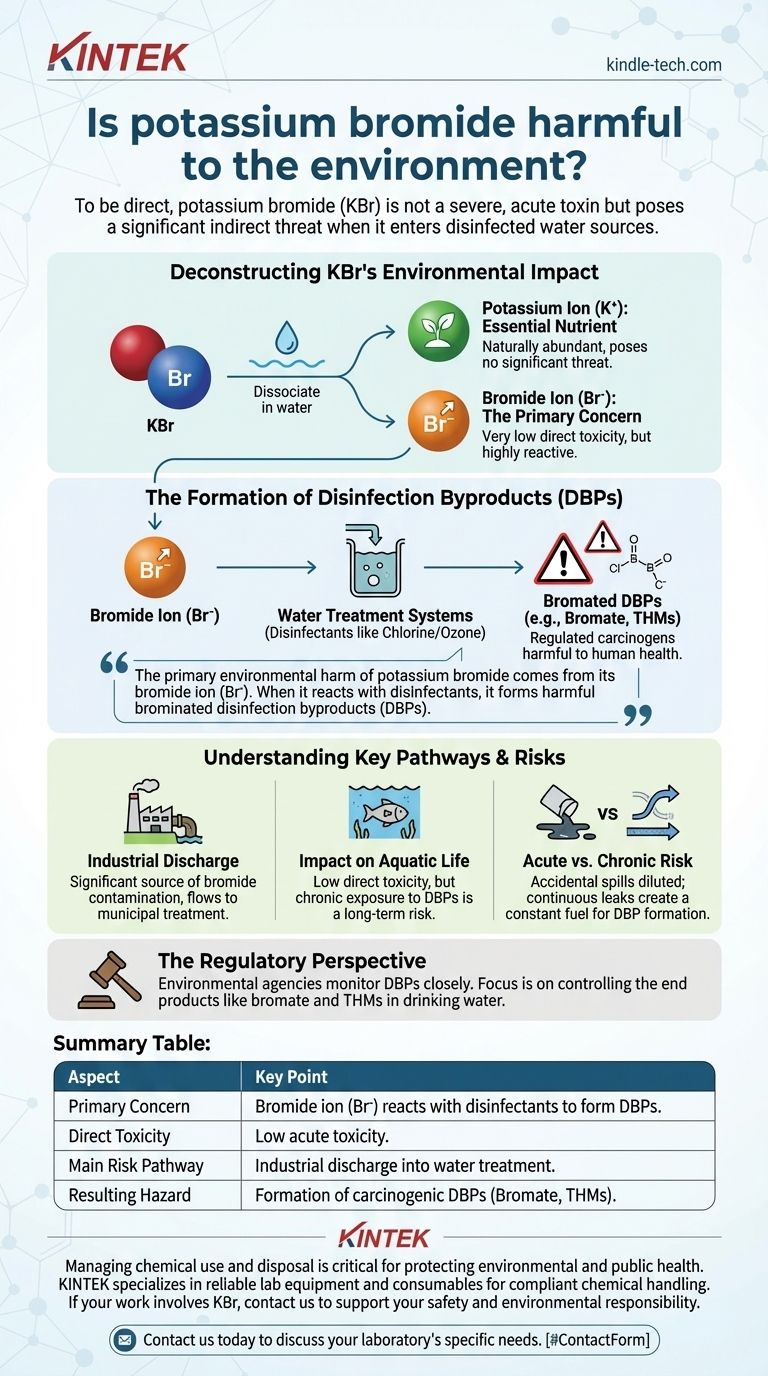
To be direct, potassium bromide (KBr) is not considered a severe, acute environmental toxin in the way that heavy metals or pesticides are. However, it poses a significant and often overlooked indirect threat to environmental and human health, primarily when it enters water sources that undergo disinfection. The core issue is not the compound itself, but the chemical reactions its bromide component can trigger.
The primary environmental harm of potassium bromide comes from its bromide ion (Br⁻). When bromide enters water treatment systems, it reacts with disinfectants like chlorine or ozone to form brominated disinfection byproducts (DBPs), which are regulated contaminants and can be harmful to human health.

Deconstructing Potassium Bromide's Environmental Impact
To understand the risk, we must look at what happens when potassium bromide enters the environment. It is a simple salt that, when dissolved in water, splits into two separate particles: potassium ions (K⁺) and bromide ions (Br⁻).
The Potassium Ion (K⁺): An Essential Nutrient
Potassium is an essential mineral for virtually all life, including plants and animals.
In the concentrations resulting from typical potassium bromide releases, the potassium ion itself poses no significant environmental threat. It is a naturally abundant element.
The Bromide Ion (Br⁻): The Primary Concern
Like potassium, the bromide ion itself has very low toxicity to aquatic life and humans at typical environmental concentrations. The real problem is its chemical reactivity.
Bromide ions persist in water and can accumulate in source waters for drinking water treatment plants. This is where the primary environmental hazard is created.
The Formation of Disinfection Byproducts (DBPs)
This is the central mechanism of harm. Municipal water treatment facilities use powerful oxidants like chlorine or ozone to kill pathogens and make water safe to drink.
When these disinfectants are added to water containing bromide ions, a series of chemical reactions occurs. These reactions create a class of compounds known as brominated disinfection byproducts (DBPs).
The most concerning of these DBPs include bromate (BrO₃⁻) and certain trihalomethanes (THMs) like bromoform. These substances are regulated by environmental agencies because they are known or suspected carcinogens.
Understanding the Key Pathways and Risks
The risk from potassium bromide is entirely dependent on where it ends up. Its high solubility in water means it travels easily within ecosystems.
Industrial and Wastewater Discharge
The most significant sources of bromide contamination are industrial processes. Industries like photography, engraving, and some manufacturing use KBr and may discharge it into wastewater.
This wastewater flows to municipal treatment plants, where the bromide can then react during disinfection, contaminating the finished drinking water.
Impact on Aquatic Life
While massive spills of any salt can disrupt the osmotic balance of aquatic organisms, the direct toxicity of KBr is low.
The more significant, long-term risk to aquatic ecosystems is the chronic exposure to the toxic and mutagenic DBPs that form downstream from a bromide source.
Navigating the Trade-offs and Context
It is critical to distinguish between different types of risk. The environmental concern around KBr is not about immediate, visible harm but about a subtle, chronic chemical pathway.
Acute vs. Chronic Risk
A small, accidental spill of KBr on soil is unlikely to cause a lasting environmental issue. The salt will be diluted by rainfall and disperse.
In contrast, a slow, continuous leak of KBr into a river that serves as a drinking water source is a serious problem. This chronic release provides a constant fuel source for the creation of harmful DBPs.
The Regulatory Perspective
Because of the DBP formation risk, environmental agencies like the U.S. EPA closely monitor substances that create them.
While bromide itself is not always regulated in source water, the resulting byproducts, like bromate and trihalomethanes, are strictly regulated in finished drinking water. The focus is on controlling the end product of the hazardous reaction chain.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Evaluating the harm of potassium bromide requires understanding its intended use and potential destination.
- If your primary focus is industrial use: Your responsibility is to prevent discharge into municipal water systems. Use designated chemical waste disposal services to ensure the bromide is handled and sequestered properly.
- If your primary focus is veterinary medicine: The environmental risk from prescribed doses for pets is negligible. The concern is proper handling and preventing accidental ingestion, not environmental contamination.
- If your primary focus is laboratory research: Adhere to standard chemical waste protocols. The small quantities used in a lab setting pose minimal risk when disposed of correctly.
- If your primary focus is public health and water quality: The goal is to minimize bromide entering source water. This involves working with industrial users and improving wastewater treatment to remove precursor chemicals before they can cause harm.
Understanding that the indirect risk of bromide is far greater than the direct risk of the salt itself is the key to its responsible management.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Point |
|---|---|
| Primary Concern | Bromide ion (Br⁻) reacts with water disinfectants (e.g., chlorine) to form harmful disinfection byproducts (DBPs). |
| Direct Toxicity | Low acute toxicity to aquatic life and humans. |
| Main Risk Pathway | Industrial discharge into wastewater that feeds into drinking water treatment plants. |
| Resulting Hazard | Formation of regulated, carcinogenic byproducts like bromate and brominated trihalomethanes (THMs). |
Managing chemical use and disposal is critical for protecting environmental and public health.
KINTEK specializes in providing reliable lab equipment and consumables, helping laboratories maintain precise control over their processes and ensure compliant chemical handling. If your work involves substances like potassium bromide, our solutions can support your commitment to safety and environmental responsibility.
Contact us today to discuss how we can meet your laboratory's specific needs. [#ContactForm]
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for PTFE Mesh F4 Sieve
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hydrothermal Synthesis Reactor Polytetrafluoroethylene Carbon Paper and Carbon Cloth Nano-growth
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Etching Flower Basket ITO FTO Developing Glue Removal
- Lab Internal Rubber Mixer Rubber Kneader Machine for Mixing and Kneading
People Also Ask
- What is the importance of a laboratory electric constant temperature drying oven? Ensure Accurate Biomass Analysis
- What materials are needed for a FTIR? Essential Guide to Sample Prep and Optics
- What are the dangers of heat in a lab? Protect Your Lab from Burns, Fires, and Data Loss
- What is target in sputtering? The Essential Source Material for Thin-Film Deposition
- What role does an open reactor play in the SHS process? Enhance Your Surface Coatings Today
- What is the meaning of physical vapor deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Coating
- How does biomass energy compare with other renewables? The Pros and Cons of On-Demand Power
- Is pyrolysis oil flammable? Understanding Its Combustible Nature and Critical Safety Risks



















