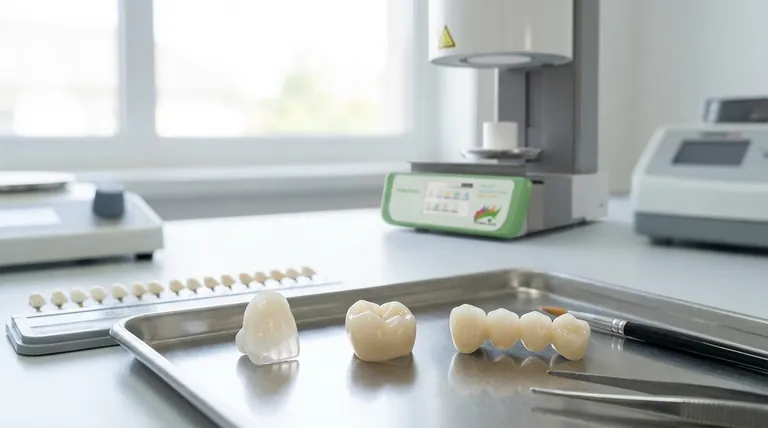
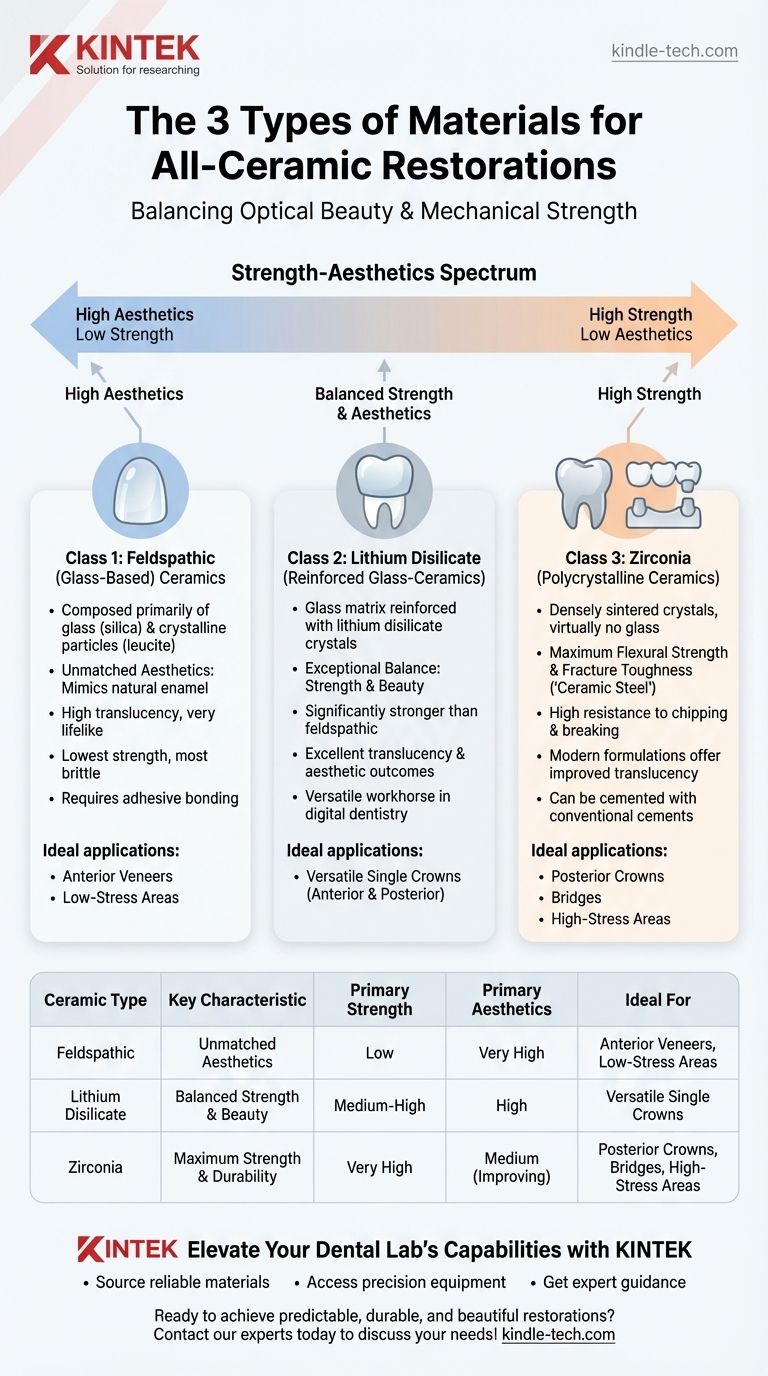
In modern restorative dentistry, all-ceramic materials are broadly classified into three fundamental categories based on their composition and structural properties. These are the traditional feldspathic (or glass-based) ceramics, the reinforced glass-ceramics like lithium disilicate, and the high-strength polycrystalline ceramics, most notably zirconia. The selection among these is dictated by the specific clinical demand for strength versus aesthetics.
The core principle in selecting an all-ceramic material is navigating the trade-off between optical beauty and mechanical strength. As a material's crystalline content increases, its durability rises, but its natural translucency typically decreases.

A Closer Look at the Three Ceramic Classes
Understanding the composition of each ceramic class is key to knowing its ideal application. Each material occupies a distinct position on the spectrum of strength and aesthetics.
Class 1: Feldspathic (Glass-Based) Ceramics
Feldspathic ceramics are the most traditional type, composed primarily of glass (silica) with crystalline particles like leucite suspended within the matrix. They are essentially a form of dental porcelain.
Their defining characteristic is unmatched aesthetics. Because of their high glass content, they scatter light almost identically to natural tooth enamel, making them exceptionally translucent and lifelike.
However, this beauty comes at the cost of strength. Feldspathic ceramics are the most brittle of the three classes and are more prone to fracture under high chewing forces.
Class 2: Lithium Disilicate (Reinforced Glass-Ceramics)
Lithium disilicate represents a significant evolution in dental ceramics. It consists of a glass matrix that is heavily reinforced with needle-like lithium disilicate crystals.
This material strikes an exceptional balance between strength and beauty. It is significantly stronger and more durable than feldspathic porcelain while still offering excellent translucency and aesthetic outcomes.
Its versatility has made it a workhorse material in digital dentistry, suitable for everything from veneers to single-unit crowns in both the front and back of the mouth.
Class 3: Zirconia (Polycrystalline Ceramics)
Zirconia, or zirconium oxide, is in a class of its own. It is a polycrystalline ceramic, meaning it is composed almost entirely of densely sintered crystals with virtually no glass matrix.
This structure gives zirconia the highest flexural strength and fracture toughness of any dental ceramic, earning it the nickname "ceramic steel." It is incredibly resistant to chipping and breaking.
Historically, this strength came with high opacity. However, modern formulations of zirconia have greatly improved translucency, making it a viable and durable option for a wider range of aesthetic applications, including anterior crowns.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material is not about which one is "best" overall, but which is best for a specific clinical situation. The decision always involves balancing competing factors.
The Strength-Aesthetics Spectrum
Think of the three classes on a spectrum. On one end, you have highly aesthetic but brittle feldspathic ceramic. On the other, you have incredibly strong but traditionally more opaque zirconia. Lithium disilicate sits comfortably in the middle, offering a blend of both properties.
Clinical Indication Dictates Material
The location and function of the restoration are critical. A delicate veneer on a front tooth with low biting force is a perfect application for feldspathic ceramic. A molar crown that endures immense chewing pressure requires the robust strength of zirconia.
Bonding vs. Cementation
The material's strength also influences how it is attached to the tooth. Weaker materials like feldspathic porcelain absolutely require adhesive bonding, where the restoration is chemically fused to the tooth structure for support. Extremely strong materials like zirconia can be secured with conventional cements, simplifying the clinical procedure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Base your material selection on the primary objective of the restoration.
- If your primary focus is maximum aesthetics for an anterior case (like veneers): Feldspathic porcelain remains the gold standard for its unparalleled ability to mimic natural enamel.
- If your primary focus is a versatile, all-around solution for single crowns: Lithium disilicate provides an excellent combination of strength for durability and aesthetics for a natural look.
- If your primary focus is absolute strength and durability (especially for posterior molars or bridges): Zirconia is the most reliable and fracture-resistant material available.
Understanding this material science empowers you to select the ideal ceramic for a predictable, durable, and beautiful outcome.
Summary Table:
| Ceramic Type | Key Characteristic | Primary Strength | Primary Aesthetics | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Feldspathic (Glass-Based) | Unmatched Aesthetics | Low | Very High | Anterior Veneers, Low-Stress Areas |
| Lithium Disilicate | Balanced Strength & Beauty | Medium-High | High | Versatile Single Crowns (Anterior/Posterior) |
| Zirconia (Polycrystalline) | Maximum Strength & Durability | Very High | Medium (Improving) | Posterior Crowns, Bridges, High-Stress Areas |
Ready to achieve predictable, durable, and beautiful restorations?
The right ceramic material is key to a successful outcome. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality dental ceramics and lab equipment, providing the materials you need to excel in modern restorative dentistry.
Let us support your practice:
- Source reliable materials for feldspathic, lithium disilicate, and zirconia restorations.
- Access precision equipment for milling, sintering, and finishing.
- Get expert guidance to select the ideal products for your specific clinical cases.
Elevate your dental lab's capabilities. Contact our experts today to discuss your needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the structure and properties of dental ceramics? Mastering the Science Behind Durable, Aesthetic Restorations
- What are the three types of dental ceramics? Choose the Right Material for Strength & Aesthetics
- What is an alternative name for a Dental Press Furnace? Understanding the Dental Ceramic Oven
- What is dental ceramic materials? Your Guide to Strong, Natural-Looking Restorations
- What is the difference between composite and ceramic restoration? Choosing the Right Material for Your Smile
- What is the mode of failure most often associated with ceramic dental implants? Understanding Fracture Risk
- Are ceramic veneers stain-resistant? Yes, Porcelain Veneers Offer Superior Stain Resistance
- Is zirconia sintered? The Essential Step for Unlocking Maximum Strength and Durability



















