In short, yes. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is widely considered an environmentally friendly coating process, especially when compared to traditional methods like electroplating or painting. Its primary environmental advantage comes from the fact that it is a dry, vacuum-based process that eliminates the use of toxic chemicals, hazardous waste, and water pollution associated with older, "wet" plating techniques.
The core environmental benefit of PVD is not that it has zero impact, but that it fundamentally shifts the process from messy, wet chemical reactions to a clean, physical transfer of material in a controlled vacuum. This virtually eliminates the chemical waste streams that define legacy coating methods.

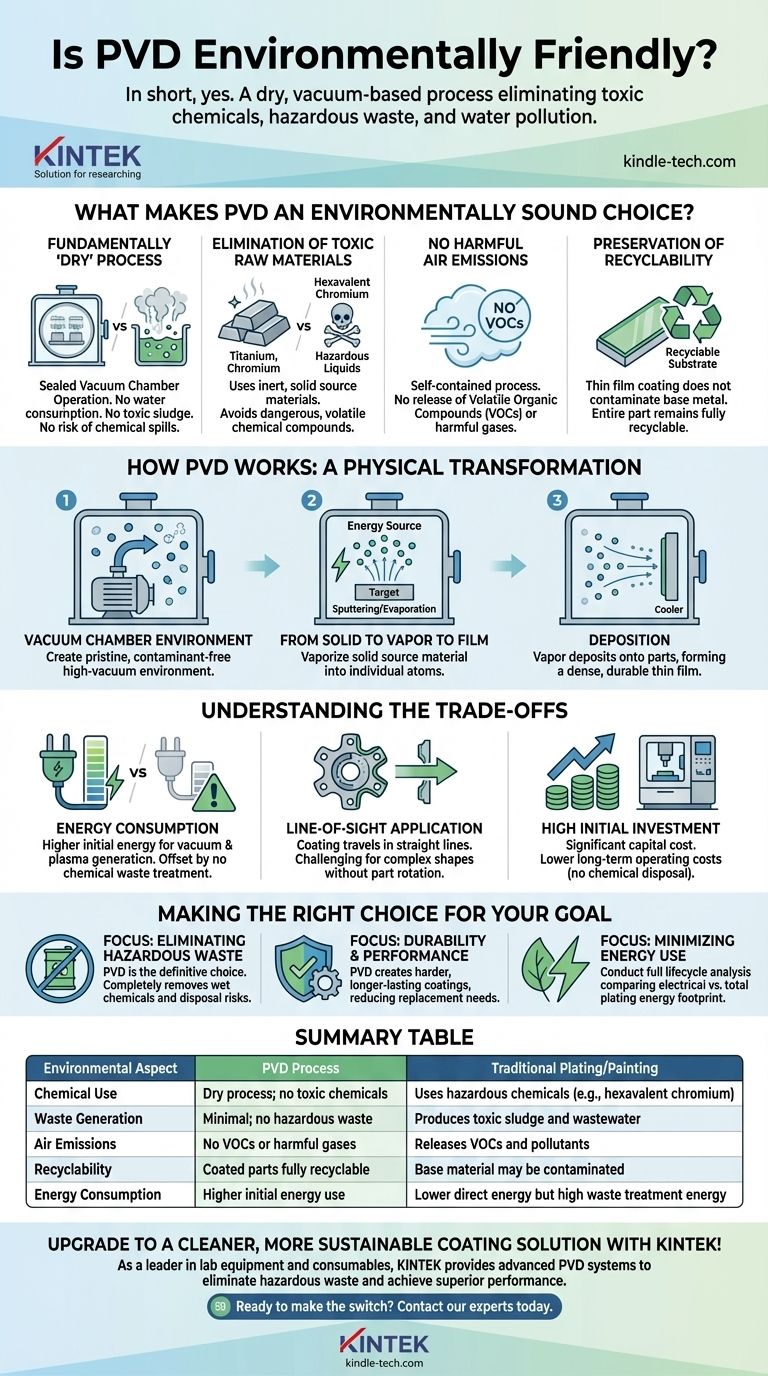
What Makes PVD an Environmentally Sound Choice?
The "green" credentials of PVD are not based on a single factor, but on the nature of the process itself. It avoids the most significant points of failure found in traditional surface finishing.
A Fundamentally 'Dry' Process
Unlike electroplating, which involves submerging parts in baths of hazardous chemical solutions, PVD is a dry process. The entire operation takes place inside a sealed vacuum chamber.
This distinction is critical. There is no chemical-laden water to be treated, no toxic sludge to be disposed of, and no risk of spills contaminating the ground or water supply.
Elimination of Toxic Raw Materials
Traditional chrome plating, for example, relies on hexavalent chromium, a known carcinogen. PVD processes use inert or non-toxic materials like titanium, chromium, and zirconium to create their coatings.
By using stable, solid source materials that are physically vaporized, PVD sidesteps the need for dangerous and volatile chemical compounds.
No Harmful Air Emissions
Painting and certain plating processes can release Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) and other air pollutants into the atmosphere. The PVD process is self-contained within the vacuum chamber.
Because it is not a chemical reaction and does not involve solvents, it produces no harmful gases or other residues that require treatment or scrubbing from the air.
Preservation of Recyclability
A significant, often overlooked benefit is that PVD coatings do not limit the recycling value of the substrate material, such as stainless steel or aluminum.
The coating is exceptionally thin (a few microns) and is metallurgically bonded to the surface. It does not contaminate the base metal, allowing the entire part to be re-melted and recycled at the end of its life.
How PVD Works: A Physical Transformation
To understand why PVD is clean, it helps to understand that it's a process of physical transfer, not chemical reaction.
The Vacuum Chamber Environment
All PVD coating occurs in a high-vacuum chamber. The first step is to pump out the air, creating a pristine environment free of contaminants that could interfere with the coating.
From Solid to Vapor to Film
A solid source material (the "target") is vaporized into individual atoms or molecules using high-energy methods like sputtering (bombardment with ions) or thermal evaporation.
These vaporized atoms then travel through the vacuum chamber in a "line-of-sight" path and deposit onto the cooler surfaces of the parts, forming a dense, durable, and uniform thin film.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No industrial process is without impact. While PVD is a vast improvement over alternatives, objectivity requires acknowledging its trade-offs.
Energy Consumption
The primary environmental trade-off for PVD is its energy consumption. Creating a high vacuum, heating the chamber, and generating the plasma required for sputtering are energy-intensive steps.
However, this energy cost must be weighed against the total environmental impact of alternatives, which includes the energy and resources required to manufacture, transport, and treat toxic chemicals and their waste products.
Line-of-Sight Application
The nature of PVD means the coating material travels in a straight line. This can make it challenging to evenly coat complex, three-dimensional shapes with deep recesses or hidden surfaces without sophisticated part rotation.
This is more of a process limitation than an environmental one, but it's a critical factor in determining if PVD is suitable for a specific application.
High Initial Investment
PVD equipment is technologically advanced and represents a significant capital investment. This can make it less accessible for smaller operations compared to setting up a traditional plating line, although the lower operating costs (no chemical disposal) can offset this over time.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
PVD represents a modern approach to surface finishing that aligns with increasing environmental standards and a focus on product longevity.
- If your primary focus is eliminating hazardous waste: PVD is the definitive choice, as it completely removes wet chemicals and their associated disposal costs and risks.
- If your primary focus is durability and performance: PVD often creates harder, more corrosion-resistant, and longer-lasting coatings, which reduces the need for replacement and has a positive secondary environmental benefit.
- If your primary focus is minimizing energy use: You must conduct a full lifecycle analysis, comparing the electrical consumption of PVD against the total energy footprint of plating (including chemical manufacturing and waste treatment).
By replacing wet chemical processes with a clean, high-performance physical one, PVD provides a responsible path forward for durable and decorative coatings.
Summary Table:
| Environmental Aspect | PVD Process | Traditional Plating/Painting |
|---|---|---|
| Chemical Use | Dry process; no toxic chemicals | Uses hazardous chemicals (e.g., hexavalent chromium) |
| Waste Generation | Minimal; no hazardous waste | Produces toxic sludge and wastewater |
| Air Emissions | No VOCs or harmful gases | Releases VOCs and pollutants |
| Recyclability | Coated parts fully recyclable | Base material may be contaminated |
| Energy Consumption | Higher initial energy use | Lower direct energy but high waste treatment energy |
Upgrade to a cleaner, more sustainable coating solution with KINTEK!
As a leader in lab equipment and consumables, KINTEK provides advanced PVD systems that help laboratories and manufacturers eliminate hazardous waste, reduce environmental impact, and achieve superior coating performance. Our expertise ensures you get a reliable, eco-friendly alternative to traditional plating methods.
Ready to make the switch? Contact our experts today to explore how PVD technology can meet your specific needs while supporting your sustainability goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- What is an example of PECVD? RF-PECVD for High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















