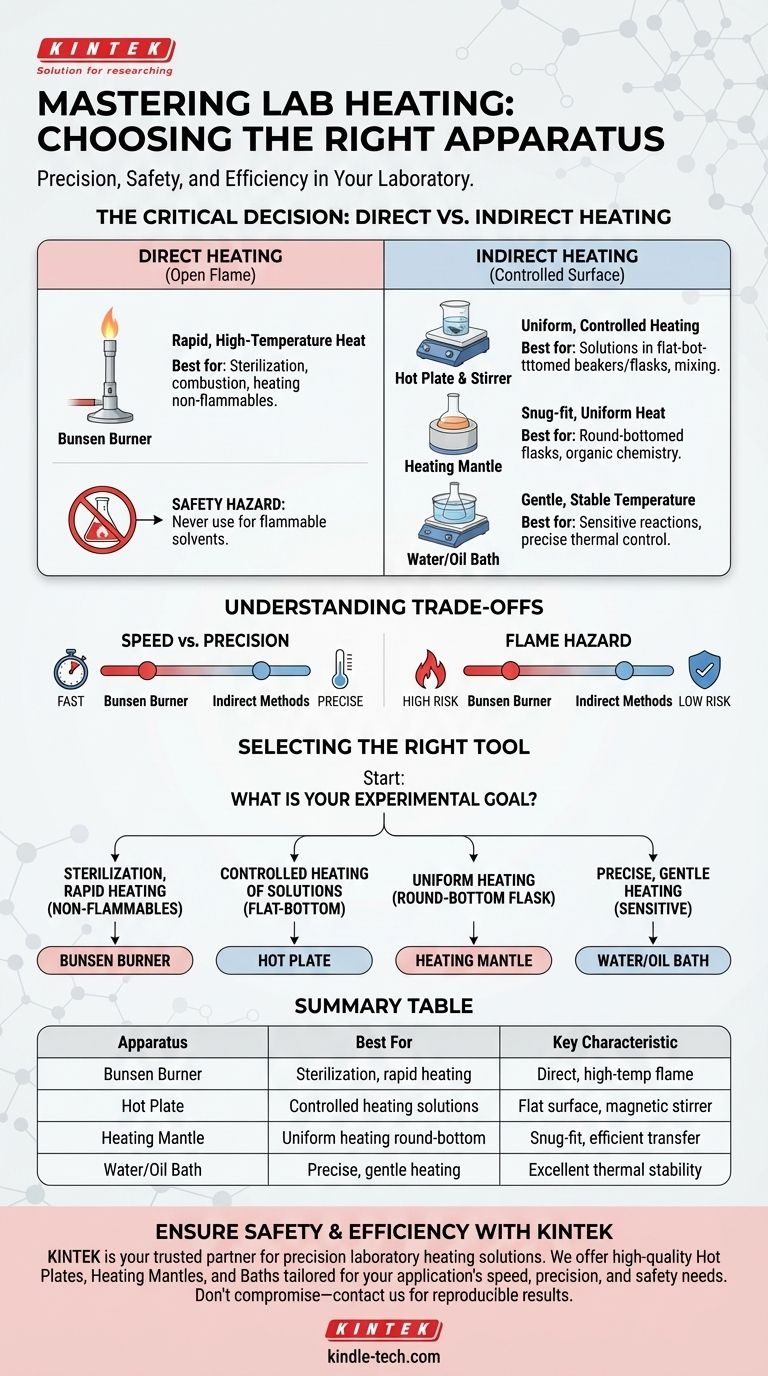
While the classic Bunsen burner is a well-known heating tool, the modern laboratory utilizes a range of specialized apparatus, each designed for a specific purpose. The choice of equipment depends entirely on the required temperature, the need for precision, and the volatility of the substances involved.
The most critical decision in laboratory heating is not just what to use, but why. Choosing between a direct open flame and a controlled electrical source is a fundamental question of safety, precision, and experimental success.
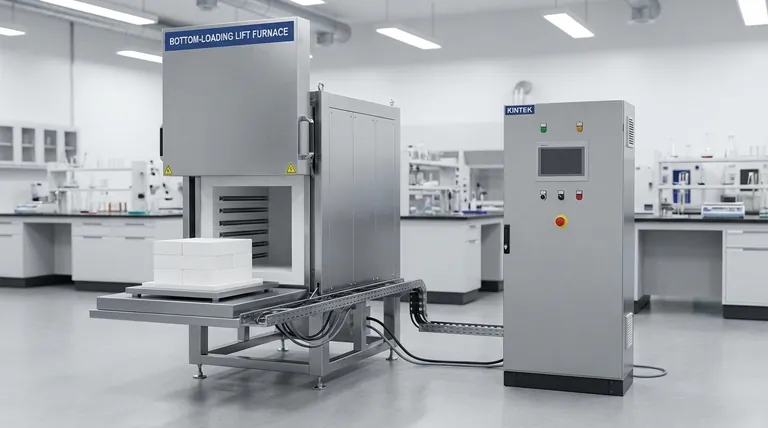

Direct vs. Indirect Heating: The Core Principle
The primary distinction between laboratory heating methods is whether you apply heat directly with a flame or indirectly through a surface or medium. This choice impacts temperature control, heat distribution, and, most importantly, safety.
The Bunsen Burner: For Direct, High-Temperature Heat
A Bunsen burner produces an open flame through the combustion of gas. It is used for tasks requiring rapid and intense heat.
Its primary applications include sterilizing equipment like inoculation loops, performing simple combustion reactions, or strongly heating stable, non-flammable materials in a crucible.
Hot Plates: For Uniform, Controlled Heating
A hot plate is one of the most common pieces of lab equipment. It provides a flat, heated surface, offering much greater temperature control than a Bunsen burner.
Most hot plates also include a magnetic stirrer, allowing a solution to be heated and mixed simultaneously. This ensures even temperature distribution and prevents localized "hot spots."
Heating Mantles: For Round-Bottomed Flasks
Standard hot plates are inefficient for heating round-bottomed flasks due to minimal surface contact. A heating mantle is a flexible fiberglass container designed to fit snugly around the bottom of the flask.
Internal heating elements provide even, direct contact and uniform heating, which is critical for many organic chemistry reactions.
Water and Oil Baths: For Gentle, Stable Temperatures
For reactions that require a stable and precise temperature below 100°C, a water bath is ideal. The vessel is immersed in heated water, which provides excellent thermal stability.
For temperatures above the boiling point of water, an oil bath (often using silicone oil on a hot plate) serves the same purpose, offering highly precise temperature control for sensitive procedures.
Understanding the Critical Trade-offs
Selecting the wrong heating apparatus can ruin an experiment or create a significant safety hazard. Understanding the trade-offs is not optional; it is essential.
Speed vs. Precision
A Bunsen burner provides heat very quickly but offers very poor temperature regulation. In contrast, an electric hot plate or water bath takes longer to reach the target temperature but provides vastly superior precision and stability.
The Open Flame Hazard
This is the single most important safety consideration. A Bunsen burner's open flame is an ignition source and must never be used to heat flammable organic solvents like ethanol, acetone, or ether. Doing so can cause a fire or explosion.
Vessel Compatibility
The shape of your glassware dictates the appropriate tool. A flat-bottomed beaker or Erlenmeyer flask is perfect for a hot plate. A round-bottomed flask requires a heating mantle for efficient and uniform heat transfer.
Selecting the Right Tool for Your Application
Your experimental goal is the sole factor that should guide your choice of heating apparatus.
- If your primary focus is sterilization or strong, rapid heating of non-flammables: A Bunsen burner is the correct tool.
- If your primary focus is controlled heating of a solution in a beaker or flat-bottomed flask: A magnetic hot plate is the industry standard.
- If your primary focus is uniform heating of a reaction in a round-bottomed flask: A heating mantle is non-negotiable for safety and efficiency.
- If your primary focus is precise, gentle heating for a temperature-sensitive reaction: A water or oil bath provides the highest degree of thermal control.
Choosing the appropriate heating instrument is a foundational lab skill that ensures safety, accuracy, and the reproducibility of your results.
Summary Table:
| Heating Apparatus | Best For | Key Characteristic |
|---|---|---|
| Bunsen Burner | Sterilization, rapid heating of non-flammables | Direct, high-temperature flame |
| Hot Plate | Controlled heating of solutions in beakers/flasks | Flat, heated surface; often with magnetic stirrer |
| Heating Mantle | Uniform heating of round-bottomed flasks | Snug-fit design for efficient heat transfer |
| Water/Oil Bath | Precise, gentle heating for sensitive reactions | Excellent thermal stability and control |
Ensure Your Lab's Safety and Efficiency with the Right Heating Equipment
Choosing the correct heating apparatus is critical for experimental success and operator safety. The wrong choice can lead to inaccurate results, damaged glassware, or even a fire hazard.
KINTEK is your trusted partner for all laboratory heating needs. We specialize in providing high-quality, reliable lab equipment and consumables, including:
- Precision Hot Plates & Stirrers for controlled heating and mixing.
- Durable Heating Mantles designed for optimal performance with round-bottomed flasks.
- Safe and Efficient Baths for temperature-sensitive applications.
Our experts understand the critical trade-offs between speed, precision, and safety. We can help you select the perfect equipment for your specific application, ensuring reproducible results and a safer laboratory environment.
Don't leave your experiments to chance. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What are the five methods of synthesis of nanoparticles? A Guide to Top-Down & Bottom-Up Approaches
- Why argon is used in magnetron sputtering? The Ideal Gas for Efficient Thin Film Deposition
- Why must product gas pass through a condenser and a drying tube? Ensure MicroGC Precision and Protection
- What is thin film industry? The Foundation of Modern Electronics, Optics, and Energy
- What is the long-term stability of viral analytes in plasma stored at -70°C? Proven for Decades of Research
- How does sintering increase density? Master the Process for Superior Material Performance
- Can aluminum be sputtered? Master the Process for High-Quality Thin Films
- What is the difference between XRF and XRD techniques? A Guide to Choosing the Right Analytical Tool



















