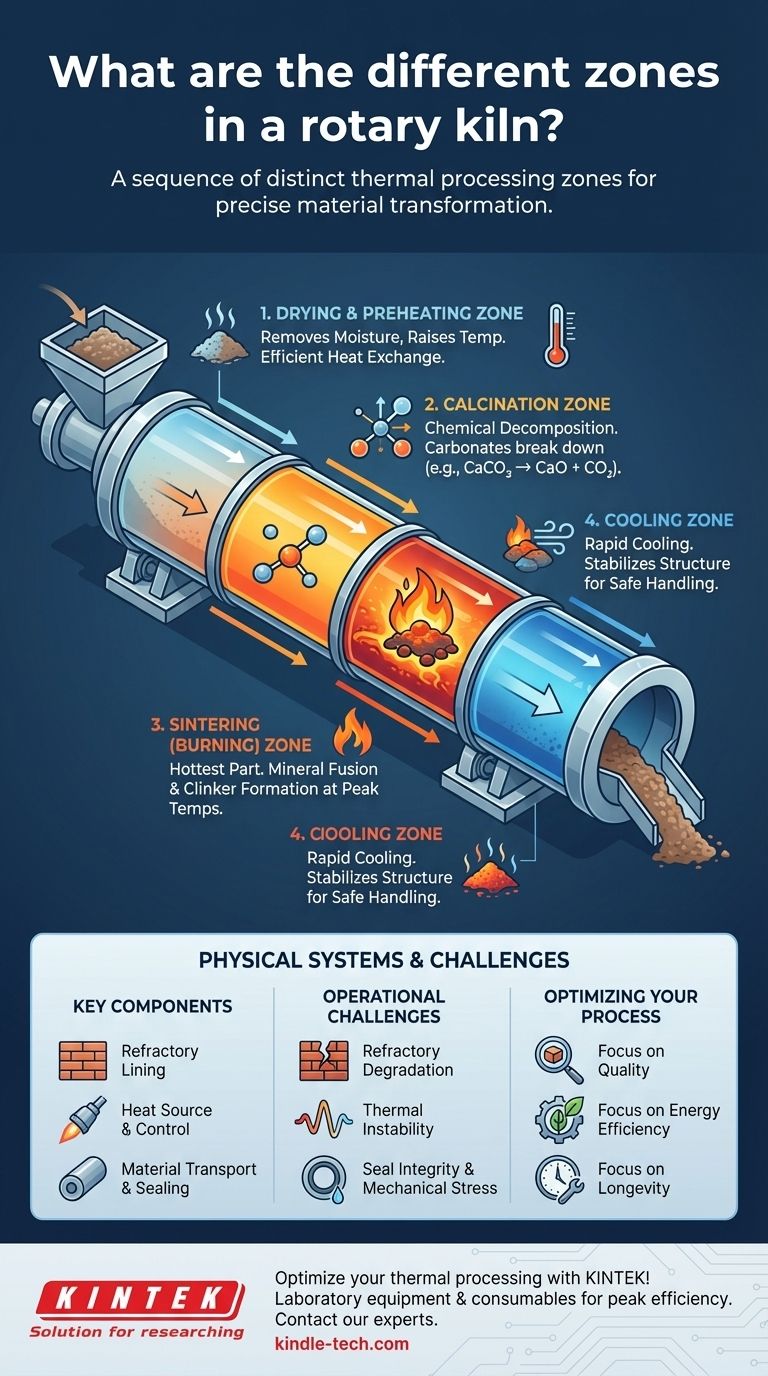
At its core, a rotary kiln is not a single furnace but a sequence of distinct thermal processing zones. Each zone performs a specific function, with the material being physically and chemically transformed as it travels from the feed end to the discharge end. The primary zones are typically for drying and preheating, calcination, sintering or burning, and finally, cooling.
The fundamental purpose of dividing a rotary kiln into zones is to create a precise, repeatable thermal profile. This controlled journey through different temperatures and atmospheres is what allows the kiln to transform raw feed into a product with specific, desired properties.

The Purpose of Zonal Division
A rotary kiln processes material continuously. Dividing its length into zones allows operators to apply the right amount of heat at the right time.
This sequential treatment is far more efficient and controllable than batch processing. It ensures every particle of material undergoes the same thermal history, leading to a highly consistent final product.
A Journey Through the Kiln: The Key Zones
As material moves down the inclined, rotating kiln, it passes through several distinct environments. While the exact number and names of zones can vary by industry (e.g., cement vs. lime), the functional stages are universal.
The Drying and Preheating Zone
This is the first section the raw material enters. Its primary purpose is to drive off any free moisture and begin raising the material's temperature toward the point of chemical reaction. Efficient heat exchange is critical here to conserve energy.
The Calcination Zone
In this intermediate-high temperature zone, the first major chemical reactions occur. For processes like cement and lime manufacturing, this is where carbonates (like calcium carbonate, CaCO₃) break down, releasing carbon dioxide (CO₂) and leaving behind oxides (like calcium oxide, CaO).
The Sintering (or Burning) Zone
This is the hottest part of the kiln, where the final material properties are forged. In cement production, this is where clinker nodules are formed through the fusion of minerals at peak temperatures. The temperature in this zone must be controlled with extreme precision.
The Cooling Zone
Though sometimes a separate piece of equipment, the cooling stage is an integral part of the process. As the hot material exits the sintering zone, it must be cooled rapidly. This locks in the desired mineral structure and makes the material safe to handle.
The Physical Systems That Create the Zones
These abstract thermal zones are created and maintained by the kiln's physical components working in concert.
The Role of the Refractory Lining
The kiln's steel shell is protected by a refractory brick lining. This lining is not uniform; different types of bricks are used in different zones to withstand the specific thermal and chemical stresses of that section. High-alumina or magnesia bricks may be used in the hot burning zone, while denser, more abrasion-resistant bricks are used at the feed end.
Heat Source and Control
A powerful burner, typically located at the discharge end, provides the primary heat source. The control system, using instruments and thyristor actuators, precisely modulates the fuel and airflow. This creates the temperature gradient along the kiln's length that defines the zones.
Material Transport and Sealing
The kiln's slight inclination and slow rotation are what move the material through each zone at a controlled rate, known as residence time. Effective seals at both the feed and discharge ends are critical for preventing cold air from entering and hot gas from escaping, which is essential for maintaining thermal efficiency and atmospheric control.
Understanding the Operational Challenges
Maintaining distinct and stable zones is the primary operational challenge of a rotary kiln. Failure to do so directly impacts product quality and operating costs.
Refractory Degradation
The combination of extreme heat, chemical attack from the product, and physical abrasion constantly wears down the refractory lining. A failure in one zone can force a complete shutdown for costly repairs.
Maintaining Thermal Stability
Fluctuations in fuel quality, feed rate, or airflow can disrupt the temperature profile. This can lead to an incomplete reaction in one zone, affecting all subsequent stages and resulting in off-spec product.
Seal Integrity
Seals are high-wear components. As they degrade, they allow false air to leak into the kiln, which can dramatically increase fuel consumption and make it difficult to maintain the target temperature in the burning zone.
Mechanical Stress and Alignment
The massive weight of the kiln, combined with thermal expansion and rotation, puts enormous stress on the shell, support rollers, and drive gear. Even slight misalignment can disrupt the flow of material and cause catastrophic wear on the support systems.
Optimizing Your Kiln for Your Process
Understanding the function and interplay of these zones is the key to mastering your specific process.
- If your primary focus is product quality: Concentrate on the precision of the control system and the consistency of the raw feed to ensure a stable temperature profile and residence time in each zone.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency: Your priority should be the integrity of the seals, the insulative quality of the refractory, and maximizing heat recovery in the preheating and cooling zones.
- If your primary focus is operational longevity: Implement a rigorous inspection program for key wear points, especially the refractory lining, seals, and mechanical alignment of the support system.
Mastering the rotary kiln begins with viewing it not as a single furnace, but as a dynamic, sequential process defined by these critical zones.
Summary Table:
| Zone | Primary Function | Key Process |
|---|---|---|
| Drying & Preheating | Removes moisture, preheats material | Heat exchange, energy conservation |
| Calcination | Breaks down carbonates (e.g., CaCO₃) | Chemical decomposition, CO₂ release |
| Sintering/Burning | Fuses minerals at peak temperatures | Clinker formation, property finalization |
| Cooling | Rapidly cools material for handling | Stabilizes structure, ensures safety |
Optimize your thermal processing with KINTEK! Whether you're in cement, lime, or minerals processing, our lab equipment and consumables help you analyze and refine each kiln zone for peak efficiency and product consistency. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Three-dimensional electromagnetic sieving instrument
People Also Ask
- What biomass is used in pyrolysis? Selecting the Optimal Feedstock for Your Goals
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the difference between calcining and roasting? A Guide to High-Temperature Processing



















