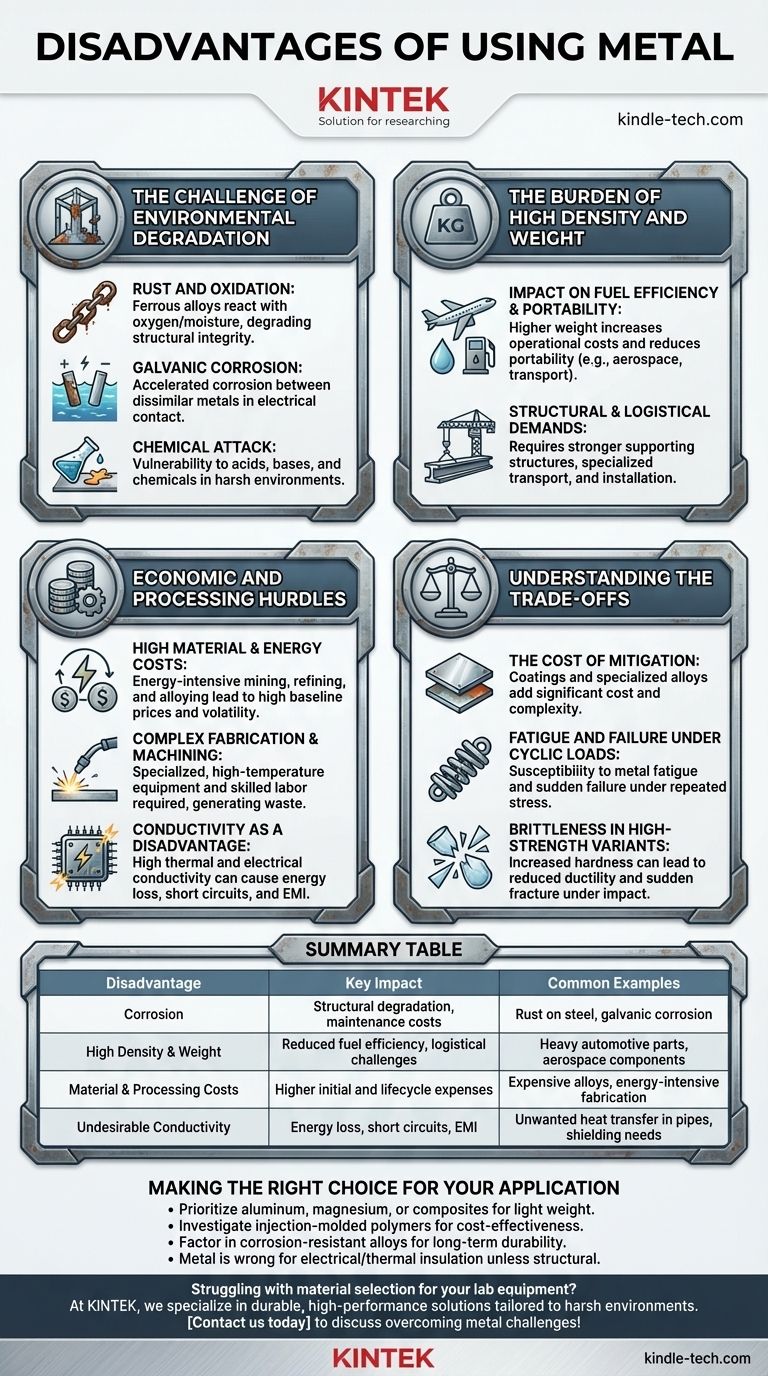
While metals form the backbone of modern industry, their use is not without significant drawbacks. The most notable disadvantages of using metal are its susceptibility to corrosion, its high density and weight, considerable material and processing costs, and undesirable thermal and electrical conductivity in certain applications. These factors often require complex engineering solutions and can impact the long-term performance and viability of a product.
The decision to use metal is rarely based on its strength alone. Its primary disadvantages—corrosion, weight, and cost—demand a holistic assessment of a product's entire lifecycle, from manufacturing and installation to ongoing maintenance and operational efficiency.

The Challenge of Environmental Degradation
One of the most persistent problems with many common metals is their inherent tendency to react with their environment, a process known as corrosion.
Rust and Oxidation
Most widely used metals, particularly ferrous alloys like steel, react with oxygen and moisture to form oxides. This process, commonly known as rust, is not just a cosmetic issue; it progressively degrades the material, reducing its thickness and compromising its structural integrity over time.
Galvanic Corrosion
When two dissimilar metals are in electrical contact in the presence of an electrolyte (like saltwater), a galvanic cell is created. This causes one of the metals to corrode at an accelerated rate. This is a frequent and often overlooked failure mode in assemblies, pipelines, and marine applications.
Chemical Attack
Beyond simple oxidation, many metals are vulnerable to attack from strong acids, bases, and other chemical agents. This limits their use in chemical processing plants, storage tanks, and other corrosive environments unless they are highly specialized—and expensive—alloys.
The Burden of High Density and Weight
Compared to polymers and many composites, most metals are exceptionally dense. This high weight-to-strength ratio creates significant engineering challenges.
Impact on Fuel Efficiency and Portability
In the aerospace, automotive, and transportation industries, weight is a direct driver of cost. Heavier components require more energy to move, leading to lower fuel efficiency and increased operational expenses. The weight of metal also makes it less suitable for portable devices and consumer electronics.
Structural and Logistical Demands
Using heavy metal components necessitates stronger, more robust supporting structures and foundations, adding to overall project complexity and cost. Furthermore, the logistics of transporting and installing heavy materials require more energy and specialized equipment.
Economic and Processing Hurdles
The journey of metal from raw ore to finished product is often expensive and energy-intensive.
High Material and Energy Costs
Mining, refining, and alloying metals are processes that consume vast amounts of energy. This gives metals a high baseline cost compared to many commodity plastics. The market price of metals can also be volatile, introducing financial risk into a project.
Complex Fabrication and Machining
While metals are highly formable, the processes required—such as casting, forging, and welding—demand specialized, high-temperature equipment and skilled labor. Machining metal to precise tolerances can be time-consuming, generate significant scrap material, and require expensive cutting tools.
Conductivity as a Disadvantage
A metal’s high thermal and electrical conductivity can be a major drawback. Unwanted heat transfer can reduce energy efficiency in buildings or require costly insulation on pipes and components. In electronics, its electrical conductivity can cause short circuits or electromagnetic interference (EMI), requiring extensive shielding.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The disadvantages of metals are often managed through mitigation strategies, but these solutions come with their own set of compromises.
The Cost of Mitigation
Engineers can prevent corrosion with coatings, galvanization, or cathodic protection. They can choose lighter, more expensive alloys like aluminum or titanium over steel. However, these solutions add significant cost and complexity to both manufacturing and long-term maintenance. The true disadvantage is often the price of overcoming the inherent weakness.
Fatigue and Failure Under Cyclic Loads
Metals are susceptible to metal fatigue, where repeated loading and unloading (cyclic stress) can cause microscopic cracks to form and grow, eventually leading to sudden and catastrophic failure. This occurs at stress levels well below the material's ultimate tensile strength and is a primary concern for any moving or vibrating part.
Brittleness in High-Strength Variants
As metals are alloyed or heat-treated to increase their hardness and strength, they often lose ductility and become more brittle. A brittle material is more likely to fracture suddenly under impact, whereas a more ductile material would bend or deform, providing a visible warning of overload.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Choosing a material requires balancing these disadvantages against your specific project goals.
- If your primary focus is light weight for mobility or fuel efficiency: Prioritize aluminum, magnesium, or composites over steel, but prepare for a higher material cost.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for a non-structural part: Investigate if an injection-molded polymer can meet your needs, as it often provides the lowest cost per part at high volumes.
- If your primary focus is long-term environmental durability: You must factor in the cost of corrosion-resistant alloys (like stainless steel) or protective coatings against the inherent stability of a polymer or ceramic.
- If your primary focus is electrical or thermal insulation: Metal is fundamentally the wrong choice unless its structural properties are non-negotiable, in which case significant design effort must be spent on insulation and shielding.
By understanding these inherent disadvantages, you can select a material based on a comprehensive view of its lifetime performance, not just its initial strength.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Key Impact | Common Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Corrosion | Structural degradation, maintenance costs | Rust on steel, galvanic corrosion in assemblies |
| High Density & Weight | Reduced fuel efficiency, logistical challenges | Heavy automotive parts, aerospace components |
| Material & Processing Costs | Higher initial and lifecycle expenses | Expensive alloys, energy-intensive fabrication |
| Undesirable Conductivity | Energy loss, short circuits, EMI | Unwanted heat transfer in pipes, shielding needs in electronics |
Struggling with material selection for your lab equipment? The right choice can save you from costly corrosion, inefficiency, and downtime. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing durable, high-performance lab equipment and consumables tailored to withstand harsh environments and demanding applications. Whether you need corrosion-resistant components or lightweight solutions for efficiency, our expertise ensures your laboratory operates at peak performance. Contact us today to discuss how we can help you overcome the challenges of using metals in your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Purity Gold Platinum Copper Iron Metal Sheets
- Metal Disc Electrode Electrochemical Electrode
- Thermally Evaporated Tungsten Wire for High Temperature Applications
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Battery Lab Applications
- Laboratory Ball Mill Jar Mill with Metal Alloy Grinding Jar and Balls
People Also Ask
- What is the purity of the gold and platinum sheets used for experiments? Ensuring 99.99% Purity for Reliable Results
- What are the guidelines for using gold or platinum sheets during an experiment? Ensure Precise and Reliable Results
- What is gold sputtered? A Guide to High-Purity Vacuum Coating for Electronics & SEM
- How hot can a metal surface get in the sun? The Surprising Science Behind Extreme Heat
- Why is platinum unreactive? The Atomic Secrets Behind Its Remarkable Stability













