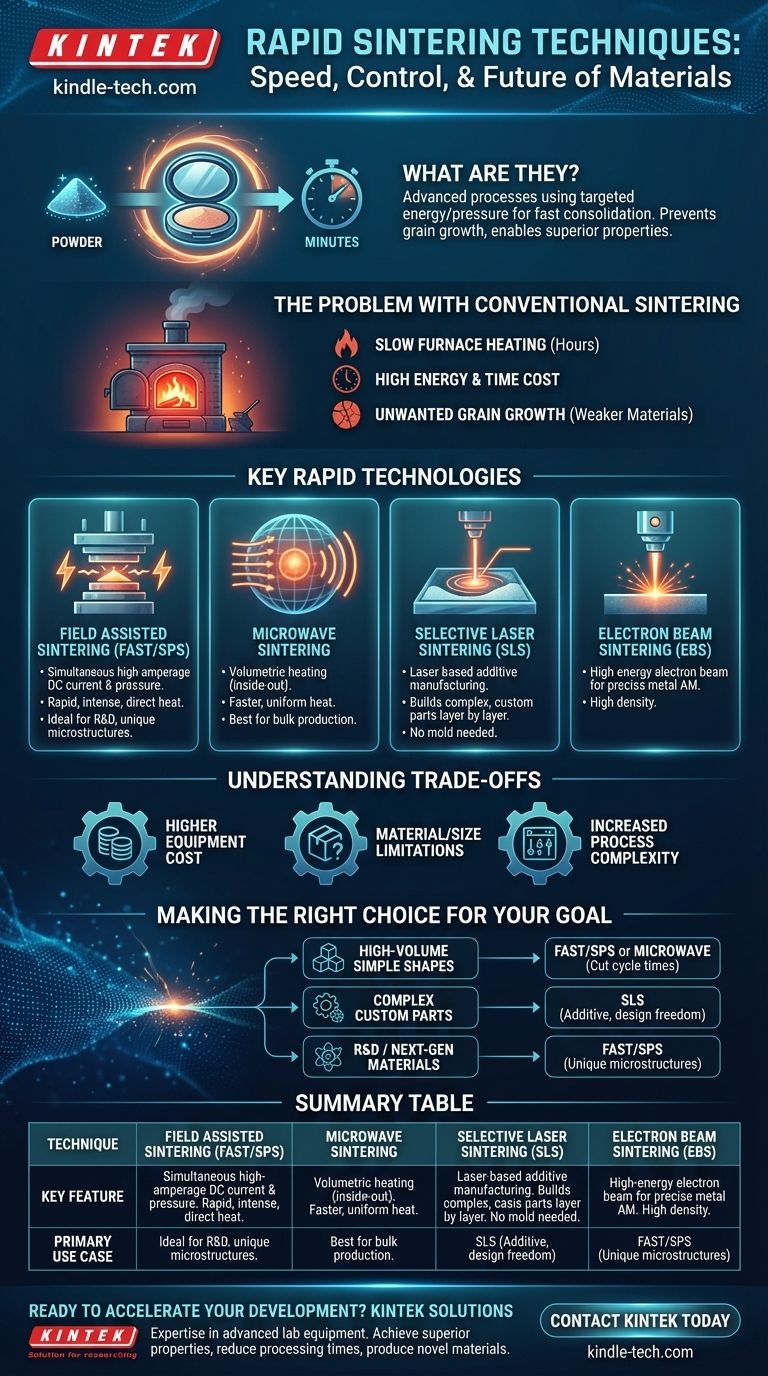
In short, rapid sintering techniques are advanced manufacturing processes that use targeted energy sources or pressure to consolidate powdered materials into a solid mass far more quickly than traditional furnace heating. These methods, such as Field Assisted Sintering (FAST/SPS) and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), reduce processing times from many hours to mere minutes, saving significant energy and enabling the production of materials with superior properties.
The true value of rapid sintering isn't just speed—it's control. By minimizing the time at high temperatures, these techniques prevent unwanted grain growth, resulting in stronger, denser materials and opening the door to novel compositions that are impossible to create with conventional methods.

The Problem with Conventional Sintering
To understand the value of rapid techniques, we must first recognize the limitations of the traditional approach. Conventional sintering has been used for millennia to create everything from pottery to structural steel parts.
The Slow Pace of Furnace Heating
Traditional sintering involves placing a compacted powder (a "green body") into a large furnace and slowly heating it for many hours. This process relies on thermal conduction to heat the part from the outside in.
The Cost of Time and Energy
This slow, brute-force heating method is incredibly time-consuming and energy-intensive. Long cycle times create a significant bottleneck in high-volume manufacturing environments.
The Challenge of Grain Growth
Most importantly, prolonged exposure to high temperatures causes the microscopic grains within the material to grow larger. This coarsening of the microstructure often degrades mechanical properties like strength and hardness.
Key Rapid Sintering Technologies
Rapid sintering techniques overcome these challenges by delivering energy to the material in a much more direct and efficient manner.
Field Assisted Sintering (FAST/SPS)
Also known as Spark Plasma Sintering (SPS), this is one of the most powerful rapid methods. It simultaneously applies high-amperage DC electrical current and mechanical pressure to the powder.
This combination generates rapid, intense heat directly within the material, promoting extremely fast consolidation. FAST/SPS often uses lower overall temperatures and pressures than other hot-pressing methods, making it ideal for creating materials with novel, high-performance characteristics.
Microwave Sintering
This technique uses microwave energy to heat the material, similar to a household microwave but far more powerful and precise.
Unlike a conventional furnace that heats from the outside, microwaves penetrate the material and heat it volumetrically (from the inside out). This results in faster, more uniform heating and a significant reduction in processing time.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
SLS is a cornerstone of additive manufacturing, or 3D printing. It uses a high-power laser to trace a part's cross-section onto a bed of powder.
The laser's focused energy rapidly heats and fuses the powder particles in a localized area. The process is repeated layer by layer to build a complex, three-dimensional object without the need for a mold.
Electron Beam Sintering (EBS)
Functionally similar to SLS, this additive manufacturing technique uses a focused beam of electrons instead of a laser. The principle remains the same: delivering precise, high-density energy to sinter powdered material layer by layer.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, these advanced techniques are not a universal replacement for traditional methods. They come with their own set of considerations.
Higher Equipment Cost
The machinery required for FAST/SPS, SLS, or microwave sintering is significantly more complex and expensive than a conventional furnace. This represents a substantial capital investment.
Material and Size Limitations
Some techniques are material-dependent. For example, FAST/SPS works best with materials that have some electrical conductivity. Additive methods like SLS and EBS can be limited by the size of the build chamber.
Increased Process Complexity
The speed and power of these techniques demand far more sophisticated process control. Fine-tuning parameters like power, pressure, and scan speed is critical to achieving the desired material density and properties without introducing defects.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the appropriate sintering method depends entirely on the intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of simple shapes: A rapid bulk technique like FAST/SPS or microwave sintering is ideal for drastically cutting cycle times and energy costs.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, custom parts: An additive method like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) is the definitive choice for its design freedom and tool-less production.
- If your primary focus is research and development of next-generation materials: FAST/SPS is an unparalleled tool for its ability to create unique microstructures and consolidate difficult-to-sinter materials.
Ultimately, adopting a rapid sintering technique is a strategic decision to move beyond the limitations of traditional processing and unlock a new level of material performance and manufacturing agility.
Summary Table:
| Technique | Key Feature | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Field Assisted Sintering (FAST/SPS) | Simultaneous current & pressure | R&D, high-performance materials |
| Microwave Sintering | Volumetric (inside-out) heating | Bulk production, uniform heating |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Layer-by-layer additive manufacturing | Complex, custom parts |
| Electron Beam Sintering (EBS) | High-energy electron beam | Additive manufacturing of metals |
Ready to accelerate your material development and manufacturing?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment, including rapid sintering solutions. Our expertise helps laboratories and R&D teams overcome the limitations of traditional furnaces, enabling you to:
- Achieve superior material properties with controlled microstructures.
- Drastically reduce processing times and energy consumption.
- Produce complex parts or novel materials that were previously impossible.
Let us help you select the right rapid sintering technology for your specific goals. Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our solutions can bring speed and precision to your lab!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Heated Vacuum Press Machine Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is DFT coating thickness? Ensure Quality and Performance with Precise Measurement
- What is a scientific mixer called? Choosing the Right Mixer for Your Lab
- What is the process of thin film deposition by sputtering? A Step-by-Step Guide to Atomic-Level Coating
- Why is a Solar Furnace necessary for verifying sulfuric acid decomposition components? Ensure Industrial Scale Success
- Does nanomaterials have potential hazards to human health? Understanding the Risks and Safe Handling
- Is heat treatment only good for ferrous metals? Mastering the Process for Aluminum, Titanium & More
- How does DC magnetron sputtering work? Achieve Superior Thin-Film Deposition
- Is biomass a renewable energy source? The truth about sustainable energy



















