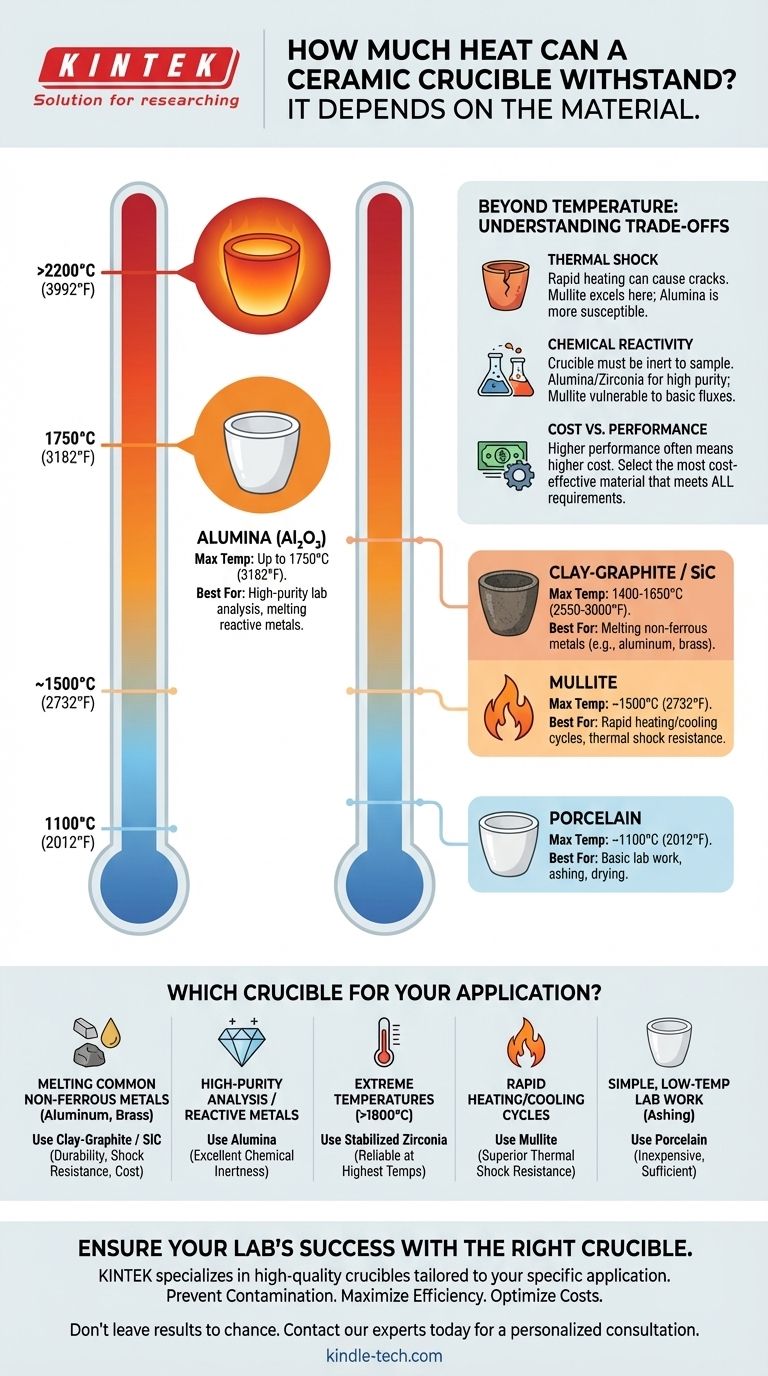
The heat a ceramic crucible can withstand depends entirely on its specific material composition, with maximum temperatures ranging from around 1100°C (2012°F) for basic porcelain to over 2200°C (3992°F) for stabilized zirconia. Simply asking about "ceramic" is too broad, as different ceramic materials are engineered for vastly different thermal and chemical environments.
The critical takeaway is not the maximum temperature a crucible can survive, but matching the right type of ceramic—like Alumina, Zirconia, or Mullite—to your specific application's temperature, heating rate, and chemical contents. Choosing incorrectly can lead to crucible failure, sample contamination, or both.

Why "Ceramic" is Too Broad a Term
The word "ceramic" describes a vast category of inorganic, non-metallic materials. A porcelain teacup and a space shuttle tile are both ceramics, yet they have fundamentally different properties.
When selecting a crucible, you are not choosing a generic "ceramic" one; you are choosing one made of a specific engineered material like aluminum oxide or zirconium oxide. Each has a distinct performance profile.
A Breakdown of Common Crucible Materials
Understanding the primary types of crucibles is the first step toward making an informed choice. The temperatures listed are typical maximums, but purity and manufacturing methods can cause variations.
Alumina (Al₂O₃) Crucibles
High-purity alumina is one of the most common and versatile crucible materials. It is known for its excellent chemical inertness and high-temperature stability.
Maximum Temperature: Typically up to 1750°C (3182°F).
Best For: Melting glass, high-purity metal alloys, and lab applications where sample contamination must be minimized.
Zirconia (ZrO₂) Crucibles
Zirconia, often stabilized with yttria, offers one of the highest service temperatures of any common ceramic. It is extremely refractory (resistant to heat and pressure) but comes at a premium cost.
Maximum Temperature: Can exceed 2200°C (3992°F).
Best For: Applications involving extremely high temperatures, such as melting platinum group metals or superalloys.
Mullite (3Al₂O₃·2SiO₂) Crucibles
Mullite is an aluminosilicate ceramic prized for its exceptional resistance to thermal shock. While its maximum temperature is lower than pure alumina, it can withstand rapid heating and cooling cycles much better.
Maximum Temperature: Around 1500°C (2732°F).
Best For: Applications with fast heating rates or where the crucible may be subject to thermal stress, such as in certain metal melting furnaces.
Clay-Graphite and Silicon Carbide (SiC) Crucibles
These are composite materials often used in foundries. The graphite or SiC provides outstanding thermal conductivity and thermal shock resistance, allowing for fast melting cycles.
Maximum Temperature: Generally between 1400°C and 1650°C (2550°F and 3000°F).
Best For: Melting non-ferrous metals like aluminum, brass, and copper in foundry settings. They are durable and cost-effective for these tasks.
Porcelain Crucibles
Glazed porcelain is a familiar lab staple. It is a cost-effective material for general-purpose, lower-temperature heating.
Maximum Temperature: Typically around 1100°C (2012°F).
Best For: Basic laboratory procedures like drying precipitates or ashing (burning off) organic samples at moderate temperatures.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Beyond Temperature
Focusing only on the maximum temperature is a common and costly mistake. The operational environment is equally important.
Thermal Shock: The Risk of Rapid Heating
Thermal shock is the stress induced in a material by a rapid change in temperature. A crucible with poor thermal shock resistance can crack or shatter if heated or cooled too quickly.
Materials like Mullite and Clay-Graphite excel here. High-purity Alumina, while having a higher temperature limit, can be more susceptible to cracking from rapid temperature changes.
Chemical Reactivity: Protecting Your Sample
A crucible must be chemically inert to the material it holds at high temperatures. The wrong combination can cause the crucible to degrade or, more commonly, contaminate your sample.
For example, highly basic fluxes or slags can attack silica-bearing crucibles like Mullite. In these cases, a more inert material like high-purity Alumina or Zirconia is a better choice.
Cost vs. Performance
There is a direct correlation between performance and cost. A porcelain crucible may cost a few dollars, while a large, high-purity Zirconia crucible can cost thousands.
Always select the most cost-effective material that meets all of your technical requirements, not just the one with the highest temperature rating.
Selecting the Right Crucible for Your Application
Use your specific goal to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is melting common non-ferrous metals (aluminum, brass): A Clay-Graphite or Silicon Carbide crucible offers the best balance of durability, thermal shock resistance, and cost.
- If your primary focus is high-purity lab analysis or melting reactive metals: High-purity Alumina is the standard choice due to its excellent chemical inertness.
- If your primary focus is working at extreme temperatures above 1800°C: Stabilized Zirconia is one of the few materials that can perform reliably in this range.
- If your primary focus is withstanding rapid heating and cooling cycles: Mullite provides superior thermal shock resistance at a lower cost than pure Alumina.
- If your primary focus is simple, low-temperature lab work like ashing: An inexpensive Porcelain crucible is perfectly sufficient.
Choosing the right crucible is about matching the tool to the specific thermal, chemical, and mechanical demands of your work.
Summary Table:
| Material | Max Temperature (°C) | Max Temperature (°F) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Porcelain | ~1100°C | ~2012°F | Basic lab work, ashing, drying |
| Mullite | ~1500°C | ~2732°F | Applications with rapid heating/cooling cycles |
| Clay-Graphite / SiC | 1400-1650°C | 2550-3000°F | Melting non-ferrous metals (e.g., aluminum, brass) |
| Alumina (Al₂O₃) | Up to 1750°C | Up to 3182°F | High-purity lab analysis, melting reactive metals |
| Zirconia (ZrO₂) | >2200°C | >3992°F | Extreme temperature applications (e.g., platinum group metals) |
Ensure Your Lab's Success with the Right Crucible
Selecting the correct crucible is critical for the safety, efficiency, and accuracy of your work. The wrong choice can lead to equipment failure, sample contamination, and costly delays.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory equipment needs. We specialize in providing high-quality crucibles and consumables tailored to your specific application, whether you're in research, quality control, or production.
We help you:
- Prevent Contamination: Match the crucible material to your sample's chemical properties.
- Maximize Efficiency: Select crucibles with the right thermal shock resistance for your heating cycles.
- Optimize Costs: Get expert advice to choose the most cost-effective solution without compromising performance.
Don't leave your results to chance. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation on the best crucible for your process.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- Why is the use of high-purity alumina crucibles necessary for NMC powders? Ensure Purity in Cathode Synthesis
- What role do high-purity alumina crucibles play in high-temperature steam oxidation? Ensure Data Integrity up to 1350°C
- How does the use of corrosion-resistant ceramic crucibles ensure the chemical purity of materials? | KINTEK
- What role does an Alumina Crucible play in the high-temperature solid-state synthesis of Na3OBr? Ensure Sample Purity



















