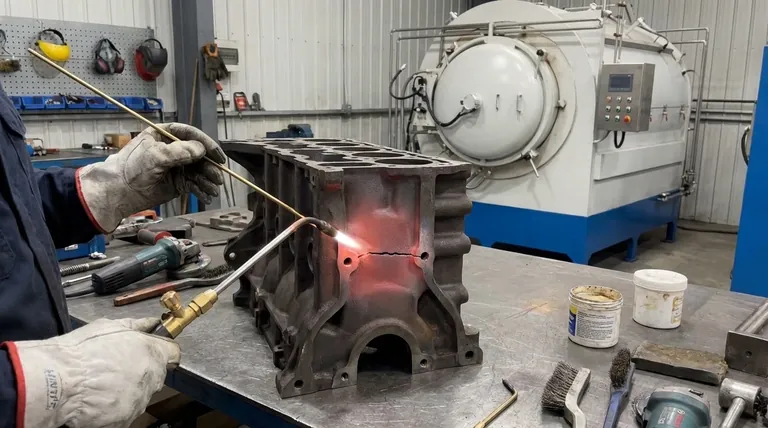
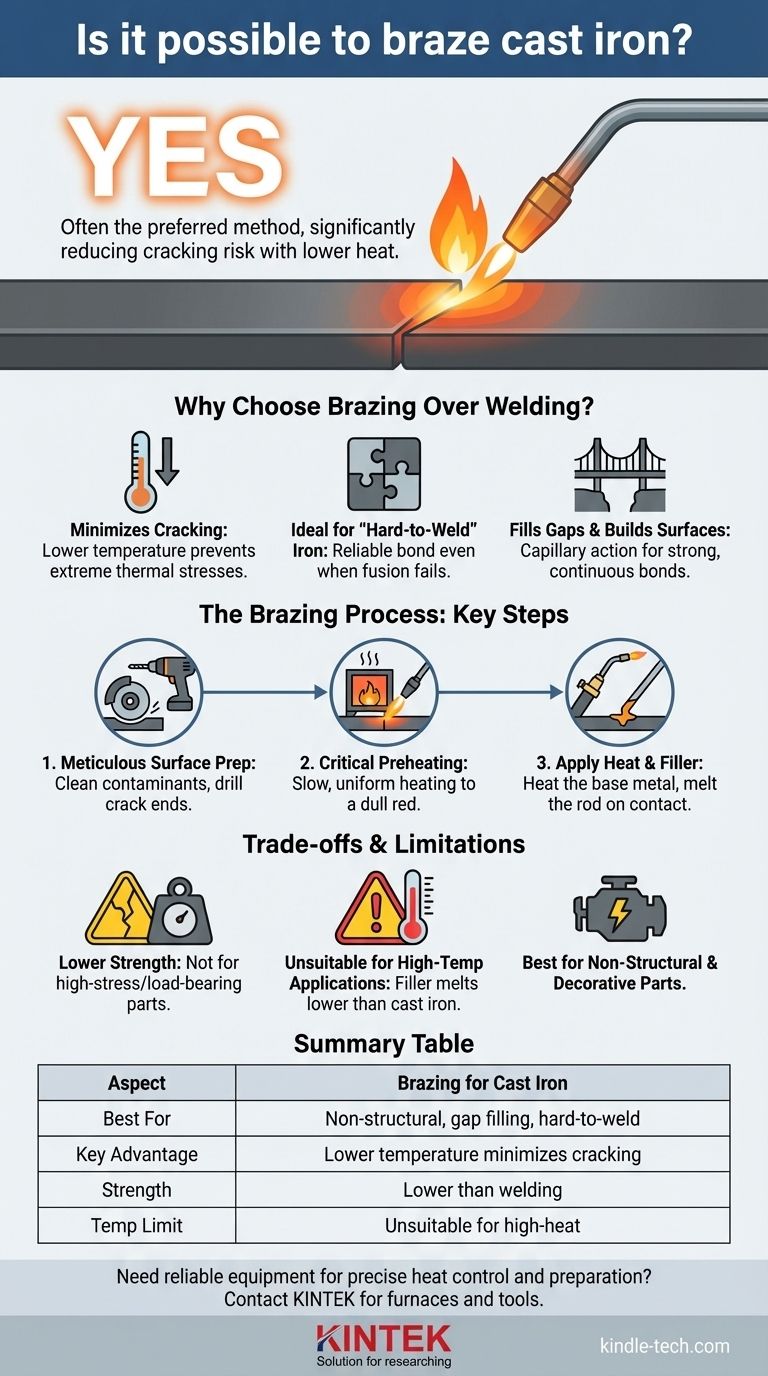
Yes, it is absolutely possible to braze cast iron. In fact, for many applications, it is not only possible but the preferred method of repair. Brazing uses a lower temperature than welding, which significantly reduces the risk of cracking the brittle cast iron, making it a reliable technique for joining and repairing parts where welding has failed or is too risky.
The central challenge with cast iron is its tendency to crack under the high, localized heat of welding. Brazing elegantly solves this by joining the metal without melting it, offering a strong, low-stress bond ideal for many non-structural repairs.

Why Choose Brazing Over Welding for Cast Iron?
Brazing isn't just an alternative to welding; it's a fundamentally different process with distinct advantages for a material as sensitive as cast iron.
Minimizing the Risk of Cracking
The primary benefit of brazing is its lower working temperature. The process heats the cast iron enough to melt a bronze or brass filler rod, but it stays well below the melting point of the iron itself.
This limited, more gentle heating prevents the extreme thermal stresses that cause cast iron to crack during the cooling phase of a traditional weld. This preserves the base metal's original properties.
Ideal for "Hard-to-Weld" Iron
Some varieties of cast iron are notoriously difficult to weld due to their specific carbon content or the presence of contaminants from years of service.
When repeated attempts at welding fail, brazing provides a reliable path forward, creating a strong bond where a fusion weld is simply not feasible.
Filling Gaps and Building Up Surfaces
Brazing is exceptionally good at bridging larger gaps between pieces. The filler metal flows into the joint via capillary action, creating a solid, continuous bond that can be stronger than the base cast iron in some cases. It's also effective for building up worn-down surfaces.
The Brazing Process for Cast Iron: Key Steps
Success in brazing cast iron hinges on methodical preparation and heat control. Rushing any of these steps is the most common cause of failure.
Step 1: Meticulous Surface Preparation
The joint surface must be completely free of any contaminants. Oil, grease, rust, and even graphite from the iron itself will prevent the filler metal from bonding properly. Grind or sand the surfaces to expose clean, bright metal.
For repairing a crack, drill a small hole at each end of the crack. This simple step relieves stress and is critical for preventing the crack from spreading further during heating and cooling.
Step 2: Critical Preheating
Cast iron cannot tolerate sudden, localized temperature changes. It must be preheated slowly and evenly to prevent thermal shock and cracking.
For smaller parts, a torch can be used to gradually heat the entire piece. For larger castings, a furnace is highly recommended for uniform heating. Heat the iron until it reaches a dull red color, indicating it's ready for brazing.
Step 3: Applying Heat and Filler Metal
Use a neutral or slightly oxidizing flame with a suitably sized brazing nozzle. The goal is to heat the cast iron base metal, not the filler rod.
Bring the joint area up to temperature. When the cast iron is hot enough, it will melt the brazing rod on contact. This ensures the filler metal "wets" the surface and flows deep into the joint, creating a proper bond.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While effective, brazing is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly and safely.
Lower Strength Compared to Welding
A properly executed weld, which fuses the base metals together, will generally create a stronger joint than a brazed one. Brazing creates a bond on the surface of the metal, not within it.
Unsuitable for High-Temperature Applications
Brazing filler metals have a much lower melting point than cast iron. Therefore, a brazed repair is not suitable for parts that operate at high temperatures, such as exhaust manifolds, cylinder heads, or other engine components. The joint will fail once its operating temperature exceeds the melting point of the filler.
Not for High-Stress or Load-Bearing Parts
Because of its lower tensile strength compared to a full-penetration weld, brazing should not be used for critical repairs on components subjected to high tension or heavy structural loads. It is best suited for housings, casings, and decorative pieces.
Making the Right Choice for Your Repair
To determine if brazing is the correct approach, consider the final function of the part.
- If your primary focus is repairing a non-structural part (like a bracket, housing, or decorative piece): Brazing is an excellent, low-risk choice that minimizes the chance of cracking the casting.
- If your primary focus is repairing a part subject to high heat (like an exhaust manifold): Brazing is not suitable; you must investigate specialized high-temperature welding procedures.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength for a load-bearing component: Brazing is likely insufficient; a proper welding repair performed by a specialist is the safer choice.
By understanding its principles and limitations, you can confidently use brazing as a powerful tool for cast iron repair.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Brazing for Cast Iron |
|---|---|
| Best For | Non-structural repairs, gap filling, hard-to-weld iron |
| Key Advantage | Lower temperature minimizes cracking risk |
| Strength | Lower than welding; not for high-stress parts |
| Temperature Limit | Unsuitable for high-heat applications (e.g., exhaust manifolds) |
| Process | Preheating, surface prep, capillary filler flow |
Need Reliable Equipment for Your Metalworking or Lab Projects?
Brazing cast iron requires precise heat control and preparation. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, including furnaces for uniform preheating and tools for meticulous surface preparation. Whether you're in a research lab or an industrial workshop, our solutions help you achieve consistent, professional results.
Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your specific cast iron repair or manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- 1700℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
People Also Ask
- Does brazing require heat? Yes, it's the catalyst for creating strong, permanent bonds.
- What are the factors that affect the strength of a brazed joint? Master the 4 Keys to a Perfect Bond
- What are some applications of brazing? Join Dissimilar Metals with Strong, Leak-Proof Bonds
- Why would you braze instead of weld? Preserve Material Integrity and Join Dissimilar Metals
- What is the major advantage that brazing has over welding? Joining Dissimilar Metals with Ease



















