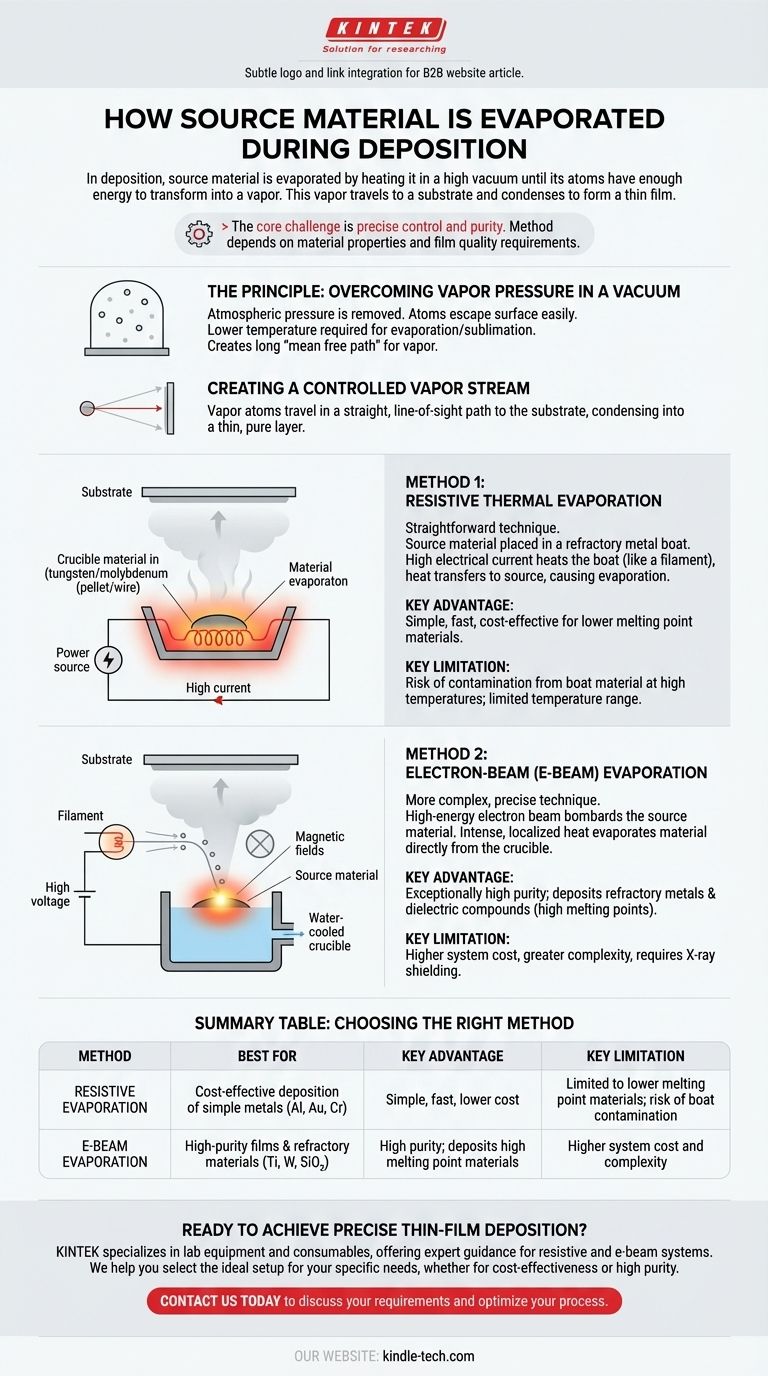
In deposition, source material is evaporated by heating it in a high vacuum until its atoms have enough energy to transform into a vapor. This process is not a single method but is primarily accomplished in two ways: by passing an electrical current through a holder containing the material (resistive heating) or by bombarding the material directly with a high-energy beam of electrons (e-beam evaporation). The vapor then travels in a straight line to the substrate, where it condenses to form a thin film.
The core challenge of evaporation is not just turning a solid into a gas, but doing so with precise control and purity. The method you use is determined by the material's properties—especially its melting point—and the quality requirements of the final film.

The Principle: Overcoming Vapor Pressure in a Vacuum
Why a Vacuum is Essential
In a high-vacuum chamber, the atmospheric pressure that normally holds atoms in a solid or liquid state is almost entirely removed. With few air molecules to collide with, the atoms of the source material can escape its surface much more easily.
This environment dramatically lowers the temperature required for a material to evaporate or sublimate (turn directly from a solid to a gas). The goal is to create a "mean free path"—the average distance a vapor atom can travel before hitting another gas molecule—that is longer than the distance to the substrate.
Creating a Controlled Vapor Stream
Once atoms leave the source, they travel in a straight, line-of-sight path until they strike a surface. By placing a substrate in this path, the vapor atoms will land on it and condense back into a solid, forming a new, highly pure layer of material.
Two Primary Evaporation Methods
The "how" of evaporation comes down to the method used to deliver thermal energy to the source material.
Method 1: Resistive Thermal Evaporation
This is the most straightforward technique. The source material, often in pellet or wire form, is placed into a small crucible or "boat" made of a refractory metal like tungsten or molybdenum.
A very high electrical current is then passed through this boat. Due to its electrical resistance, the boat heats up rapidly—much like a filament in an incandescent light bulb. This heat is transferred to the source material, causing it to melt and then evaporate.
Method 2: Electron-Beam (E-Beam) Evaporation
This method is more complex but far more powerful and precise. It is used for materials with very high melting points (like titanium or ceramics) or when ultra-high film purity is required.
A filament generates a stream of electrons, which are then accelerated by high voltage and guided by magnetic fields to strike the surface of the source material. The immense kinetic energy of the electrons is instantly converted into intense, localized heat upon impact, causing the material to evaporate directly from the crucible without significantly heating the crucible itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method is a critical engineering decision based on balancing cost, capability, and desired film quality.
Resistive Evaporation: Simplicity vs. Limitations
Resistive heating is simple, fast, and cost-effective. However, it is limited to materials with lower evaporation temperatures.
A significant risk is contamination. At high temperatures, the boat material itself can begin to evaporate, incorporating impurities into the film. It also offers less precise control over the deposition rate compared to e-beam.
E-Beam Evaporation: Precision vs. Complexity
E-beam evaporation delivers exceptionally high purity because only the source material is heated, not the water-cooled copper crucible holding it. This allows for the deposition of refractory metals and dielectric compounds that are impossible to evaporate resistively.
The downsides are significantly higher system cost, greater complexity, and the generation of X-rays, which requires proper shielding.
The Challenge of Alloying
When attempting to evaporate an alloy (a mixture of metals), the element with the higher vapor pressure will evaporate faster. This changes the composition of the vapor over time, meaning the resulting film will not have the same composition as the source material. While e-beam can sometimes mitigate this with high power, true alloy deposition often requires co-evaporation from multiple, independently controlled sources.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your choice of evaporation method directly impacts the cost, quality, and type of material you can deposit.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for simple metals (like Aluminum, Gold, or Chrome): Resistive thermal evaporation is the efficient and standard choice.
- If your primary focus is high-purity films or refractory materials (like Titanium, Tungsten, or SiO₂): Electron-beam evaporation is the only viable option.
- If your primary focus is depositing a precise alloy composition: You must consider a system with multiple, individually controlled sources, which are most often e-beam sources.
Understanding the mechanism of evaporation empowers you to select the precise tool needed to achieve your desired film properties.
Summary Table:
| Method | Best For | Key Advantage | Key Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resistive Evaporation | Cost-effective deposition of simple metals (Al, Au, Cr) | Simple, fast, and lower cost | Limited to lower melting point materials; risk of boat contamination |
| E-Beam Evaporation | High-purity films & refractory materials (Ti, W, SiO₂) | High purity; can deposit high melting point materials | Higher system cost and complexity |
Ready to Achieve Precise Thin-Film Deposition?
The right evaporation method is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, offering expert guidance and solutions for both resistive and e-beam evaporation systems. We help laboratories like yours select the ideal setup for high-purity films, refractory materials, or cost-effective metal deposition.
Contact us today to discuss your specific requirements and let our experts help you optimize your deposition process. Get in touch via our contact form!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between sputtering and thermal evaporation? Choose the Right PVD Method for Your Thin Film
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- What are the drawbacks of thermal evaporation? Understanding the Limitations for High-Performance Applications
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition



















