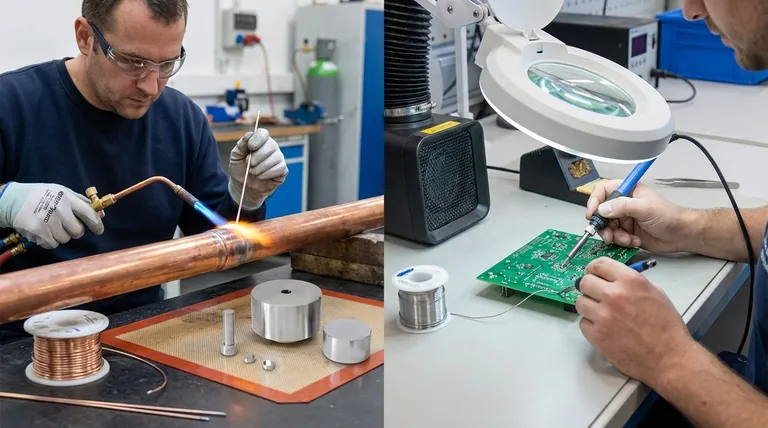
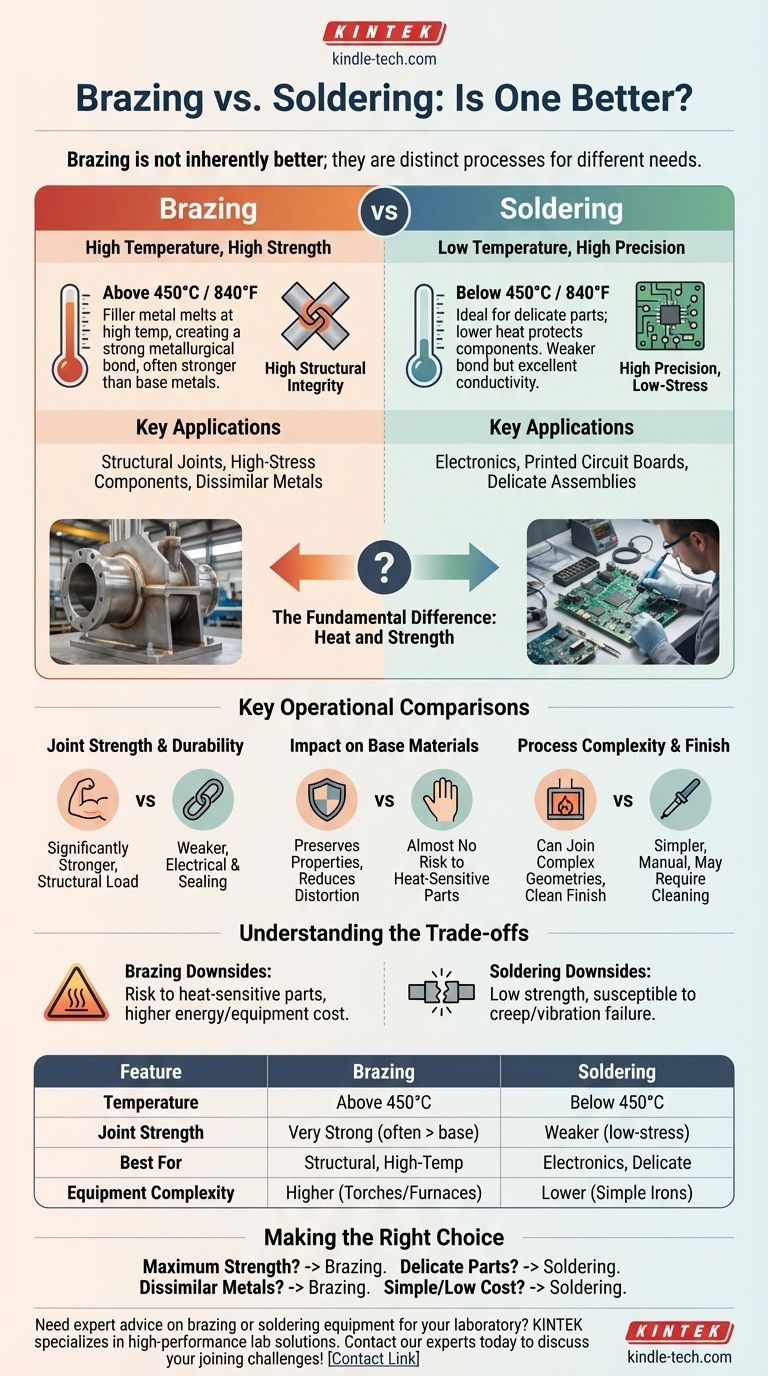
In practice, brazing is not inherently "better" than soldering; it is a different process used for applications demanding much higher strength and temperature resistance. Brazing creates a significantly stronger metallurgical bond by using a filler metal that melts at a much higher temperature (above 450°C / 840°F), resulting in joints that can often be stronger than the base metals themselves. Soldering, in contrast, is a lower-temperature process ideal for joining delicate components where high strength is not the primary requirement.
The choice between brazing and soldering is dictated entirely by the application's demands. Brazing is the solution for high-strength, high-temperature structural joints, while soldering is the correct process for lower-temperature, electrically conductive, or delicate assemblies.

The Fundamental Difference: Heat and Strength
The core distinction that drives every other difference between these two processes is temperature. This single factor determines the type of filler metal used, the resulting joint strength, and the impact on the materials being joined.
Brazing: High Temperature, High Strength
Brazing occurs at temperatures above 450°C (840°F) but always below the melting point of the base metals.
The filler metal is drawn into the joint through capillary action, creating a very strong, permanent bond. This high-heat process provides significant structural integrity.
Soldering: Low Temperature, High Precision
Soldering occurs at temperatures below 450°C (840°F).
This lower heat makes it ideal for applications like electronics, where excessive heat would destroy the components. The resulting joint is weaker than a brazed joint but provides excellent electrical conductivity and is sufficient for many mechanical needs.
Key Operational Comparisons
Understanding how the process differences play out in practice is key to selecting the right method for your project.
Joint Strength and Durability
Brazing creates a significantly stronger joint. A properly brazed joint can be stronger than the base materials it connects, making it suitable for high-stress and load-bearing applications.
Soldered joints are much weaker and are not intended for high-stress structural roles. Their strength is more than adequate for holding electronic components or sealing low-pressure plumbing.
Impact on Base Materials
Because it does not melt the base metals, brazing preserves their fundamental properties. The uniform heating and cooling, especially in furnace brazing, reduces thermal distortion and residual stress.
Soldering involves very localized, lower-level heat, posing almost no risk of altering the mechanical properties of the parts being joined. This is critical for heat-sensitive components.
Process Complexity and Finish
Brazing, particularly specialized methods like furnace brazing, can join complex geometries and multiple joints at once with excellent consistency and a clean finish that often requires no post-process cleaning.
Soldering is generally a simpler, more manual process. It often requires the use of flux to clean the joint area, which may need to be cleaned off after the joint is made.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is a universal solution. The advantages of one process are often the disadvantages of the other.
The Downside of Brazing's Heat
The high temperatures required for brazing can damage or destroy heat-sensitive components, making it entirely unsuitable for applications like printed circuit boards. It also requires more energy and more sophisticated heating equipment, like torches or furnaces.
The Limitation of Soldering's Strength
The primary drawback of soldering is its low strength. Soldered joints are susceptible to failure from vibration, shock, and high temperatures, a phenomenon known as "creep." This makes it inappropriate for any application where the joint must bear a significant mechanical load.
Cost and Accessibility
Soldering equipment is inexpensive and widely accessible, requiring minimal training to achieve a functional result.
Brazing equipment is more costly and requires a higher level of skill to perform safely and effectively, though automated systems can provide rapid and reproducible results.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your final decision should be based entirely on the specific requirements of your assembly.
- If your primary focus is maximum joint strength and performance under stress: Brazing is the only suitable choice, as it creates a true structural bond.
- If you are joining delicate, heat-sensitive components like electronics: Soldering is the correct method, as its low temperature protects the components from damage.
- If you need to join dissimilar metals for a structural purpose: Brazing excels at this, creating strong bonds between a wide variety of materials.
- If you need a simple, low-cost method for sealing or low-stress connections: Soldering is the more efficient and accessible option.
Choosing the right joining method is about matching the process capabilities to your application's specific demands.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Brazing | Soldering |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Above 450°C (840°F) | Below 450°C (840°F) |
| Joint Strength | Very strong, often stronger than base metals | Weaker, suitable for low-stress applications |
| Best For | Structural joints, high-temperature applications | Electronics, delicate components, electrical conductivity |
| Equipment Complexity | Higher (torches, furnaces) | Lower (simple irons) |
Need expert advice on brazing or soldering equipment for your laboratory? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment and consumables for all your metal joining needs. Whether you require precision brazing furnaces for structural applications or reliable soldering systems for delicate electronic work, our solutions deliver consistent results and enhanced efficiency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your specific joining challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
- Metallographic Specimen Mounting Machine for Laboratory Materials and Analysis
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What role do high-strength graphite molds play during vacuum hot pressing? Enhance Precision in CuAlMn Composites
- What is the role of graphite molds during the hot pressing of LSLBO ceramics? Essential for High-Density Electrolytes
- What role does a high-purity graphite mold play during hot pressing? Optimize Boron Carbide Sintering at 1850°C
- What are the specific functions of graphite molds in the vacuum hot-press sintering process? Expert Insights for Ceramics
- Why is precise temperature and pressure control necessary for combustible cartridge cases? Ensure Structural Integrity


















