At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a sophisticated coating process used across a vast range of industries. Its applications include creating semiconductor devices like thin-film solar panels, applying the durable titanium nitride coatings on metal-cutting tools, and producing the reflective aluminized film found inside food packaging.
PVD is not defined by a single use case but by its fundamental capability: applying an exceptionally thin, high-performance film to a surface. This allows engineers to enhance a product's mechanical, optical, electronic, or decorative properties without altering the underlying material.

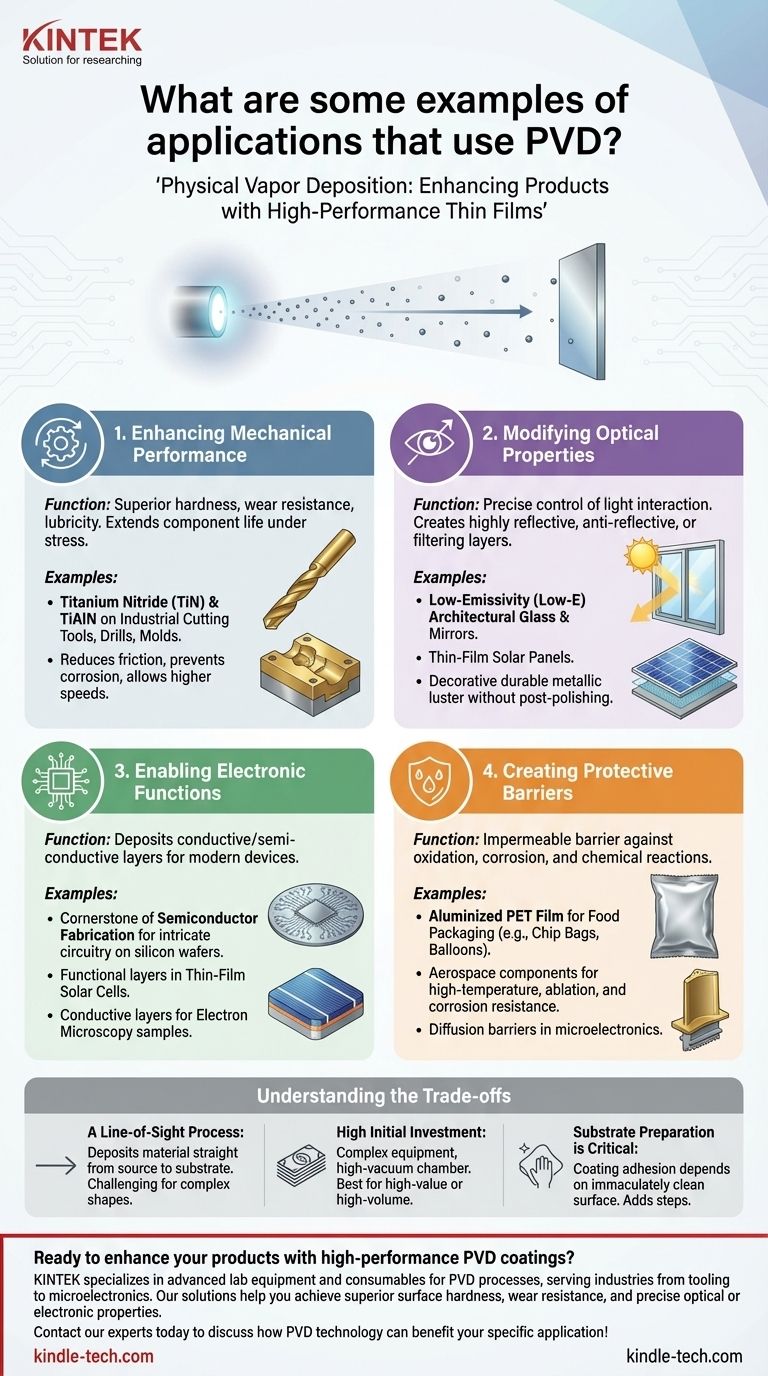
The Functional Roles of PVD Coatings
Instead of simply listing applications, it is more insightful to understand the specific problems PVD solves. Applications are best categorized by the function the thin-film coating is designed to perform.
Enhancing Mechanical Performance
PVD is a primary method for imparting superior surface hardness, wear resistance, and lubricity. This dramatically extends the life and performance of components subjected to intense physical stress.
Common examples include coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) and Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiAlN) on industrial cutting tools, drills, and molds. These coatings reduce friction and prevent corrosion, allowing tools to operate at higher speeds and last significantly longer.
Modifying Optical Properties
The process allows for precise control over how a surface interacts with light. PVD can be used to create highly reflective, anti-reflective, or specific light-filtering layers.
This is critical for manufacturing low-emissivity (Low-E) architectural glass, mirrors, and thin-film solar panels. In decorative applications, it creates a brilliant, durable metallic luster on items without the need for post-polishing.
Enabling Electronic Functions
In the electronics industry, PVD is essential for depositing the conductive and semi-conductive layers that form the basis of modern devices.
It is a cornerstone of semiconductor fabrication, where thin films create the intricate circuitry on silicon wafers. It's also used to apply conductive layers for electron microscopy samples and to build the functional layers within thin-film solar cells.
Creating Protective Barriers
Many PVD films serve as an impermeable barrier against environmental factors. These coatings protect the substrate from oxidation, corrosion, and chemical reactions.
The most common consumer-facing example is the aluminized PET film used for food packaging (like chip bags) and balloons. This ultra-thin metal layer acts as an excellent barrier to oxygen and moisture, preserving the contents. In microelectronics, PVD films act as diffusion barriers between different material layers.
Common Industries and Everyday Examples
While the functions are technical, the applications are found in both high-tech manufacturing and common consumer products.
High-Technology and Aerospace
In aerospace, PVD coatings are applied to components to improve their resistance to high temperatures, ablation, and corrosion. The precision of the process is vital for parts with tight engineering tolerances.
Industrial and Tooling
This is a classic application for PVD. Coating drill bits, milling cutters, and forming dies improves performance, reduces the need for lubricants, and drastically increases the tool's working lifespan, providing a clear economic benefit.
Consumer and Decorative Goods
PVD provides a finish that is far more durable and corrosion-resistant than traditional plating. It is widely used for jewelry, kitchen and bathroom hardware, high-end watches, and other decorative items where both aesthetics and longevity are critical.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While incredibly versatile, PVD is not a universal solution. Understanding its limitations is key to appreciating where it provides the most value.
A Line-of-Sight Process
PVD deposits material in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This makes it challenging to uniformly coat complex shapes with internal channels or hidden surfaces.
High Initial Investment
The process takes place within a high-vacuum chamber, and the required equipment is complex and expensive. This makes PVD best suited for high-value components or high-volume production where the cost can be amortized.
Substrate Preparation is Critical
The success of the coating is entirely dependent on its adhesion to the substrate. The surface must be immaculately clean and properly prepared, which adds steps and complexity to the manufacturing process.
How to Recognize PVD in Your World
By understanding its key characteristics, you can begin to identify PVD applications all around you.
- If your primary focus is performance tools: Look for the distinctive gold (TiN), black, or iridescent coatings on high-quality drill bits and cutting blades; this is almost certainly PVD for wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is consumer products: That shiny, metallic-looking snack bag or the durable, non-tarnishing matte black finish on a modern faucet is a direct result of a PVD coating.
- If your primary focus is advanced technology: The reflective sheen on energy-efficient windows and the very existence of modern microchips rely on the precise thin-film deposition that PVD enables.
Ultimately, PVD is a foundational manufacturing technology that quietly improves the durability, function, and beauty of countless modern products.
Summary Table:
| Function | Industry Examples | Common PVD Coatings |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Enhancement | Cutting tools, industrial drills, molds | Titanium Nitride (TiN), TiAlN |
| Optical Modification | Low-E glass, mirrors, solar panels | Reflective and anti-reflective layers |
| Electronic Enablement | Semiconductors, microchips, solar cells | Conductive and semi-conductive films |
| Protective Barrier | Food packaging, aerospace components | Aluminized films, corrosion-resistant coatings |
Ready to enhance your products with high-performance PVD coatings? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for PVD processes, serving industries from tooling to microelectronics. Our solutions help you achieve superior surface hardness, wear resistance, and precise optical or electronic properties. Contact our experts today to discuss how PVD technology can benefit your specific application!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How are PECVD and CVD different? A Guide to Choosing the Right Thin-Film Deposition Process
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition



















