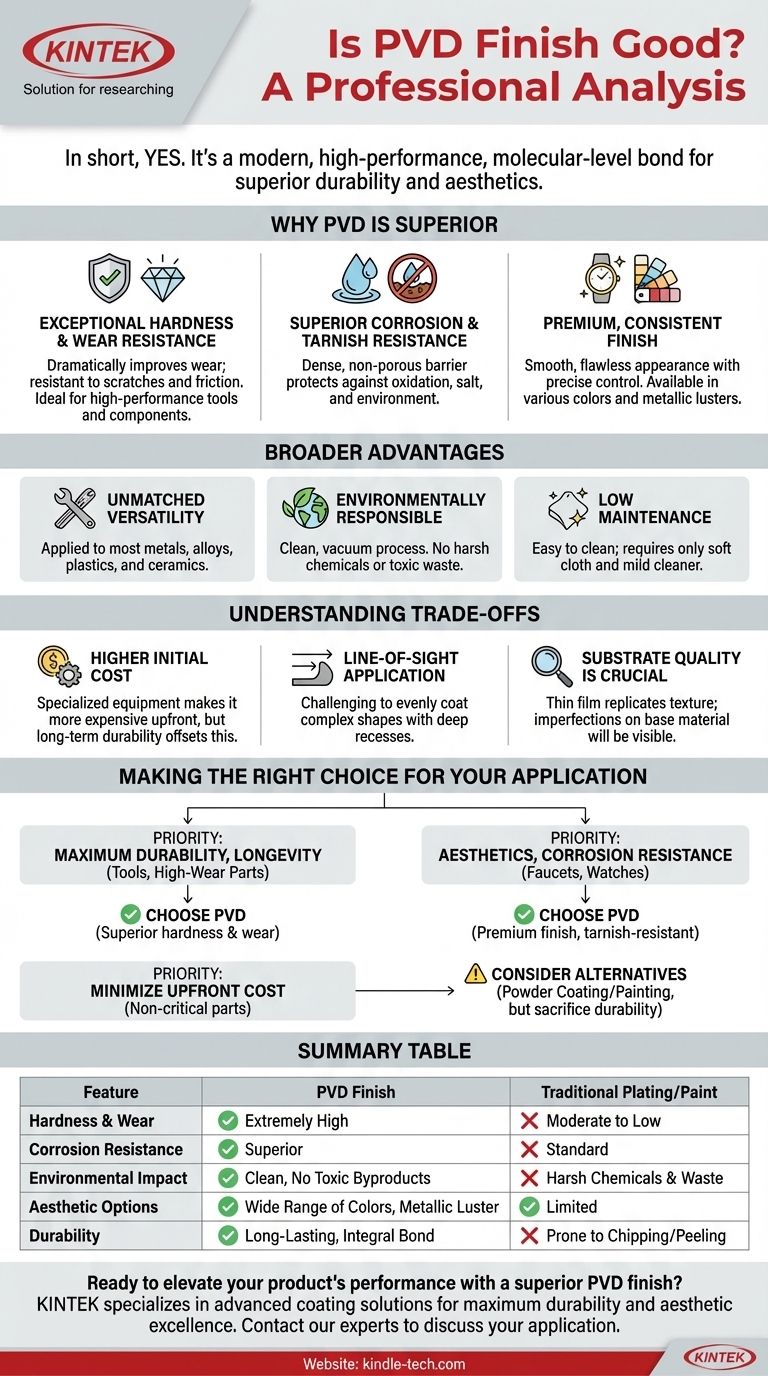
In short, yes, a PVD finish is exceptionally good. It is a modern, high-performance coating process that creates a surface layer that is significantly more durable, corrosion-resistant, and harder than most traditional coating methods. Unlike paint or standard electroplating, PVD bonds to the material on a molecular level, resulting in a finish that is not just a covering, but an integral part of the surface.
The core reason PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is considered an excellent finish is that it's not simply applied to a surface; it's bonded with it in a high-tech vacuum process. This creates a finish defined by superior hardness and longevity that far surpasses older methods like electroplating or painting.

What Makes PVD a Superior Coating Technology?
To understand if PVD is the right choice, you need to look beyond a simple "good" or "bad" label. The value of PVD lies in the specific, measurable advantages of its application process.
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance
PVD coatings are extremely hard, dramatically improving the wear resistance of the base material. This is why it is trusted for high-performance applications like industrial tools, medical implants, and engine components.
The finish is highly resistant to scratches and friction, maintaining its original appearance even with heavy use. This often eliminates the need for any protective clear topcoats.
Superior Corrosion and Tarnish Resistance
The PVD process creates a dense, non-porous barrier that is inherently resistant to oxidation, tarnish, and corrosion from salt, air, and other environmental factors.
This makes it an ideal choice for items that are frequently handled or exposed to the elements, such as watches, jewelry, and high-end plumbing fixtures.
A Premium, Consistent Finish
Beyond its functional benefits, PVD offers a wide range of aesthetic options. It can produce finishes in various colors with a rich, metallic luster.
The process allows for precise control over the coating's thickness and uniformity, resulting in a smooth, flawless, and high-quality appearance.
The Broader Advantages of the PVD Process
The benefits of PVD extend beyond the physical properties of the final product. The process itself offers distinct advantages over traditional alternatives.
Unmatched Versatility
PVD can be applied to a vast array of materials, including most metals, alloys, and even some plastics and ceramics. This makes it a flexible solution for nearly any industry.
An Environmentally Responsible Choice
Traditional coating processes like chrome electroplating involve harsh chemicals and produce toxic waste. PVD, in contrast, is an environmentally clean process.
It takes place in a vacuum and transfers the coating material physically, atom by atom, without producing harmful chemical byproducts.
Low Maintenance
Surfaces coated with PVD are very easy to clean and maintain. They typically require nothing more than a soft cloth and mild cleaner to restore their original luster.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No technology is perfect for every situation. To make an informed decision, it's critical to understand the limitations of PVD.
Higher Initial Cost
The specialized equipment and vacuum environment required for PVD make it a more expensive process upfront compared to traditional painting or electroplating. The long-term durability, however, can often offset this initial investment.
Line-of-Sight Application
In most PVD processes, the coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the target. This can make it challenging to evenly coat complex shapes with deep recesses or internal channels.
Substrate Quality is Crucial
PVD is a very thin film. It will replicate the texture of the underlying surface, not hide it. Any imperfections, scratches, or blemishes on the base material will be visible through the PVD coating.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a finish depends entirely on your project's priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and longevity (e.g., tools, high-wear parts): PVD is one of the best choices available due to its superior hardness and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is aesthetics and corrosion resistance (e.g., faucets, watches, architectural hardware): PVD provides a premium, tarnish-resistant finish in various colors that will far outlast traditional plating.
- If your primary focus is environmental impact: PVD is a significantly cleaner and more responsible choice than processes like traditional chrome plating.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront cost on a non-critical part: A simpler method like powder coating or painting might be more suitable, but you will be sacrificing durability.
Ultimately, choosing a PVD finish is an investment in superior performance, longevity, and quality.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD Finish | Traditional Plating/Paint |
|---|---|---|
| Hardness & Wear | Extremely High | Moderate to Low |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior | Standard |
| Environmental Impact | Clean, No Toxic Byproducts | Harsh Chemicals & Waste |
| Aesthetic Options | Wide Range of Colors, Metallic Luster | Limited |
| Durability | Long-Lasting, Integral Bond | Prone to Chipping/Peeling |
Ready to elevate your product's performance with a superior PVD finish? KINTEK specializes in advanced coating solutions for industries requiring maximum durability and aesthetic excellence. Our PVD technology ensures your components are harder, more corrosion-resistant, and built to last. Whether you're in medical, automotive, or consumer goods, we provide the finish that meets your high standards. Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can transform your application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















