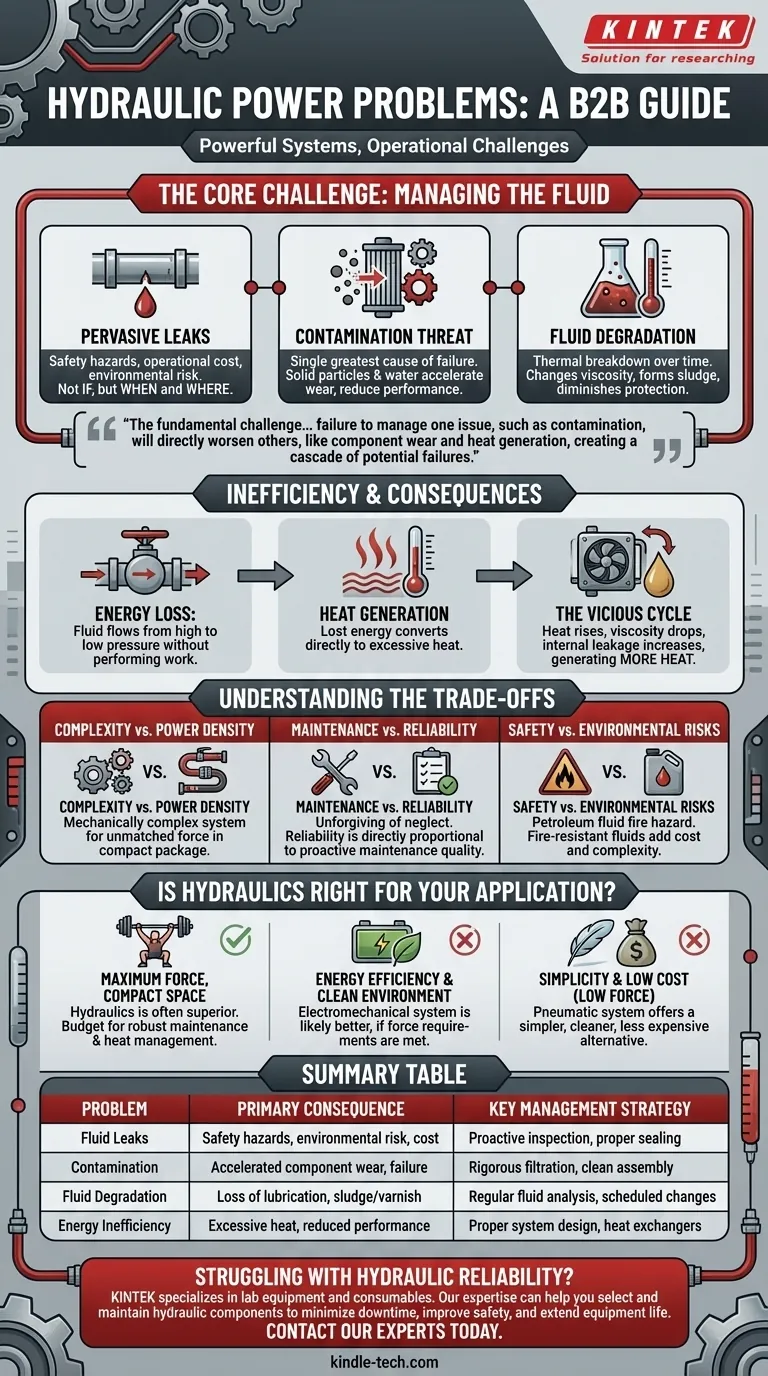
While incredibly powerful, hydraulic systems present a distinct set of operational challenges that must be actively managed. The most significant problems are a high susceptibility to contamination, the near-inevitability of fluid leaks, inherent energy inefficiencies that generate waste heat, and the complexity that demands specialized maintenance.
The fundamental challenge of hydraulic power is not that these problems exist, but that they are interconnected. A failure to manage one issue, such as contamination, will directly worsen others, like component wear and heat generation, creating a cascade of potential failures.

The Core Challenge: Managing the Fluid
At the heart of most hydraulic issues is the fluid itself. It is both the system's lifeblood and its most common point of failure.
The Pervasive Problem of Leaks
A common saying among technicians is, "It's not a matter of if a hydraulic system will leak, but when and where." Leaks, even minor ones, have significant consequences.
They create safety hazards, from simple slips and falls to dangerous high-pressure injection injuries if a pinhole leak pierces the skin. Leaks also represent a direct operational cost in lost fluid and an environmental risk that requires costly cleanup.
The Constant Threat of Contamination
Contamination is the single greatest cause of hydraulic component failure. Solid particles (dirt, metal shavings) and water are the primary culprits.
These contaminants act like a liquid abrasive, accelerating wear on the tight tolerances inside pumps, valves, and cylinders. This leads to reduced performance, internal leakage, and eventual catastrophic failure. Effective filtration and clean assembly practices are not optional; they are essential for system survival.
The Inevitability of Fluid Degradation
Hydraulic fluid does not last forever. Over time, high temperatures and pressure cause the fluid's additives to break down, a process known as thermal degradation.
As the fluid degrades, its viscosity changes, and its ability to lubricate and protect components diminishes. This old fluid can form varnish and sludge that clogs filters and small orifices within valves, leading to erratic system behavior.
Inefficiency and Its Consequences
Hydraulic systems are renowned for force, not for energy efficiency. This inefficiency manifests primarily as heat.
Where Energy Is Lost
Significant energy is lost whenever hydraulic fluid flows from a high-pressure area to a low-pressure area without performing useful work. This happens constantly across relief valves, flow control valves, and even through internal component leakage.
This lost energy is converted directly into heat, which is absorbed by the hydraulic fluid.
The Vicious Cycle of Heat
Excessive heat is a system killer. As the fluid temperature rises, its viscosity drops, making it thinner and a less effective lubricant.
This reduction in viscosity increases internal leakage within components, which in turn generates even more heat. To combat this, many systems require large heat exchangers (coolers), adding cost, complexity, and another potential point of failure.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The problems of hydraulics are best understood as the trade-offs made to achieve their primary benefit: unmatched power density.
Complexity vs. Power Density
A hydraulic system is mechanically complex, involving a power unit, pumps, valves, actuators, filters, and a network of hoses and tubes. This complexity is the price paid for the ability to generate and control immense force from a relatively small package. An electric actuator of equivalent force would be significantly larger and heavier.
Maintenance Burden vs. Reliability
Hydraulic systems are not inherently unreliable, but they are unforgiving of neglect. Their reliability is directly proportional to the quality of the maintenance they receive. A proactive maintenance plan—involving regular fluid analysis, filter changes, and leak inspections—is critical to preventing costly downtime.
Safety and Environmental Risks
The use of petroleum-based hydraulic fluid introduces a significant fire hazard, especially in environments with ignition sources like welding or hot metal. While fire-resistant fluids are available, they are more expensive, can be less forgiving, and may require special seals and hoses, adding another layer of design trade-offs.
Is Hydraulics Right for Your Application?
Choosing to use hydraulic power requires a clear understanding of your operational priorities and a commitment to managing its inherent challenges.
- If your primary focus is maximum force in a compact space: Hydraulics is often the superior or only viable option, but you must budget for robust maintenance and heat management.
- If your primary focus is energy efficiency and a clean environment: A modern electromechanical system is likely a better choice, provided it can meet your force requirements.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and low cost for low-force tasks: A pneumatic system offers a simpler, cleaner, and often less expensive alternative.
By anticipating these challenges, you can design and maintain a hydraulic system that is not just powerful, but also dependable and cost-effective over its entire service life.
Summary Table:
| Problem | Primary Consequence | Key Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Fluid Leaks | Safety hazards, environmental risk, operational cost | Proactive inspection and proper sealing |
| Contamination | Accelerated component wear and system failure | Rigorous filtration and clean assembly |
| Fluid Degradation | Loss of lubrication, sludge/varnish formation | Regular fluid analysis and scheduled changes |
| Energy Inefficiency | Excessive heat generation, reduced performance | Proper system design and use of heat exchangers |
Struggling with hydraulic system reliability? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise can help you select and maintain the right hydraulic components to minimize downtime, improve safety, and extend equipment life. Contact our experts today to optimize your hydraulic systems for maximum dependability.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Manual Lab Heat Press
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Laboratory Manual Hydraulic Pellet Press for Lab Use
- Hydraulic Diaphragm Lab Filter Press for Laboratory Filtration
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What does a manual press do? Understand the Two Key Types for Your Lab or Industrial Needs
- What are the parts of a manual hydraulic press? A Guide to Its Core Components and Operation
- What are the potential hazards in a hydraulic press? Understanding the Risks of Crushing, Injection, and Failure
- What is a hydraulic press in simple words? Harness Immense Force for Shaping and Crushing
- What is the efficiency of a hydraulic press? Harness Unmatched Force Multiplication for Your Lab













