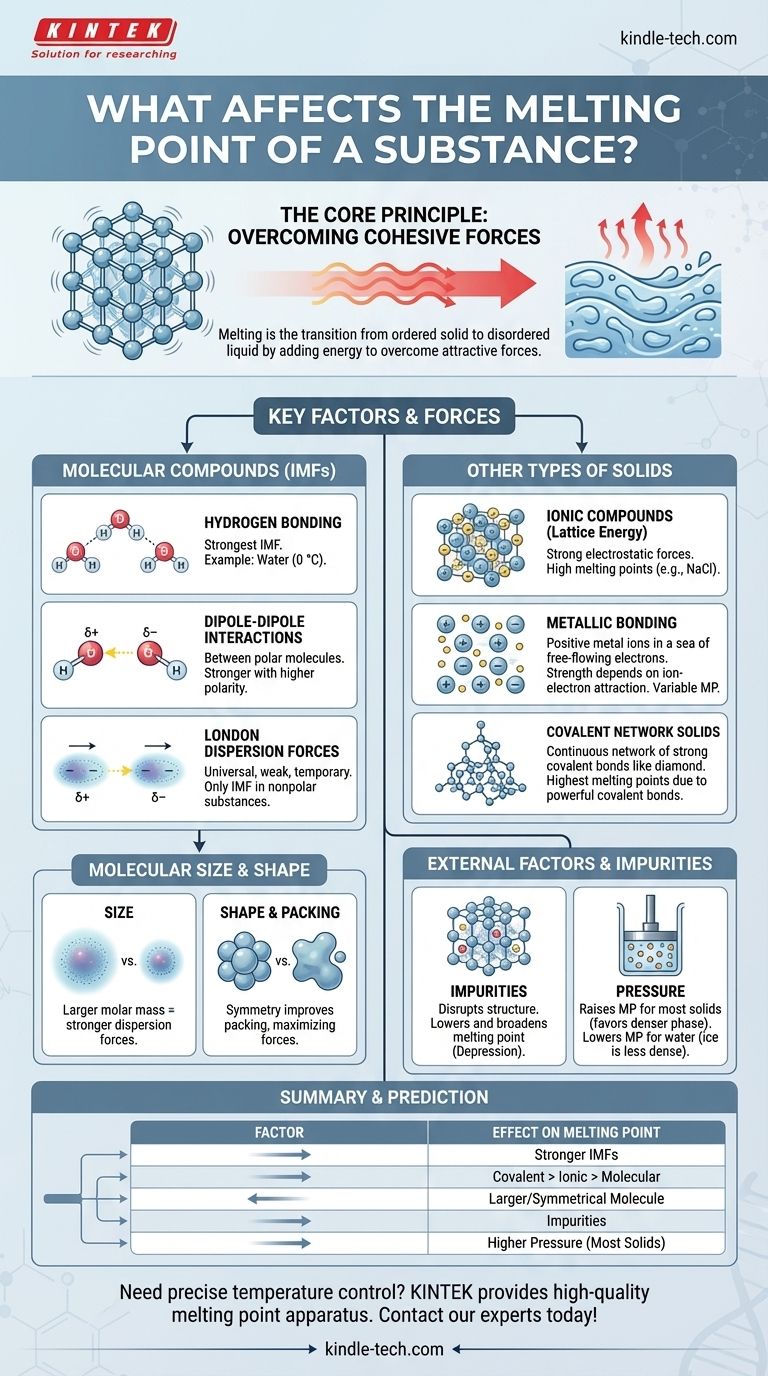
At its core, a substance's melting point is determined by the energy needed to overcome the attractive forces holding its particles in a fixed, three-dimensional structure. The primary factors are the strength of these forces—whether chemical bonds or weaker intermolecular forces—and the way the particles pack together. Factors like molecular size, shape, and the presence of impurities also play a crucial role.
The central principle is simple: stronger attractive forces between particles require more thermal energy to break, resulting in a higher melting point. The entire story of melting points is an exploration of what creates and modifies these forces.

The Core Principle: Overcoming Cohesive Forces
Melting is a physical transformation from an ordered solid state to a disordered liquid state. Understanding this transition is key to understanding the factors that control it.
What is Melting?
In a solid, atoms, ions, or molecules are locked into a fixed arrangement called a crystal lattice. They vibrate in place but do not move past one another.
Melting occurs at the specific temperature where these particles gain enough kinetic energy from heat to break free from their fixed positions and begin to flow.
Energy vs. Cohesion
The heat you add to a substance increases the kinetic energy of its particles, causing them to vibrate more intensely. The melting point is the equilibrium temperature where this vibrational energy becomes powerful enough to overcome the cohesive forces holding the lattice together.
Key Factors for Molecular Compounds
For substances made of discrete molecules (like water, wax, or sugar), the forces between the molecules—not the bonds within them—are what break during melting. These are called intermolecular forces (IMFs).
Hydrogen Bonding: The Strongest IMF
A hydrogen bond is a powerful type of dipole-dipole interaction that occurs when hydrogen is bonded to a highly electronegative atom like nitrogen (N), oxygen (O), or fluorine (F).
Water (H₂O) is a classic example. Its high melting point (0 °C) compared to similarly sized molecules is due entirely to the strong network of hydrogen bonds holding the molecules together in ice.
Dipole-Dipole Interactions
These forces exist between polar molecules, which have permanent partial positive and partial negative ends. The positive end of one molecule attracts the negative end of its neighbor.
The greater the molecule's polarity, the stronger the dipole-dipole attraction, and the higher the melting point.
London Dispersion Forces: The Universal Force
These temporary, weak attractions exist in all molecules, both polar and nonpolar. They arise from momentary fluctuations in the electron cloud around a molecule, creating fleeting dipoles.
For nonpolar substances like methane (CH₄) or octane (C₈H₁₈), London dispersion forces are the only IMFs present.
The Role of Molecular Size and Shape
Size (Molar Mass): Larger molecules have larger electron clouds, which are more easily distorted. This leads to stronger London dispersion forces and, consequently, higher melting points. This is why large, waxy hydrocarbons are solid at room temperature while small ones like methane are gases.
Symmetry and Packing: Molecules that are symmetrical and compact can pack more tightly and efficiently into a crystal lattice. This close packing maximizes the effectiveness of intermolecular forces, leading to a higher melting point than for irregularly shaped isomers of the same size.
Beyond Molecules: Other Types of Solids
Not all solids are made of discrete molecules. In many materials, melting requires breaking powerful chemical bonds that extend throughout the entire structure.
Ionic Compounds and Lattice Energy
In ionic compounds like table salt (NaCl), positive and negative ions are held in a rigid lattice by strong electrostatic forces (ionic bonds). Melting these substances requires overcoming this immense attraction, which is measured by lattice energy.
Because ionic bonds are far stronger than intermolecular forces, ionic compounds have very high melting points.
Metals and Metallic Bonding
Metals are held together by metallic bonds, where a "sea" of delocalized electrons flows freely among a fixed lattice of positive metal ions.
The strength of the attraction between the ions and this electron sea determines the melting point. Metals like tungsten and titanium form very strong metallic bonds and have exceptionally high melting points.
Covalent Network Solids
In these materials, atoms are joined by a continuous network of strong covalent bonds. There are no individual molecules.
To melt a covalent network solid like diamond (carbon) or quartz (silicon dioxide), you must break these powerful covalent bonds. This requires a tremendous amount of energy, giving them the highest melting points of any class of substance.
Understanding the Trade-offs and External Factors
The intrinsic properties of a substance are not the only influence. External conditions and composition also have a significant impact.
The Effect of Impurities: Melting Point Depression
The presence of an impurity disrupts the uniform structure of a crystal lattice. This weakened, disorganized lattice requires less energy to break apart.
This phenomenon is known as melting point depression. It is why a pure substance has a sharp, distinct melting point, while an impure substance melts over a broad, lower temperature range. It's also the principle behind using salt to melt ice on winter roads.
The Influence of Pressure
For most substances, the solid phase is denser than the liquid phase. Increasing pressure favors the denser state, pushing the particles closer together and making it harder for them to break free. Therefore, for most materials, higher pressure raises the melting point.
Water is a famous exception. Because ice is less dense than liquid water, increasing pressure favors the liquid state, thereby lowering the melting point.
How to Predict Relative Melting Points
Use these principles to compare different substances and predict their behavior.
- If you are comparing a covalent network, ionic, and molecular compound: The covalent network (e.g., diamond) will be highest, followed by the ionic (e.g., salt), with the molecular compound (e.g., sugar) being far lower.
- If you are comparing molecular compounds: First, check for hydrogen bonding, which is a dominant factor. If absent, compare polarity. If they are all nonpolar or have similar polarity, the one with the larger molar mass will generally have the higher melting point.
- If you are comparing ionic compounds: The compound with the higher charges on its ions and/or smaller ionic radii will have a stronger lattice energy and a higher melting point.
- If you need to assess purity: A substance that melts sharply at its known melting point is likely pure, whereas one that melts gradually over a range below its expected point is impure.
By understanding these fundamental forces, you can effectively predict how a substance's microscopic structure dictates its melting behavior.
Summary Table:
| Factor | Effect on Melting Point | Key Principle |
|---|---|---|
| Intermolecular Forces (IMFs) | Higher with stronger IMFs | Hydrogen bonding > dipole-dipole > London dispersion |
| Chemical Bonding Type | Covalent network > Ionic > Metallic > Molecular | Strength of bonds that must be broken |
| Molecular Size/Shape | Higher with larger molar mass & symmetrical shape | Increases London forces and improves lattice packing |
| Impurities | Lowers (Melting Point Depression) | Disrupts crystal lattice, requiring less energy to melt |
| Pressure | Raises (for most solids); Lowers (for ice/water) | Favors the denser phase (solid for most, liquid for water) |
Need precise temperature control for your materials analysis? Understanding melting points is critical for material characterization, purity assessment, and process development. KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment, including melting point apparatus and furnaces, to help your laboratory achieve accurate and reliable results. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the two classifications of heat treatments? Mastering the Balance of Strength and Ductility
- What is a braze repair process? A Low-Heat Solution for Strong, Seamless Metal Joining
- What is the vacuum level of a thermal evaporator? Achieve Purity with High Vacuum (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁷ Torr)
- What are the different types of plate and frame filter press? Choose the Right Dewatering Solution
- What does sputtering mean in business? A Strategic Manufacturing Process for Competitive Advantage
- What is the process of vacuum thermoforming? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective Plastic Shaping
- What is the effect of sintering on microstructures? Achieve Precise Control of Material Properties
- What is the purpose of post-deposition heat treatment at 700°C for Al coatings? Enhance Oxidation Resistance



















