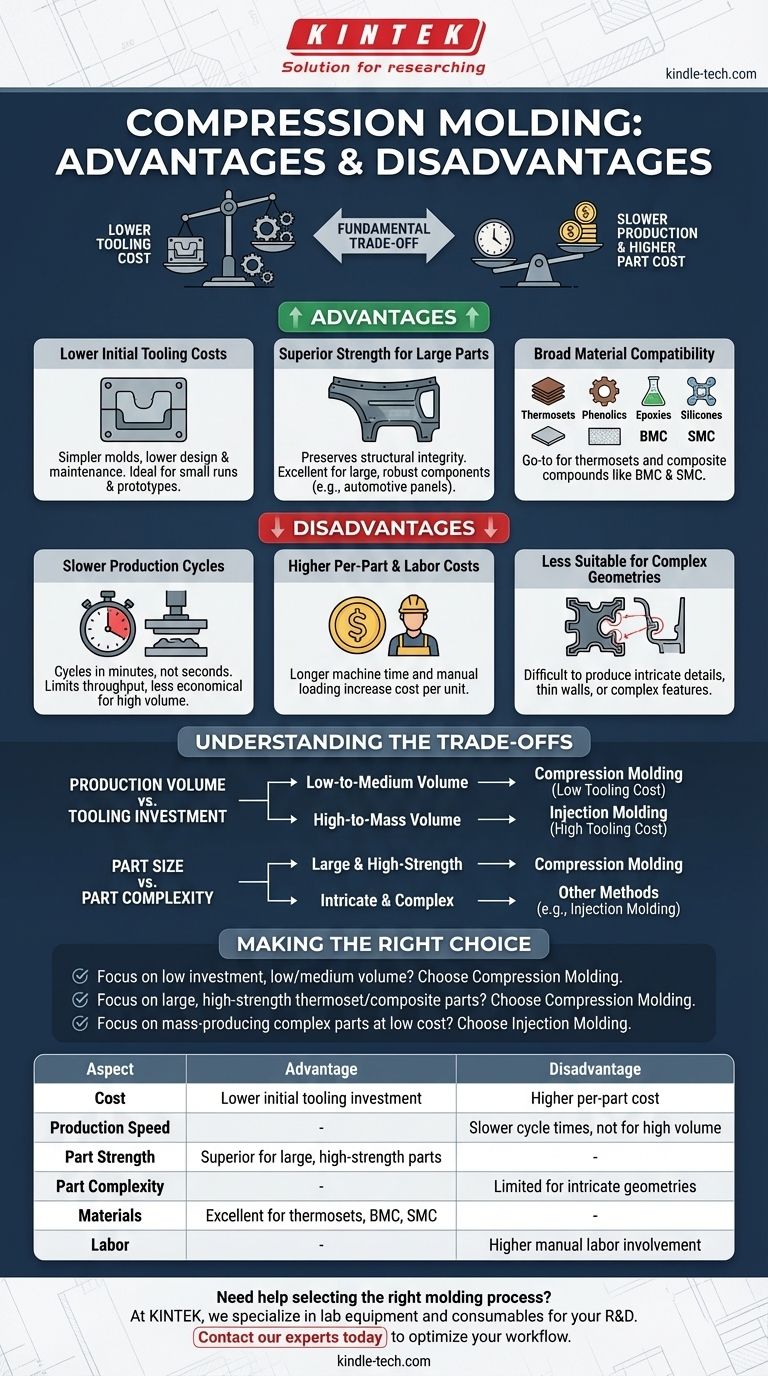
At its core, compression molding excels at producing large, high-strength parts with significantly lower initial tooling costs compared to other methods like injection molding. However, this advantage comes at the cost of slower production cycles, higher labor involvement, and limitations in creating complex part geometries, which often results in a higher cost per individual part.
The fundamental trade-off of compression molding is simple: you exchange lower upfront tooling investment for slower production speeds and higher per-part costs. This makes it an ideal process for low-to-medium volume runs, especially for large components made from thermoset plastics or composites.

The Core Advantages of Compression Molding
Compression molding's benefits are most apparent when the application aligns with its specific strengths in cost, material handling, and part integrity.
Lower Initial Tooling Costs
The molds, or tools, used in compression molding are significantly simpler than those for injection molding. They do not require the complex network of runners, sprues, and gates needed to inject material under high pressure.
This simplicity directly translates to lower design, manufacturing, and maintenance costs for the mold itself, making the process accessible for smaller production runs or prototypes.
Superior Strength for Large Parts
This process is exceptionally well-suited for producing large, robust components, such as automotive panels and electrical enclosures.
Because the material (often a pre-formed charge or "prepreg") is placed directly into the mold cavity, long reinforcing fibers (like glass or carbon) remain intact. This preserves the structural integrity of the composite material, resulting in parts with superior strength and stiffness.
Broad Material Compatibility
Compression molding is the go-to method for thermoset materials like phenolics, epoxies, and silicones, which undergo an irreversible chemical curing process under heat and pressure.
It also excels with bulk molding compounds (BMC) and sheet molding compounds (SMC), which are difficult or impossible to process using other methods.
The Inherent Disadvantages and Limitations
While powerful, the process has clear limitations that make it unsuitable for many mass-production scenarios.
Slower Production Cycles
The primary drawback is the cycle time. The process involves loading the material, closing the press, and holding the part under heat and pressure for the material to cure, which can take several minutes.
This is substantially slower than injection molding, where cycles are often measured in seconds. This directly limits throughput and makes the process less economical for high-volume manufacturing.
Higher Per-Part and Labor Costs
The slower cycle times and the often-manual process of loading the material charge into the mold result in higher labor costs per unit.
When you combine longer machine time with increased labor, the cost of each finished part is typically higher than one produced by a more automated, high-speed process.
Less Suitable for Complex Geometries
The nature of pressing a material charge into a cavity makes it difficult to produce parts with highly intricate details, thin walls, or complex features like undercuts.
The material flow is not as controlled as in injection molding, which can lead to inconsistencies and an inability to fill very fine or complex sections of a mold.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing compression molding is a strategic decision based on a clear understanding of its economic and physical trade-offs.
Production Volume vs. Tooling Investment
The central trade-off is upfront cost versus per-part cost. The low cost of tooling makes compression molding ideal for production runs from hundreds to tens of thousands of parts.
For runs in the hundreds of thousands or millions, the higher per-part cost becomes prohibitive, and the significant investment in an injection mold is easily justified.
Part Size vs. Part Complexity
Compression molding shines where part size and strength are the primary design drivers. It is one of the most cost-effective ways to create very large plastic or composite components.
However, if the design priority is intricate detail or complex geometry in a smaller part, the limitations of the process will likely require you to consider other methods.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must first define your project's most critical priority.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial investment for low-to-medium volume production: Compression molding's low tooling cost makes it the superior financial choice for getting your project started.
- If your primary focus is producing large, high-strength parts from thermosets or composites: Compression molding offers a level of structural integrity that is difficult to achieve with other methods.
- If your primary focus is mass-producing complex parts at the lowest possible per-unit cost: The high speed and automation of injection molding will be the more logical and economical path.
By understanding the fundamental relationship between tooling cost and production speed, you can confidently select the right molding process for your specific application.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | Lower initial tooling investment | Higher per-part cost due to slower cycles |
| Production Speed | - | Slower cycle times, not ideal for high volume |
| Part Strength | Superior for large, high-strength parts | - |
| Part Complexity | - | Limited for intricate geometries and thin walls |
| Materials | Excellent for thermosets, BMC, SMC | - |
| Labor | - | Higher manual labor involvement |
Need help selecting the right molding process for your lab or production needs?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the right lab equipment and consumables to support your material processing and R&D. Whether you're working with thermoset composites or exploring new materials, our expertise can help you optimize your workflow and achieve superior results.
Contact our experts today to discuss your specific requirements and discover how KINTEK's solutions can bring value to your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Split Electric Lab Pellet Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press Machine for Glove Box
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Rubber Vulcanizer Vulcanizing Machine Plate Vulcanizing Press for Lab
People Also Ask
- Why is it necessary to use high-precision temperature-controlled heating furnaces? Secure Natural Fiber Integrity.
- What is the temperature range for compression molding? Optimize Your Process for Perfect Parts
- Does a hydraulic press have heat? How Heated Platens Unlock Advanced Molding and Curing
- What are the pros and cons of hot forging? Unlock Superior Strength for Critical Components
- What role do molds play in the formation of Ruthenium sheets? Master High-Density Ruthenium Fabrication



















