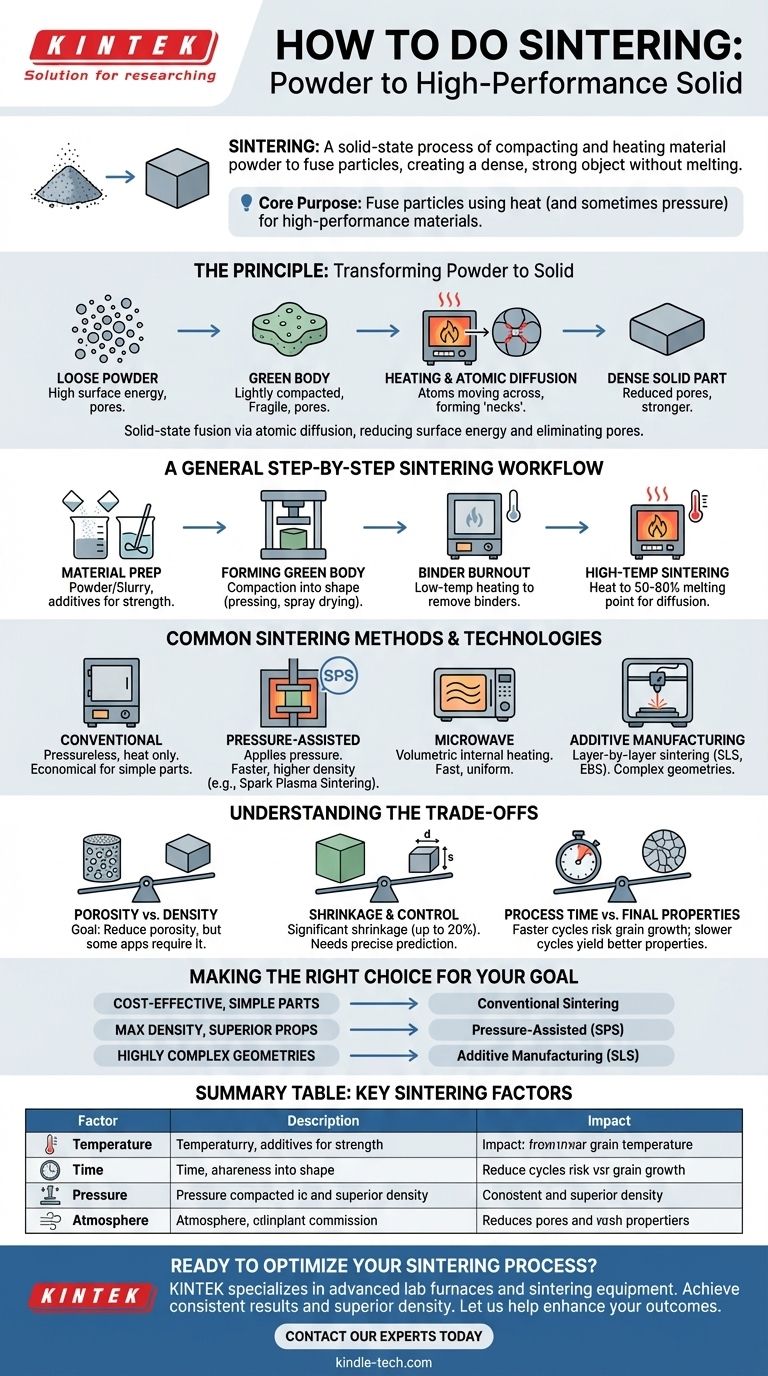
To perform sintering, you compact a material powder into a desired shape (a "green body") and then heat it to a high temperature, but below its melting point. This controlled heating gives the atoms in the powder particles enough energy to diffuse across their boundaries, fusing them together and transforming the loose powder into a dense, solid object. For many processes, especially with ceramics, this involves mixing the powder into a slurry, spray drying it, pressing it into a mold, and performing a low-temperature burn-off to remove binders before the final high-temperature sintering.
Sintering is not about melting; it's a solid-state process for creating dense objects from powders. Its core purpose is to fuse particles together using heat and sometimes pressure, making it the essential manufacturing method for high-performance ceramics and metals with extremely high melting points.
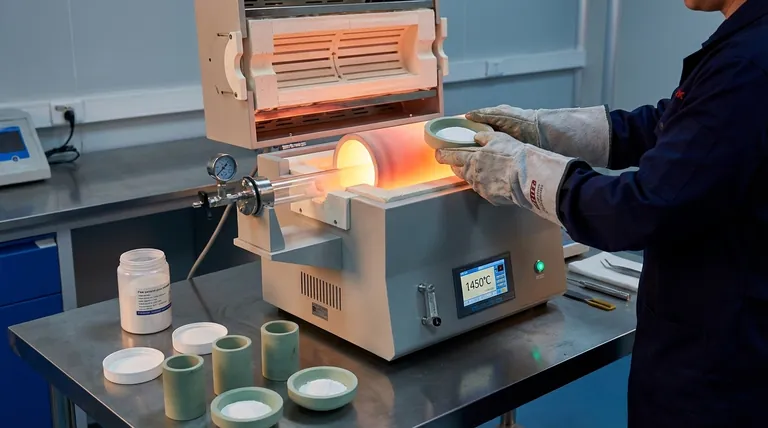

The Principle: How Sintering Transforms Powder to Solid
Sintering works by reducing the surface energy of a collection of particles. By applying heat, you encourage the system to eliminate the empty spaces (pores) between particles, resulting in a stronger, denser final part.
The "Green Body": An Unfired Foundation
The process begins by compacting the initial material powder into a shape. This pre-sintered object is called a green body.
The green body has the desired geometry but is mechanically fragile, held together only by particle friction or a temporary binding agent.
The Role of Heat and Atomic Diffusion
When the green body is heated in a furnace, the atoms gain thermal energy. They become mobile and begin to migrate or diffuse.
This diffusion happens most rapidly at the points of contact between particles. Atoms move to fill the gaps and create "necks" that connect adjacent particles, effectively welding them together on a microscopic scale.
Achieving Density Without Melting
The critical aspect of sintering is that this fusion occurs entirely in the solid state. The material never reaches its melting point to become a liquid.
As the process continues, the necks between particles grow, and the pores shrink. The entire part becomes denser and stronger, often shrinking in overall volume as the internal voids are eliminated.
A General Step-by-Step Sintering Workflow
While specific parameters vary by material, most conventional sintering processes follow a similar path from powder to finished part.
Step 1: Material Preparation
The starting material is a fine powder. It may be mixed with a binder to improve the strength of the green body or other additives to aid the sintering process. This mixture can be formed into a watery slurry.
Step 2: Forming the Green Body
The powder is compacted into the desired shape. This is commonly done by pressing it into a die or mold, a process known as compaction. For slurries, spray drying may be used to create uniform granules before pressing.
Step 3: Binder Burnout (Debinding)
If a binder was used, the green body undergoes a low-temperature heating cycle. This step is designed to slowly burn away the binder without disrupting the fragile part before the primary sintering begins.
Step 4: High-Temperature Sintering
The part is heated in a controlled furnace to the sintering temperature, which is typically 50-80% of the material's absolute melting point. It is held at this temperature for a set time to allow for sufficient atomic diffusion and densification.
Common Sintering Methods and Technologies
Beyond the conventional furnace method, several advanced techniques offer greater speed, control, and final part quality.
Conventional (Pressureless) Sintering
This is the most common and straightforward method, relying solely on heat in a controlled atmosphere furnace to drive densification. It is widely used for ceramics, pottery, and some metal parts.
Pressure-Assisted Sintering
Applying external pressure during heating significantly accelerates the densification process. This helps close pores more effectively and can be done at lower temperatures. Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS) is an advanced form that uses a pulsed electrical current to generate heat and pressure simultaneously.
Microwave Sintering
This technique uses microwave radiation to heat the material internally and volumetrically, rather than from the outside in. This can lead to much faster heating rates and more uniform microstructures.
Additive Manufacturing Sintering
Techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) and Electron Beam Sintering (EBS) are 3D printing methods. They use a focused energy beam to sinter powdered material one layer at a time, allowing for the creation of highly complex geometries that are impossible with traditional molding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Sintering is a powerful process, but it requires careful control to achieve the desired outcome. Its success is a balance between competing factors.
Porosity vs. Density
The primary goal of sintering is to reduce porosity (the empty space within a part). While high density is often desired for strength, some applications, like filters, require intentionally retaining a certain level of porosity.
Shrinkage and Dimensional Control
As a part becomes denser, it shrinks. This shrinkage can be significant (up to 20% in volume) and must be accurately predicted and accounted for in the initial mold and green body design to achieve the correct final dimensions.
Process Time vs. Final Properties
Faster sintering cycles at higher temperatures can reduce manufacturing time, but they risk abnormal grain growth, which can weaken the final part. Slower, more controlled cycles typically yield superior and more consistent material properties.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best sintering approach depends entirely on your material, desired part complexity, and performance requirements.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective production of simple ceramic or metal parts: Conventional, pressureless sintering in a furnace is the most established and economical choice.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum density and superior mechanical properties: Pressure-assisted methods like SPS provide the best densification and microstructural control, especially for advanced materials.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing highly complex, one-off geometries: Additive manufacturing techniques like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) are the ideal solution.
Ultimately, mastering sintering is about controlling heat and pressure to transform simple powder into a high-performance solid component.
Summary Table:
| Key Sintering Factor | Description | Impact on Final Part |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Typically 50-80% of material's melting point. | Drives atomic diffusion for particle fusion. |
| Time | Duration held at sintering temperature. | Controls densification and grain growth. |
| Pressure | Applied force during heating (in some methods). | Increases density, reduces porosity & temperature. |
| Atmosphere | Controlled gas environment in the furnace. | Prevents oxidation, ensures proper chemical reactions. |
Ready to Optimize Your Sintering Process?
Whether you are developing new materials or scaling up production, achieving precise control over temperature, atmosphere, and pressure is critical for success.
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab furnaces and sintering equipment designed for researchers and manufacturers working with ceramics, metals, and advanced powders. Our solutions help you achieve consistent results, superior density, and controlled microstructures.
Let us help you enhance your sintering outcomes.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific application and find the perfect furnace or press for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What are the advantages of using an alumina liner in a tube furnace for biomass combustion corrosion simulations?
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control
- How do you clean an alumina tube furnace? Extend Tube Life with Proper Maintenance
- What temperature is alumina activated? Unlock Optimal Porosity for Adsorption



















