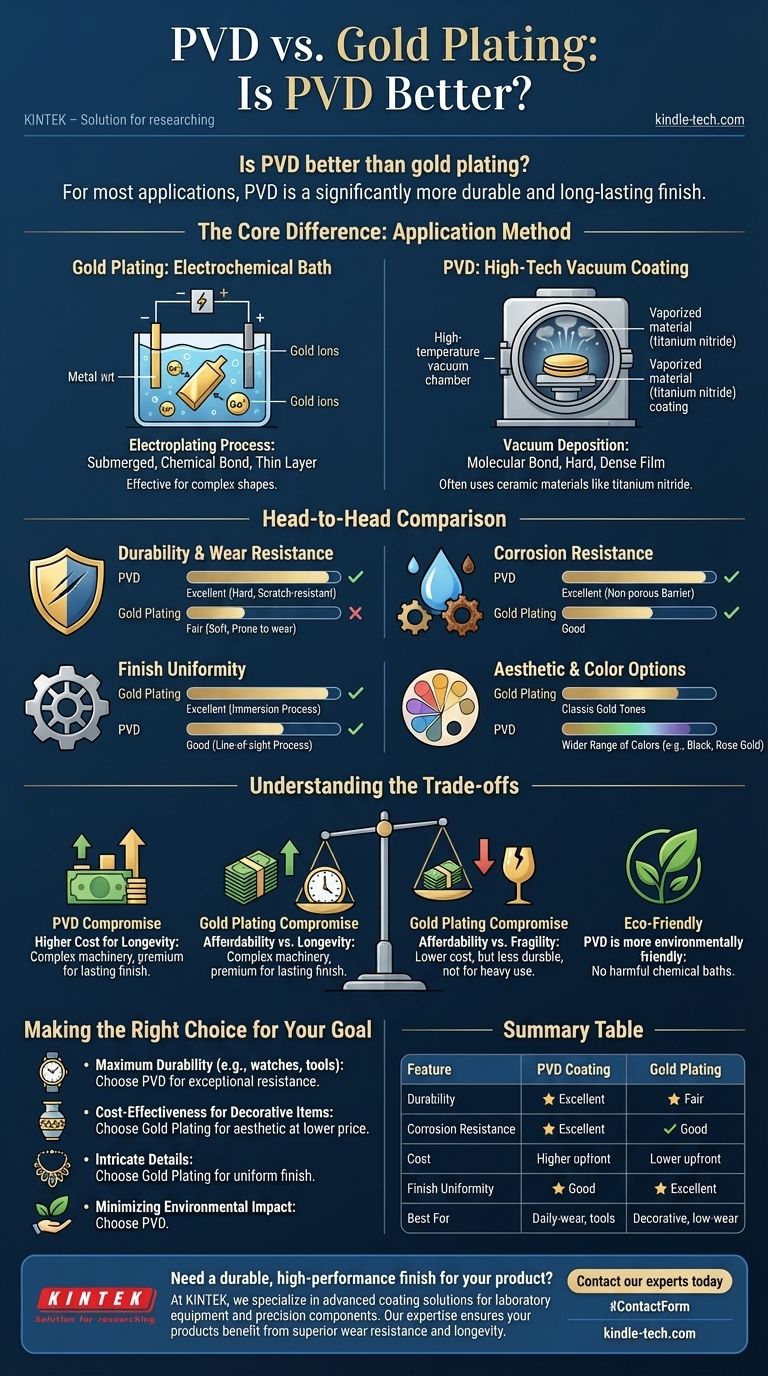
For most applications, PVD is a significantly more durable and long-lasting finish than traditional gold plating. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) creates a harder, more corrosion-resistant surface that excels in situations involving daily wear and tear. While traditional gold plating is less expensive, its thin, electroplated layer is much softer and more susceptible to scratching and fading over time.
The choice between PVD and gold plating is a classic trade-off between long-term performance and upfront cost. PVD provides superior physical resilience for items that need to last, while gold plating offers the desired aesthetic for a lower price, albeit with a shorter lifespan.

The Core Difference: Application Method
The vast difference in performance between PVD and gold plating comes from their fundamentally distinct application processes. Understanding this is key to choosing the right finish.
Gold Plating: An Electrochemical Bath
Gold plating is an electroplating process. The base metal object is submerged in a chemical solution containing gold ions, and a low-voltage electrical current is used to bond a thin layer of gold onto its surface.
This process is highly effective at covering complex shapes evenly.
PVD: A High-Tech Vacuum Coating
PVD, or Physical Vapor Deposition, is a modern vacuum coating technique. Inside a high-temperature vacuum chamber, a solid coating material is vaporized into a plasma of atoms and molecules.
This vapor is then deposited onto the object, bonding at a molecular level to form a dense, hard, and thin film. While this coating can have the color of gold, the material itself is often a highly durable ceramic like titanium nitride.
A Head-to-Head Comparison
Each finishing method has clear advantages in specific categories.
Durability and Wear Resistance
PVD is the undisputed winner. The PVD coating is molecularly bonded to the base metal, resulting in a finish that is vastly harder and more resistant to scratches and abrasion than the soft, thin layer of traditional gold plating.
When a gold-plated item is scratched, the base metal underneath is often exposed.
Corrosion Resistance
PVD offers superior protection. The PVD process creates a dense, non-porous coating that serves as an excellent barrier against sweat, oxidation, and other environmental factors that cause tarnish and corrosion.
Finish Uniformity
Gold plating often has an edge. Because it's an immersion process, electroplating can provide a more even and uniform coating on items with very complex geometries or deep, recessed areas that PVD's line-of-sight process might not reach as consistently.
Aesthetic and Color Options
Both methods produce a high-quality, smooth surface with a rich metallic luster. However, PVD offers a much wider range of color choices beyond traditional gold tones, as different materials can be used in the process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither method is perfect for every scenario. Recognizing their inherent compromises is crucial for making an informed decision.
The PVD Compromise: Higher Cost for Longevity
The primary drawback of PVD is its cost. The complex machinery, high temperatures, and vacuum environment make it a more expensive process than electroplating. You are paying a premium for a finish that will last significantly longer and maintain its appearance through heavy use.
The Gold Plating Compromise: Affordability vs. Fragility
Gold plating's main advantage is its lower cost. It provides the classic gold look for a fraction of the price of PVD. However, this comes at the cost of durability. It is not suitable for items that will see frequent contact or abrasion.
The Environmental Factor
PVD is widely considered a more environmentally friendly process. It takes place in a contained vacuum and does not emit harmful chemicals. Traditional electroplating, by contrast, often involves chemical baths that require careful handling and disposal.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Select your coating method based on the intended use and priorities for the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity (e.g., watches, tools, daily-wear jewelry): PVD is the superior choice due to its exceptional scratch and corrosion resistance.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for decorative items with low physical contact: Gold plating offers an excellent aesthetic at a more accessible price point.
- If your primary focus is coating an object with highly intricate or recessed details: Gold plating may provide a more uniform and complete finish.
- If your primary focus is minimizing environmental impact: PVD is the more eco-friendly process compared to traditional electroplating.
Ultimately, your choice depends on balancing the need for long-term performance against the constraints of your budget and design.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Coating | Gold Plating |
|---|---|---|
| Durability | Excellent (Hard, scratch-resistant) | Fair (Soft, prone to wear) |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (Non-porous barrier) | Good |
| Cost | Higher upfront cost | Lower upfront cost |
| Finish Uniformity | Good (Line-of-sight process) | Excellent (Immersion process) |
| Best For | Daily-wear items, tools, high-durability needs | Decorative items, low-wear applications |
Need a durable, high-performance finish for your product?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced coating solutions for laboratory equipment and precision components. Our expertise ensures your products benefit from superior wear resistance and longevity.
Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD coating can enhance your project's durability and performance.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Custom CVD Diamond Coating for Lab Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
People Also Ask
- What are diamond coated films? Enhance Materials with Super-Hard, Transparent Layers
- What is CVD diamond coating? Grow a Super-Hard, High-Performance Diamond Layer
- How long does diamond coating last? Maximize Lifespan with the Right Coating for Your Application
- How are tools coated with diamond? Achieve Superior Hardness and Low Friction for Your Tools
- What is the process of CVD diamond coating? Grow a Superior, Chemically-Bonded Diamond Layer



















