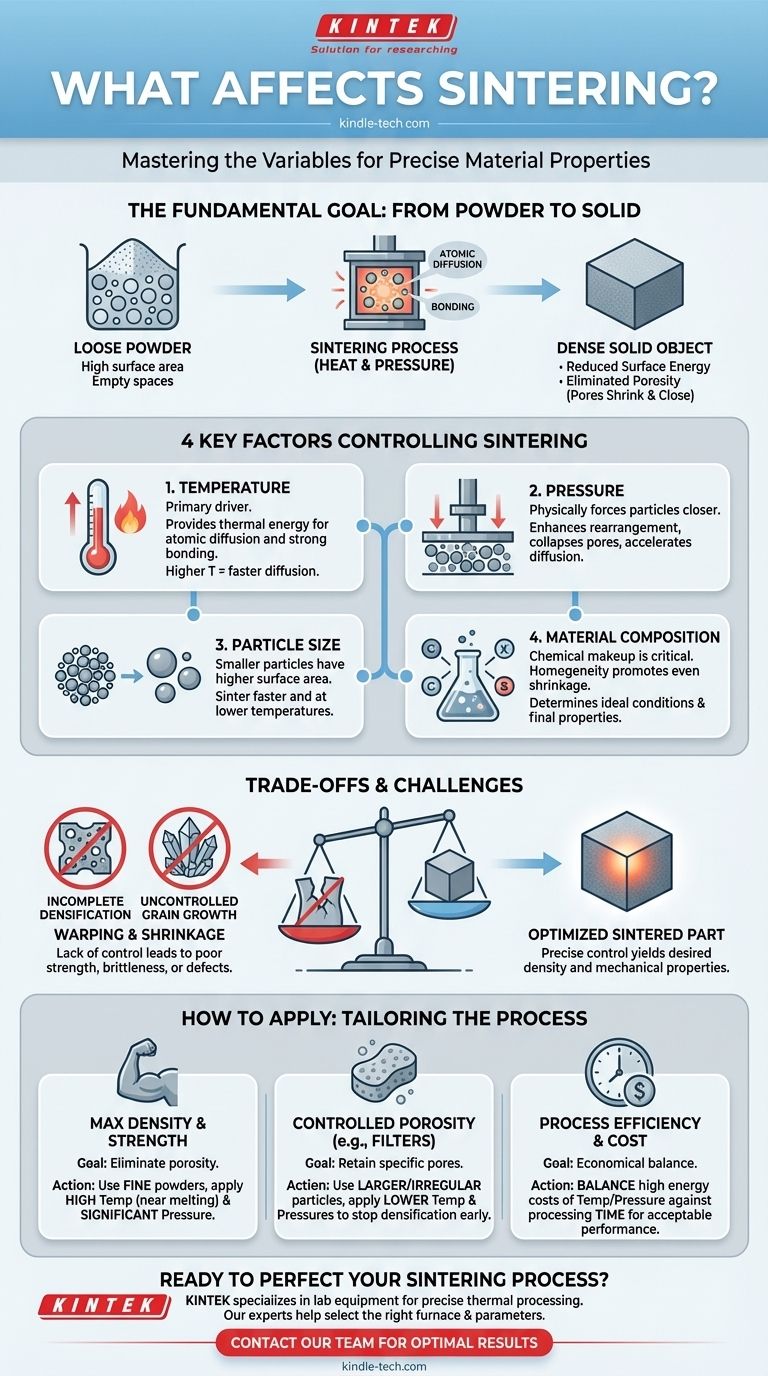
The sintering process is primarily affected by four key factors. These are the process temperature, the applied pressure, the size of the initial powder particles, and the material's composition. Each of these variables must be carefully controlled to transform a loose powder into a dense, solid object with specific mechanical properties.
Sintering is fundamentally a game of energy and geometry. The goal is to use heat and pressure to encourage individual particles to bond together, systematically eliminating the empty spaces between them to create a solid, unified mass.

The Fundamental Goal: From Powder to Solid
Sintering is a thermal treatment for compacting powder into a solid piece. It works by applying heat at a temperature below the material’s melting point, causing atoms to diffuse across the boundaries of the particles, fusing them together.
Reducing Surface Energy
A collection of loose powder has an incredibly high surface area. This high surface area corresponds to high surface energy, an unstable state. Sintering provides a path for the system to lower its energy by reducing the total surface area as individual particles bond and merge.
Eliminating Porosity
The gaps between particles are known as pores. The primary objective of most sintering operations is to reduce or eliminate this porosity. As particles fuse, these pores shrink and eventually close, leading to a denser, stronger final component.
Key Factors that Control the Sintering Process
Mastering the sintering process requires understanding how each variable contributes to the final outcome. These factors work in concert to drive the densification of the material.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is the primary driver of sintering. It provides the thermal energy necessary for atoms to become mobile and diffuse across particle boundaries, forming strong atomic bonds. Without sufficient heat, this diffusion process is too slow to be effective.
The Impact of Pressure
Applying external pressure physically forces the powder particles into closer contact. This enhances particle rearrangement, collapses larger pores, and accelerates the diffusion process that bonds the particles together.
Why Particle Size Matters
Sintering behavior is highly dependent on the size of the initial particles. Smaller particles have a higher surface-area-to-volume ratio, which provides a greater driving force for densification, allowing the process to occur at lower temperatures or in less time.
The Influence of Material Composition
The chemical makeup of the powder is critical. A homogeneous composition, where all particles are uniform and well-mixed, promotes even shrinkage and consistent properties. Different materials and alloys have vastly different ideal sintering temperatures and behaviors.
The Effect of Heating Rate
The speed at which the target temperature is reached can also influence the outcome. A carefully controlled heating rate can affect the final density and grain structure of the material, preventing defects like cracking.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
Achieving a perfect sintered part involves balancing competing factors. A lack of control can lead to undesirable outcomes that compromise the integrity of the component.
Incomplete Densification
If the temperature is too low, the pressure is insufficient, or the processing time is too short, the part will not fully densify. This leaves behind significant porosity, resulting in a component with poor mechanical strength and reliability.
Uncontrolled Grain Growth
While high temperatures promote densification, holding a part at peak temperature for too long can cause the internal crystalline structures (grains) to grow too large. Overly large grains can often make a material, especially a ceramic, more brittle.
Warping and Shrinkage
As the material densifies and pores are eliminated, the entire part shrinks. If the initial powder is not packed uniformly or if heating is uneven, this shrinkage can be non-uniform, causing the part to warp, distort, or even crack.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Your specific goal will determine how you manipulate the key sintering variables. The process is not one-size-fits-all; it must be tailored to the desired properties of the final product.
- If your primary focus is maximum density and strength: Use fine, uniform powders and apply high temperatures (approaching the melting point) and significant pressure to eliminate as much porosity as possible.
- If your primary focus is creating a controlled porous structure (e.g., for filters): Use larger or more irregular particles with lower temperatures and pressures to intentionally stop the densification process before all pores are closed.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and cost: Balance the high energy costs of temperature and pressure against processing time to find the most economical path to achieving an acceptable level of performance for your application.
By mastering these variables, you gain precise control over the final properties of your material, from its strength to its density.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Primary Effect on Sintering |
|---|---|
| Temperature | Drives atomic diffusion for particle bonding and densification. |
| Pressure | Forces particles into closer contact, accelerating bonding. |
| Particle Size | Smaller particles sinter faster and at lower temperatures. |
| Material Composition | Determines ideal sintering temperature and final properties. |
Ready to perfect your sintering process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise thermal processing. Our experts can help you select the right furnace and parameters to achieve your desired material density, strength, and structure. Contact our team today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and ensure optimal results for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the use of muffle furnace in food analysis? Master Ashing for Accurate Mineral Content
- What is the construction of a muffle furnace? Discover the Precision Engineering for Pure, Controlled Heating
- What is a muffle furnace used for in pharma? Ensuring Purity and Regulatory Compliance
- What is the purpose of calcination? Transform and Purify Materials for Industrial Use
- What is the function of a muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Contamination-Free Heating



















