In most modern energy markets, no, biomass electricity is not considered cheap. Compared to prevailing sources like utility-scale solar, wind, and natural gas, the cost to generate electricity from biomass is typically higher. Its price is heavily influenced by fuel sourcing and logistics, which often makes it a more expensive option for large-scale power generation.
The true cost of biomass power is a story of logistics, not just technology. While it offers the unique benefit of being a dispatchable (on-demand) renewable energy source, its economic viability is almost entirely dependent on the availability of a cheap, local, and consistent supply of fuel.
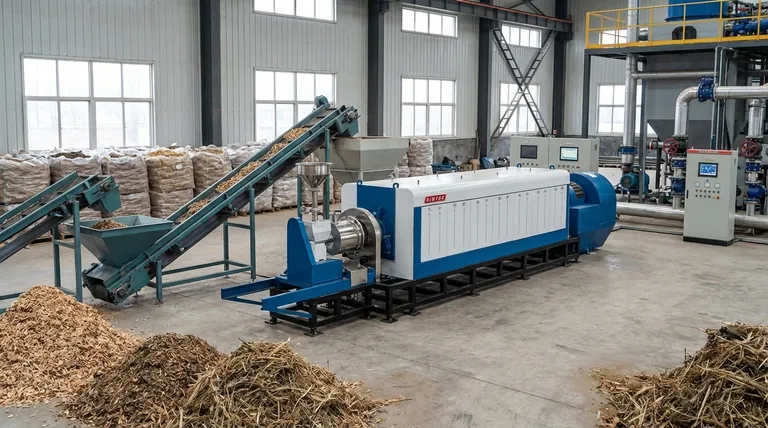

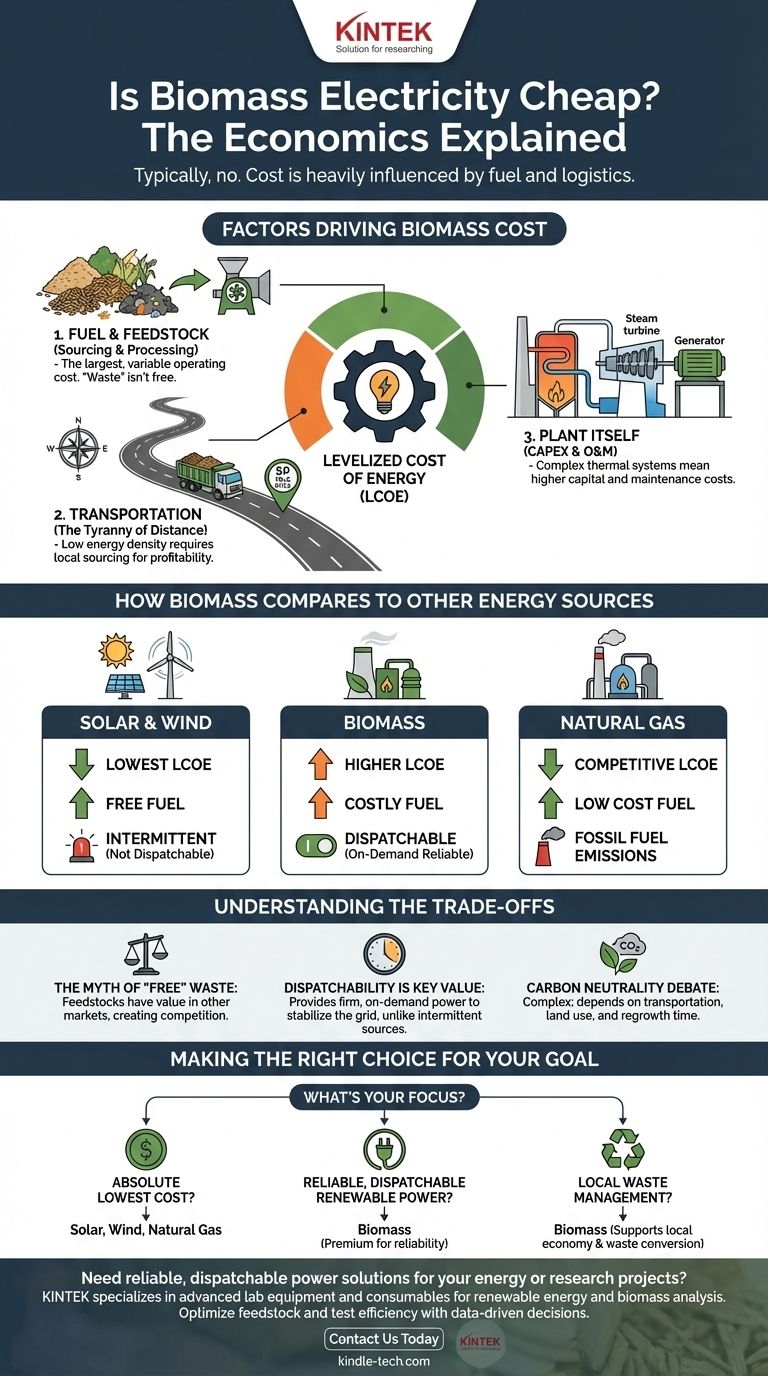
The Factors Driving Biomass Cost
To understand why biomass isn't typically the cheapest option, you must look at its entire cost structure, which is far more complex than that of solar or wind. The key metric used for comparison is the Levelized Cost of Energy (LCOE), which represents the average revenue per unit of electricity generated that would be required to recover the costs of building and operating a plant over its lifetime.
The Dominant Cost: Fuel and Feedstock
The single largest and most variable operating cost for a biomass plant is the fuel, known as feedstock. This isn't a "free" resource, even when it's waste.
Costs include sourcing, collecting, processing (e.g., chipping and drying), and transporting materials like wood pellets, agricultural residues, or municipal solid waste. This creates a complex supply chain where price can fluctuate significantly.
The Tyranny of Distance: Transportation
Biomass feedstocks are not energy-dense. A truck full of wood chips contains far less potential energy than a tanker of natural gas.
This makes transportation a major economic barrier. Most viable biomass plants operate on a "50-mile rule," meaning their feedstock must be sourced within a roughly 50-mile radius to keep transport costs from making the entire operation unprofitable.
The Plant Itself: Capital and Operating Costs
A biomass power plant is a thermal generator, much like a small-scale coal plant. It involves a boiler, steam turbine, and generator, along with complex systems for fuel handling and emissions control.
This results in higher capital costs (CAPEX) to build and higher ongoing operations and maintenance (O&M) costs compared to solar or wind farms, which have fewer moving parts.
How Biomass Compares to Other Energy Sources
When comparing LCOE figures, biomass occupies a specific niche—it's more expensive than the leading renewables but provides a different kind of value.
Biomass vs. Solar and Wind
Utility-scale solar and onshore wind have the lowest LCOE of nearly any new-build electricity source. Their fuel (sun and wind) is free, and their operating costs are very low.
However, they are intermittent, meaning they only produce power when the sun is shining or the wind is blowing. Biomass is dispatchable, meaning it can be turned on and off on demand to meet grid needs, similar to a fossil fuel plant. You pay a premium for this reliability.
Biomass vs. Natural Gas
In most regions, electricity from a new, efficient natural gas plant is cheaper than electricity from a new biomass plant. The primary driver is the low cost and high energy density of natural gas.
However, this can change in regions with high natural gas prices or where carbon taxes are implemented, which would penalize the fossil fuel emissions from natural gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an energy source is never about a single factor. The decision to use biomass is a balance of cost, reliability, and environmental goals.
The Myth of "Waste" as Free Fuel
While feedstocks like forest residue or crop waste may seem like "free" leftovers, they have value in other markets (e.g., mulch, animal bedding, particleboard). A biomass plant must compete for these resources, and creating a stable supply chain has significant costs.
Dispatchability is the Key Value
The primary reason to build a biomass plant today, despite its higher cost, is for its firm, dispatchable power. It can stabilize a grid that relies heavily on intermittent solar and wind, providing power when those sources are unavailable.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate
Biomass is often categorized as "carbon neutral" because the carbon released during combustion was recently captured from the atmosphere by the plants. However, this is a simplification.
Factors like transportation emissions, land-use changes, and the time it takes for forests to regrow mean its true carbon footprint is a subject of ongoing scientific and policy debate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Biomass is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Its value depends entirely on the specific goal you are trying to achieve.
- If your primary focus is the absolute lowest electricity cost: Onshore wind, utility-scale solar, and natural gas are your most economical choices for new generation.
- If your primary focus is reliable, dispatchable renewable power: Biomass is a viable, though often more expensive, option that provides on-demand power that solar and wind cannot.
- If your primary focus is local waste management: Biomass can be an excellent solution for converting a local waste stream (like forestry residue or agricultural waste) into a valuable energy resource, supporting local economies.
Ultimately, evaluating biomass on price alone misses its primary strategic value as a firm and renewable power source in a changing energy grid.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Impact on Cost | Key Insight |
|---|---|---|
| Fuel & Feedstock | High & Variable | Largest operating cost; 'waste' isn't free. |
| Transportation | Major Barrier | Limited by the '50-mile rule' for viability. |
| Plant (CAPEX & O&M) | Higher than Solar/Wind | Complex thermal systems increase costs. |
| Dispatchability | Premium Value | Provides on-demand power, unlike intermittent sources. |
Need reliable, dispatchable power solutions for your energy or research projects? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, supporting innovations in renewable energy and biomass analysis. Whether you're optimizing feedstock or testing energy efficiency, our tools help you make data-driven decisions. Contact us today to explore how our solutions can enhance your biomass or energy research!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Proton Exchange Membrane for Batteries Lab Applications
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output







