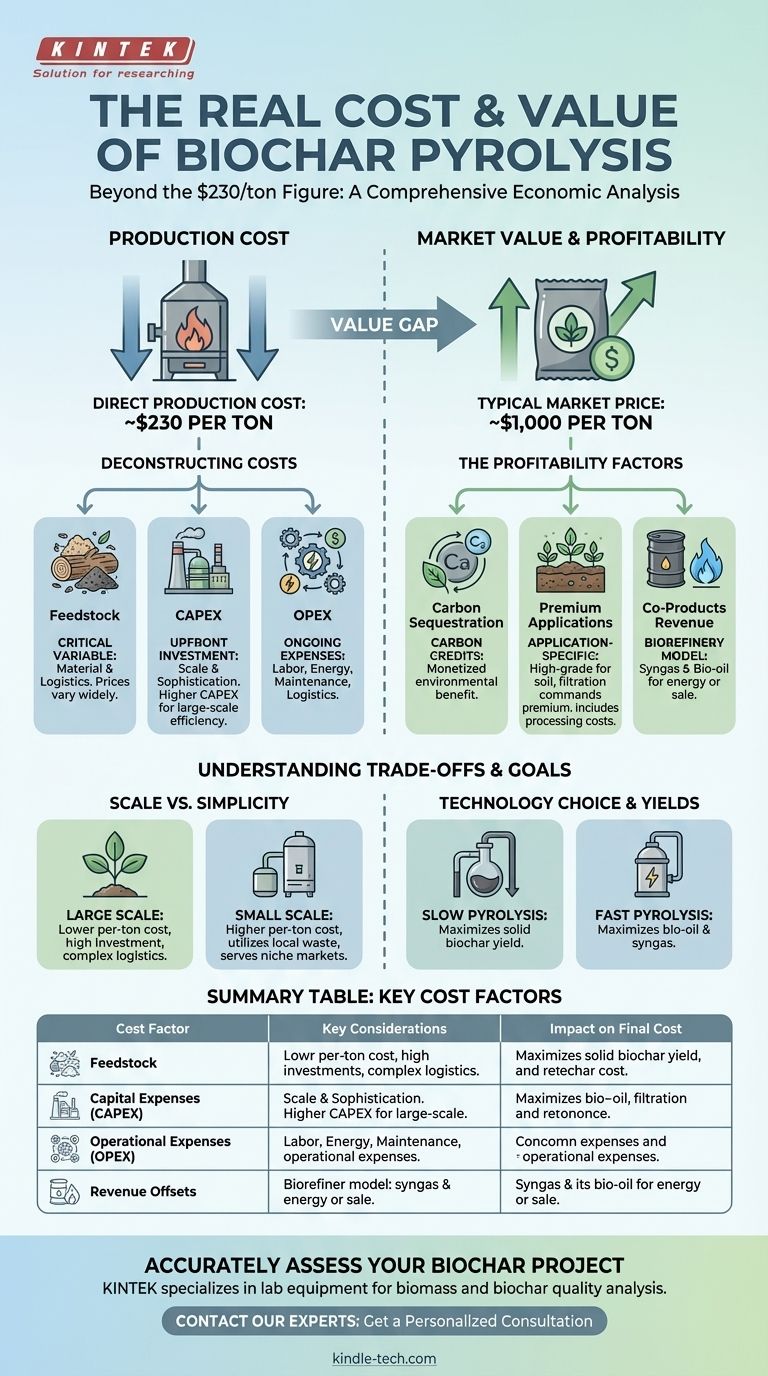
To be clear, the direct production cost for biochar via pyrolysis is often cited around $230 per ton. However, this single figure is deceptively simple and represents only one part of a much larger economic equation. The final cost and overall financial viability are heavily influenced by feedstock expenses, operational scale, and the technology used.
The core issue isn't a single production cost, but understanding the entire value chain. The significant gap between the ~$230 production cost and a market price of ~$1,000 per ton is where the real analysis of profitability lies, driven by factors beyond the pyrolysis unit itself.

Deconstructing the Full Cost of Biochar
The $230 per ton figure is a helpful benchmark, but to assess a real-world project, you must break down the costs into their core components.
The Critical Role of Feedstock
The raw material, or feedstock, is often the single most significant variable in the cost equation. Its price can range from a net cost (for agricultural waste) to a significant expense.
The type of feedstock (e.g., wood chips, manure, crop residue) also dictates the quality and characteristics of the final biochar, directly impacting its market value.
Capital Expenses (CAPEX)
This is the upfront cost of the pyrolysis equipment. These costs vary dramatically based on the scale and sophistication of the technology.
A small, farm-scale unit might have a relatively low initial cost, while a large, continuous industrial plant represents a major investment but offers significant economies of scale, lowering the per-ton production cost.
Operational Expenses (OPEX)
These are the ongoing costs required to run the facility. Key operational costs include labor, energy for drying feedstock, routine maintenance, and logistics.
Automation can reduce labor costs in larger facilities, but requires a higher initial CAPEX.
Why the Market Price is Much Higher
The large gap between the production cost and the typical market price of $1,000 per ton is not just profit margin. It reflects the additional value created after the char leaves the pyrolysis unit.
Value from Carbon Sequestration
A major driver of biochar's high value is its ability to sequester carbon for long periods. This environmental benefit is monetized through carbon credits.
These credits can be sold, creating a substantial revenue stream that is entirely separate from the physical sale of the biochar product itself.
Application-Specific Value and Processing
Not all biochar is created equal. High-grade biochar designed for specific applications, such as soil amendment for high-value crops or for use in advanced filtration, commands a premium.
Costs for post-production processing, such as grinding, pelletizing, bagging, and transportation, must also be factored into the final price.
Revenue from Co-Products
Modern pyrolysis systems are biorefineries. They also produce syngas (a combustible gas) and bio-oil, which can be used to generate heat and power for the operation or sold as products.
Effectively utilizing these co-products can offset operational costs and significantly improve the overall profitability of the project.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right approach requires balancing several key factors. There is no single "best" solution; the optimal setup depends entirely on your specific goals.
Scale vs. Simplicity
Large-scale, centralized plants benefit from economies of scale, producing biochar at a lower per-ton cost. However, they require massive initial investment and complex logistics for feedstock supply.
Small, decentralized units have a higher per-ton production cost but can process local waste streams, eliminating transportation costs and serving niche markets effectively.
Technology Choice and Yields
The type of pyrolysis directly impacts the output. Slow pyrolysis maximizes the yield of biochar, making it ideal if the solid product is your primary goal.
Fast pyrolysis operates at higher temperatures and produces more bio-oil and syngas. This approach is better suited for projects focused on energy production or biorefining.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine the true cost and potential of a biochar project, you must first define its primary purpose.
- If your primary focus is waste management and soil improvement: A smaller-scale system may be ideal, as the main value comes from eliminating waste disposal costs and improving your own land.
- If your primary focus is commercial biochar production: A detailed feasibility study is critical to secure a consistent, low-cost feedstock source and identify a high-value end market.
- If your primary focus is maximizing revenue and energy generation: An integrated biorefinery model that captures and utilizes bio-oil and syngas is necessary to create multiple, stable revenue streams.
Ultimately, a successful biochar venture depends on a holistic understanding of the entire economic and operational ecosystem, from feedstock sourcing to final market application.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Key Considerations | Impact on Final Cost |
|---|---|---|
| Feedstock | Type (wood, manure, etc.), sourcing, and transportation costs. | Often the largest variable cost; can be a net expense or a credit. |
| Capital Expenses (CAPEX) | Scale of the pyrolysis unit (small farm-scale vs. large industrial plant). | Higher upfront cost for large-scale systems, but lower per-ton cost. |
| Operational Expenses (OPEX) | Labor, energy for drying, maintenance, and logistics. | Ongoing costs influenced by automation and system efficiency. |
| Revenue Offsets | Value of carbon credits, sales of co-products (syngas, bio-oil). | Can significantly reduce net cost and improve profitability. |
Ready to accurately assess the cost and profitability of your biochar project?
The $230/ton figure is just the starting point. Your specific costs and revenue potential depend on your unique feedstock, operational goals, and technology choice. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for analyzing biomass and biochar quality, helping you make data-driven decisions from the start.
Contact our experts today to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can help you optimize your pyrolysis process, validate biochar quality, and maximize your return on investment.
Get a Personalized Consultation
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Laboratory Jaw Crusher
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products



















