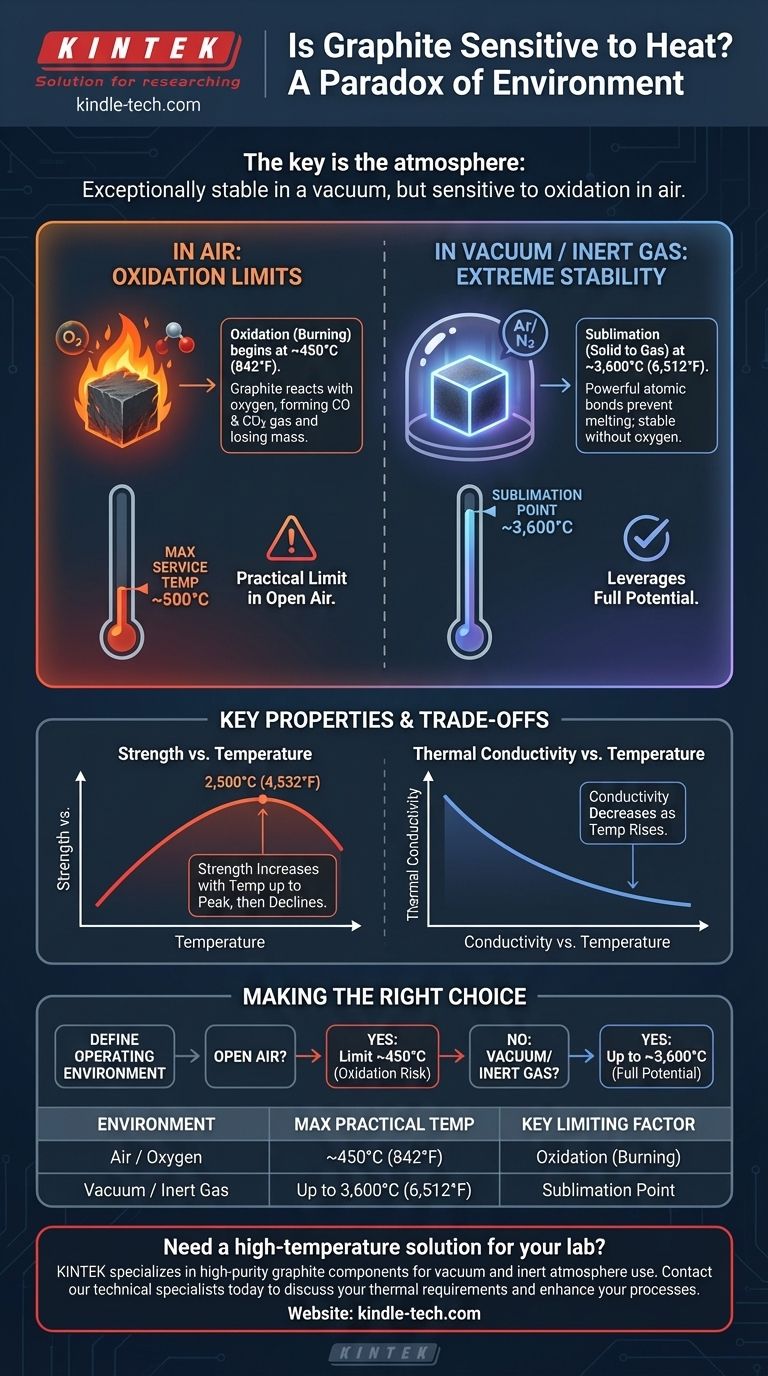
In short, graphite's sensitivity to heat is paradoxical and entirely dependent on its environment. While it possesses one of the highest sublimation points of any known material, making it exceptionally resistant to melting, its practical use at high temperatures is often limited by its reaction with oxygen in the air.
The crucial takeaway is that graphite's heat tolerance is not a single number. In a vacuum or inert atmosphere it is remarkably stable, but in the presence of air, its "sensitivity" is defined by its tendency to oxidize and burn away at temperatures far below its sublimation point.

The Two Faces of Graphite's Heat Resistance
Graphite’s behavior at high temperatures is best understood as a story of two competing properties: its incredibly strong atomic bonds and its chemical reactivity with the environment.
Exceptionally High Sublimation Point
Graphite is an allotrope, or a specific structural form, of carbon. The carbon atoms are linked by powerful covalent bonds into flat sheets, which are then stacked together.
Breaking these bonds requires an immense amount of energy. As a result, graphite does not melt at atmospheric pressure. Instead, it sublimes—turning directly from a solid into a gas—at a staggering temperature of approximately 3,600°C (6,512°F).
This property alone makes graphite one of the most heat-resistant materials available.
The Decisive Factor: The Atmosphere
The key to graphite's real-world performance is the atmosphere it's in. While it can withstand extreme heat when isolated, it behaves very differently when exposed to other elements, most notably oxygen.
The Real-World Limiter: Oxidation
For most practical applications that occur in air, the theoretical sublimation point is irrelevant. The true limiting factor is oxidation.
What is Oxidation?
In this context, oxidation is the chemical reaction between the carbon atoms in graphite and oxygen in the air. At elevated temperatures, this reaction forms carbon monoxide (CO) and carbon dioxide (CO2) gas.
Essentially, the solid graphite material slowly burns away and converts into a gas, losing mass and structural integrity.
The Oxidation Temperature Threshold
Graphite begins to oxidize in air at a much lower temperature, typically starting around 450°C (842°F).
While the process is slow at this initial temperature, the rate of oxidation increases dramatically as the temperature rises. For many applications, 500°C is considered the maximum long-term service temperature for uncoated graphite in an open-air environment.
Overcoming Oxidation
Engineers leverage graphite's full potential by controlling its environment. In a vacuum or an inert atmosphere (like argon or nitrogen), oxygen is eliminated, and the oxidation reaction cannot occur.
This is why graphite is a primary material for vacuum furnace components, rocket nozzles, and casting molds, where it can perform reliably at temperatures exceeding 2,000°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Heat affects more than just graphite's chemical stability; it also changes its mechanical properties in ways that can be both beneficial and challenging.
Strength Increases with Temperature
Unusually, the tensile strength of many grades of graphite actually increases with temperature, peaking at around 2,500°C (4,532°F). At this point, it can be twice as strong as it is at room temperature.
This makes it an exceptional material for high-temperature structural applications, provided it is protected from oxidation. Above this peak, its strength begins to decline rapidly.
Thermal Conductivity Varies
Graphite is an excellent thermal conductor at room temperature, often used for heat sinks and spreaders. However, its thermal conductivity decreases as temperatures rise.
This must be accounted for in thermal management design, as its ability to dissipate heat will be lower in a high-temperature operational state compared to a cold state.
Grade and Purity Matter
Not all graphite is the same. The temperature at which oxidation begins can be influenced by the graphite's purity, density, and grain structure. Higher-purity, higher-density grades generally offer slightly better oxidation resistance.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To determine if graphite is suitable for your purpose, you must first define the operating environment.
- If your primary focus is use in an open-air environment: Your practical limit is the oxidation temperature, roughly 450°C, above which the material will begin to degrade.
- If your primary focus is use in a vacuum or inert gas: You can leverage graphite's full potential, using it safely up to temperatures approaching its 3,600°C sublimation point.
- If your primary focus is high strength at extreme temperatures: Graphite is a unique candidate, as its strength increases up to about 2,500°C, but only if it is completely protected from oxygen.
By understanding the critical difference between graphite's sublimation point and its oxidation temperature, you can confidently engineer solutions for extreme thermal environments.
Summary Table:
| Environment | Maximum Practical Temperature | Key Limiting Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Air / Oxygen | ~450°C (842°F) | Oxidation (Burning) |
| Vacuum / Inert Gas | Up to 3,600°C (6,512°F) | Sublimation Point |
Need a high-temperature solution for your lab?
Graphite's unique properties make it ideal for demanding applications, but only when used correctly. The experts at KINTEK specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables, including high-purity graphite components designed for vacuum and inert atmosphere use.
We help laboratories like yours overcome material limitations and achieve reliable, high-temperature performance.
Contact our technical specialists today to discuss your specific thermal requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can enhance your processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Ultra-High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Furnace High Thermal Conductivity Film Graphitization Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why is industrial-grade platinum mesh preferred as the counter electrode? Ensure Purity in Copper Deposition
- How do you prepare the polishing setup for an electrode? Achieve a Flawless Mirror Finish for Reliable Electrochemistry
- Why are graphite granules preferred as electrode materials in a fixed-bed anode system? Maximize Microbial Flux
- What is the role of platinum electrodes in electrolytic etching? Reveal Precise Stainless Steel Microstructure
- Is silver silver chloride a reference electrode? A Guide to Stable & Safe Electrochemical Measurements
- How should a carbon fiber brush be pre-treated to enhance microbial attachment? Optimize Your Bioelectrochemical System
- How should a platinum sheet electrode be operated during an experiment? Ensure Accurate and Reproducible Results
- What is a graphite rod used for in smelting? The Engine of Modern Electric Arc Furnaces



















