluster mills is a direct response to roll deflection. Under immense rolling pressure, a simple roll will bend like a bow, making the resulting sheet thinner at the edges and thicker in the middle. Backup rolls are the solution to counteract this force and maintain a flat, uniform product.
Reduction vs. Versatility
A simple Two-High mill might be versatile but offers low thickness reduction per pass. A Planetary mill offers enormous reduction in one pass but is a highly specialized machine with limited versatility. Four-High mills offer a practical balance of good reduction and operational flexibility.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best mill is the one engineered for the specific task.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of standard sheet or plate: A Continuous (Tandem) line of Four-High mills is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is processing hard, thin materials to a high-quality finish (like stainless steel foil): A Cluster (Sendzimir) Mill is the necessary tool.
- If your primary focus is initial breakdown of large ingots or blooms: A powerful Two-High or Three-High reversing mill is the typical choice for this "cogging" stage.
- If your primary focus is achieving massive thickness reduction in a single pass for specialty alloys: A Planetary Mill provides a unique and powerful solution.
Ultimately, the design of a rolling mill is a direct and elegant answer to a specific material and production challenge.
Summary Table:
| Mill Type | Key Feature | Primary Application |
|---|---|---|
| Two-High | Simple, two opposing rolls | Initial breakdown of ingots, versatile |
| Three-High | Three rolls for efficient reversing | Roughing passes |
| Four-High | Small work rolls + large backup rolls | High-volume sheet/plate production |
| Cluster (Sendzimir) | Multiple backup rolls for extreme rigidity | Thin, hard materials (e.g., stainless steel foil) |
| Planetary | Massive single-pass reduction | Specialty alloys requiring >90% reduction |
| Continuous (Tandem) | Multiple stands in a line | High-speed, high-volume production lines |
Optimize Your Material Processing with KINTEK
Selecting the right rolling mill is critical to achieving your production goals for quality, efficiency, and cost. The wrong equipment can lead to inconsistent product thickness, surface defects, and unnecessary downtime.
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables to support your R&D and quality control processes. Whether you are testing new alloys or verifying material properties, our solutions help you make informed decisions before scaling to full production.
Let us help you ensure your processes are built on a foundation of precision and reliability.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK's lab solutions can enhance your operational success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- Laboratory Ten-Body Horizontal Jar Mill for Lab Use
- Laboratory Horizontal Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of a two-high rolling mill? Cost-Effective Durability for Heavy Reduction
- What is the difference between extruded and co extruded? A Guide to Single vs. Multi-Layer Plastic Profiles
- What fillers for rubber compounds? Choose the Right Filler for Performance vs. Cost
- What is the manufacturing process of rubber molding? Injection, Compression, or Transfer Molding?
- What is a two-roll differential speed mill? Achieve Superior Polymer Mixing & Dispersion
- How many types of rolling are there? A Guide to Metal Forming Processes
- Why is the dynamic mixing mode necessary for high-strength HPE-CSPE? Unlock Superior Elastomer Performance
- How profitable is injection molding? Unlock High-Volume Manufacturing Profitability



















