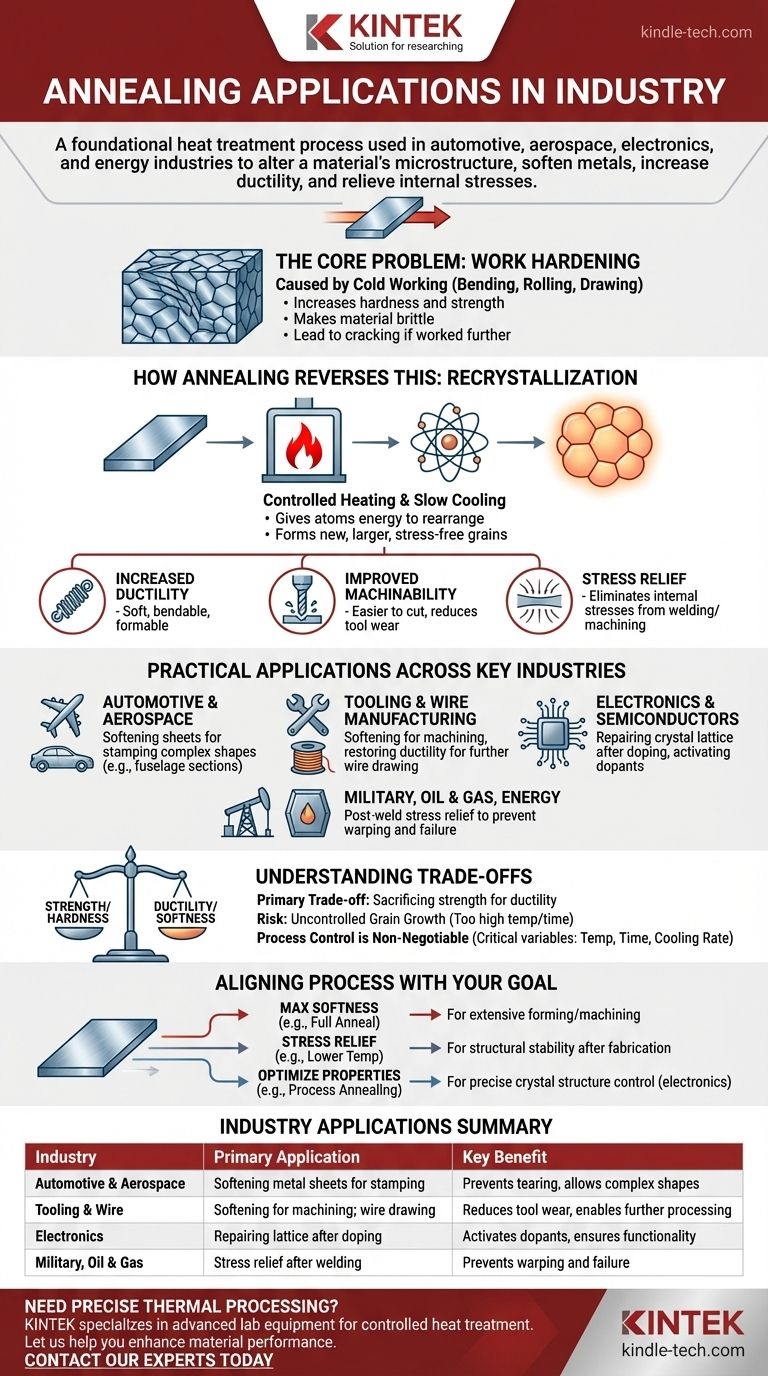
In industries ranging from automotive and aerospace to electronics and energy, annealing is a foundational heat treatment process. It is used to alter a material's microstructure, primarily to soften metals, increase their ductility (ability to be deformed without fracturing), and relieve internal stresses that accumulate during manufacturing.
Annealing should be understood not as a strengthening process, but as a restorative one. Its fundamental purpose is to reverse the negative effects of manufacturing—like hardening and brittleness—to make a material more workable and structurally stable for its next stage of life.
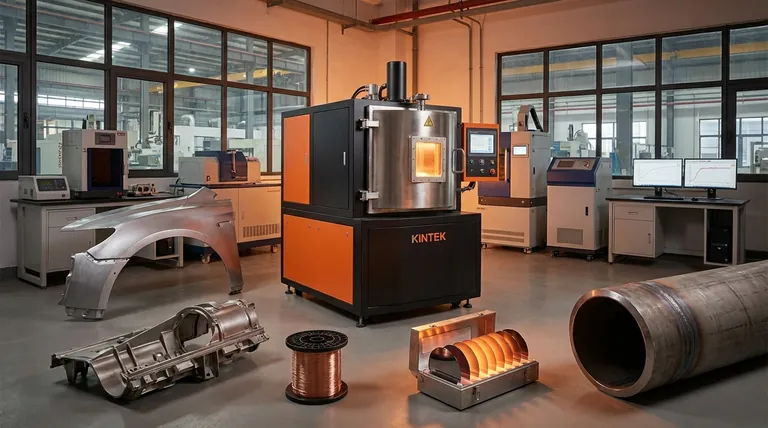

The Core Problem Annealing Solves: Work Hardening
To understand annealing's value, you must first understand the problem it corrects. Many manufacturing processes inherently damage the material they are shaping.
What is Work Hardening?
When a metal is bent, rolled, drawn, or hammered at room temperature (a process called "cold working"), its internal crystal structure becomes distorted and stressed.
This makes the metal harder and stronger, but it also makes it more brittle and difficult to shape further. Eventually, it will crack if more work is attempted.
How Annealing Reverses This
Annealing is a process of controlled heating and cooling. The material is heated to a specific temperature, held there for a period, and then cooled slowly.
This heat gives the atoms within the crystal structure the energy to move. They rearrange themselves into new, larger, and stress-free "grains," a process known as recrystallization.
The Three Key Outcomes
By resetting the material's internal structure, annealing achieves three primary goals:
- Increased Ductility: The metal becomes softer and can be bent, stretched, or formed into complex shapes without failing.
- Improved Machinability: A softer material is easier to cut, drill, or mill, which reduces tool wear and lowers manufacturing costs.
- Stress Relief: It eliminates the internal stresses built up during processes like welding or heavy machining, which could otherwise lead to warping or premature failure.
Practical Applications Across Key Industries
The benefits of annealing are applied differently depending on the industry's unique demands.
Automotive and Aerospace
Manufacturers of car body panels or aircraft fuselage sections rely on annealing. Sheets of aluminum or steel are annealed to make them ductile enough to be stamped and pressed into complex aerodynamic shapes without tearing.
Tooling and Wire Manufacturing
Before a block of tool steel can be precisely machined into a die or a mold, it is often annealed to make it soft and easy to cut. After machining, it is re-hardened for its final use.
Similarly, in wire drawing, a thick rod is pulled through progressively smaller dies. The wire becomes work-hardened after each step and must be annealed to restore its ductility before it can be drawn further.
Electronics and Semiconductors
In the semiconductor industry, annealing is a high-precision process. After ions are implanted into a silicon wafer to change its electrical properties (doping), the crystal lattice is damaged.
A carefully controlled anneal is used to repair this lattice damage and "activate" the dopants, ensuring the microchip functions correctly.
Military, Oil & Gas, and Energy
For components like armor plating, pipelines, or pressure vessels, welding induces immense localized stress. A post-weld anneal (specifically, a stress-relief anneal) is critical to remove these stresses and prevent catastrophic failures under pressure or impact.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, annealing is not a universal solution and involves clear compromises. It is an intermediate step, not typically an end-state for structural parts.
The Primary Trade-off: Strength for Ductility
The most significant trade-off is sacrificing hardness and strength for ductility. The very act of softening a metal to make it workable means it cannot be used in that state for applications requiring high strength. It must often be re-hardened later.
Risk of Uncontrolled Grain Growth
If the annealing temperature is too high or the holding time is too long, the new crystal grains can grow too large. Overly large grains can degrade a material's toughness and other mechanical properties, making it unsuitable for its intended purpose.
Process Control is Non-Negotiable
Annealing is not simply "heating something up." The exact temperature, time at temperature, and cooling rate are all critical variables that depend entirely on the specific alloy and the desired outcome. Incorrect parameters can ruin the material.
Aligning the Process with Your Goal
Choosing the right annealing approach depends entirely on what you need to achieve.
- If your primary focus is preparing for extensive forming or machining: Use a full anneal to achieve maximum softness and ductility, accepting the temporary loss of strength.
- If your primary focus is ensuring structural stability after fabrication: Use a stress-relief anneal at a lower temperature to remove internal stresses from welding or machining without significantly softening the material.
- If your primary focus is optimizing physical properties: Use specialized cycles, like process annealing in electronics, where precise control of the crystal structure is more important than mechanical softness.
Ultimately, annealing provides the metallurgical control required to make materials workable, reliable, and perfectly suited for their final application.
Summary Table:
| Industry | Primary Application of Annealing | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive & Aerospace | Softening metal sheets for stamping and forming | Prevents tearing, allows complex shapes |
| Tooling & Wire | Softening steel before machining; restoring ductility in wire drawing | Reduces tool wear, enables further processing |
| Electronics | Repairing silicon wafer crystal lattice after doping | Activates dopants, ensures chip functionality |
| Military, Oil & Gas | Stress relief after welding critical components | Prevents warping and catastrophic failure |
Need precise thermal processing for your materials?
KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment, including furnaces and ovens, for controlled heat treatment processes like annealing. Whether you are in R&D or quality control, our solutions help you achieve the exact material properties—like ductility and stress relief—required for your industry's demanding applications.
Let us help you enhance your material performance and manufacturing reliability. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace Nitrogen Inert Atmosphere Furnace
- Controlled Nitrogen Inert Hydrogen Atmosphere Furnace
- 1400℃ Controlled Atmosphere Furnace with Nitrogen and Inert Atmosphere
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of heat treatment process for steel? Tailor Strength, Hardness & Toughness
- What is a vacuum heat treatment furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Controlled Atmosphere Processing
- What is the process of vacuum quenching? Achieve Superior Hardness with a Pristine Surface Finish
- How does heat treatment process work? Tailor Material Properties for Your Application
- What is the difference between annealing hardening and tempering? Master Metal Properties for Your Lab



















