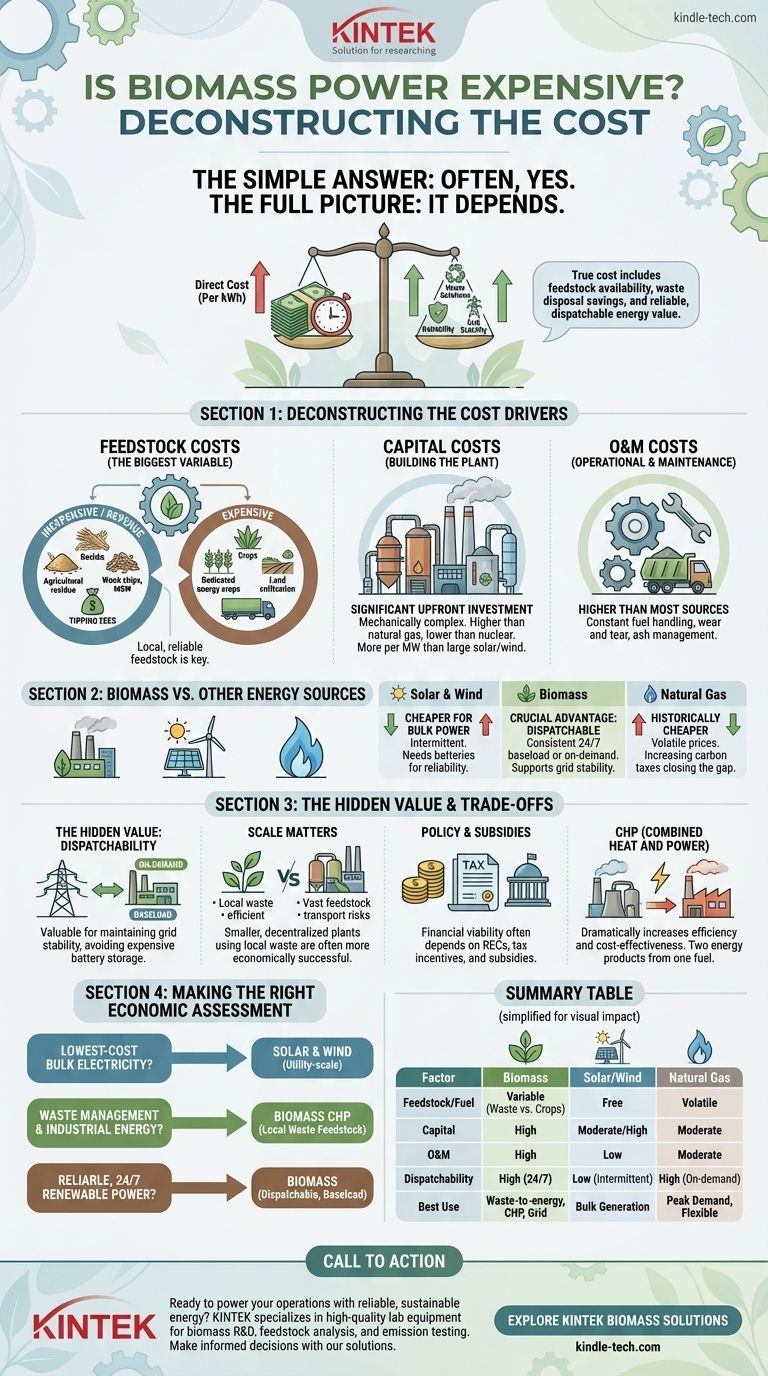
In short, yes, biomass power is often more expensive than other major energy sources like utility-scale solar, wind, and natural gas when measured on a simple cost-per-kilowatt-hour basis. However, this direct comparison overlooks the unique financial and operational context where biomass can be highly cost-effective, particularly when it solves waste management problems or provides reliable, on-demand power.
The true cost of biomass power isn't just about generating electricity; it's about the total economic equation, including feedstock availability, waste disposal savings, and the high value of its reliable, dispatchable energy.

Deconstructing the Cost of Biomass Power
To understand if biomass is expensive for a specific application, we must break down its primary cost drivers. The final price is a composite of fuel, construction, and operational expenses.
Feedstock Costs: The Biggest Variable
The single greatest factor influencing biomass cost is the fuel, or feedstock. This is not a uniform commodity like natural gas.
Sources like agricultural residue (corn stover, straw), forestry byproducts (wood chips, sawdust), and municipal solid waste can be very inexpensive or even generate revenue through "tipping fees" paid by others to dispose of their waste.
Conversely, using dedicated energy crops grown specifically for power generation is far more expensive, as it involves land, cultivation, and harvesting costs that drive up the price significantly.
Transportation is another critical factor. The low energy density of biomass means that transporting it over long distances can make a project economically unviable. Successful biomass facilities almost always have a local, reliable feedstock source.
Capital Costs: Building the Plant
Building a biomass power plant involves significant upfront investment. These facilities are mechanically complex, requiring robust material handling systems, specialized boilers, steam turbines, and advanced emissions controls.
While the capital costs are generally lower than for a new nuclear plant, they are typically higher than for a natural gas plant of similar capacity and significantly higher per megawatt than large-scale solar or wind farms.
Operational & Maintenance (O&M) Costs
Biomass plants have higher O&M costs than most other power sources. The constant handling of solid fuel causes wear and tear on machinery, and managing ash disposal adds another layer of operational expense.
This stands in stark contrast to solar and wind, which have very low O&M costs due to their lack of moving parts (in the case of solar PV) and no need for a constant fuel supply.
How Biomass Compares to Other Energy Sources
A simple cost-per-megawatt-hour comparison can be misleading. The value of electricity changes dramatically based on when and how reliably it can be delivered.
Comparison with Solar and Wind
For pure, bulk electricity generation, new utility-scale solar and wind are now almost always cheaper than new biomass power. The falling costs of photovoltaic panels and wind turbines have made them the leaders in low-cost energy.
The critical difference, however, is intermittency. Solar and wind only produce power when the sun is shining or the wind is blowing.
The Hidden Value: Dispatchability
This is where biomass has a crucial advantage. Biomass is a dispatchable energy source, meaning its output can be controlled. It can provide consistent baseload power 24/7 or be ramped up and down to meet peak demand.
This reliability is extremely valuable for maintaining grid stability, a service for which solar and wind must rely on expensive battery storage to replicate.
Comparison with Fossil Fuels
Historically, coal and natural gas have been cheaper than biomass. However, the volatility of fossil fuel prices and the increasing implementation of carbon pricing or taxes are closing this gap.
In many regions, government incentives and carbon policies are designed to level the playing field, making biomass more competitive with fossil fuels.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing biomass involves navigating a distinct set of economic and logistical challenges that are critical to understand.
The Impact of Scale
The principle of "economy of scale" is complex for biomass. While larger plants can be more efficient, they also require vast amounts of feedstock, increasing the risk and cost associated with fuel transportation and supply chain security.
Often, the most economically successful biomass projects are smaller-scale, decentralized facilities that use local waste streams, such as a sawmill powering itself with wood scraps.
The Role of Subsidies and Policy
The financial viability of many biomass projects today depends heavily on government policy. Renewable energy credits (RECs), tax incentives, and direct subsidies are often necessary to make biomass competitive with other energy sources.
Any evaluation of biomass cost must include a thorough analysis of the current and future policy landscape.
Combined Heat and Power (CHP)
Biomass truly shines in Combined Heat and Power (CHP) applications. In this setup, the waste heat from electricity generation is captured and used for industrial processes or district heating.
This "co-generation" approach dramatically increases the overall energy efficiency of the system, often making the project highly cost-effective by providing two energy products from a single fuel source.
Making the Right Economic Assessment
To determine if biomass is the right choice, you must look beyond the simple price of electricity and focus on the primary goal of the project.
- If your primary focus is the absolute lowest-cost bulk electricity: Utility-scale solar and wind are superior choices in most markets.
- If your primary focus is waste management and industrial energy: A biomass CHP plant using local waste feedstock is often an extremely cost-effective and resilient solution.
- If your primary focus is reliable, 24/7 renewable power: Biomass is one of the few renewable options that can provide dispatchable, baseload energy, making it a valuable contributor to a stable grid.
Ultimately, evaluating the cost of biomass requires a holistic view that weighs its higher direct costs against its significant benefits in waste reduction and grid reliability.
Summary Table:
| Cost Factor | Biomass Power | Solar/Wind | Natural Gas |
|---|---|---|---|
| Feedstock/Fuel Cost | Highly variable (low for waste, high for energy crops) | Free (sun, wind) | Subject to market volatility |
| Capital Cost | High (complex plants) | Moderate to High (panels/turbines) | Moderate |
| O&M Cost | High (fuel handling, ash disposal) | Low (minimal moving parts) | Moderate |
| Dispatchability | High (24/7 baseload power) | Low (intermittent) | High (on-demand) |
| Best Use Case | Waste-to-energy, CHP, grid stability | Bulk electricity generation | Peak demand, flexible power |
Ready to power your operations with reliable, sustainable energy?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your biomass research and development. Whether you're analyzing feedstock efficiency, optimizing combustion processes, or testing emissions, our solutions help you make informed decisions about biomass energy.
Contact us today to explore how our equipment can enhance your biomass projects and drive cost-effective, sustainable outcomes for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Benchtop Laboratory Vacuum Freeze Dryer
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- Why is a precision vibrating sieve shaker essential for metal leaching research? Optimize Your Particle Size Analysis
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- What is the primary purpose of using standard sieves? Master Particle Uniformity for High-Quality Catalyst Preparation
- What is the function of sieving equipment in CuAlMn alloys? Master Pore Size Precision



















