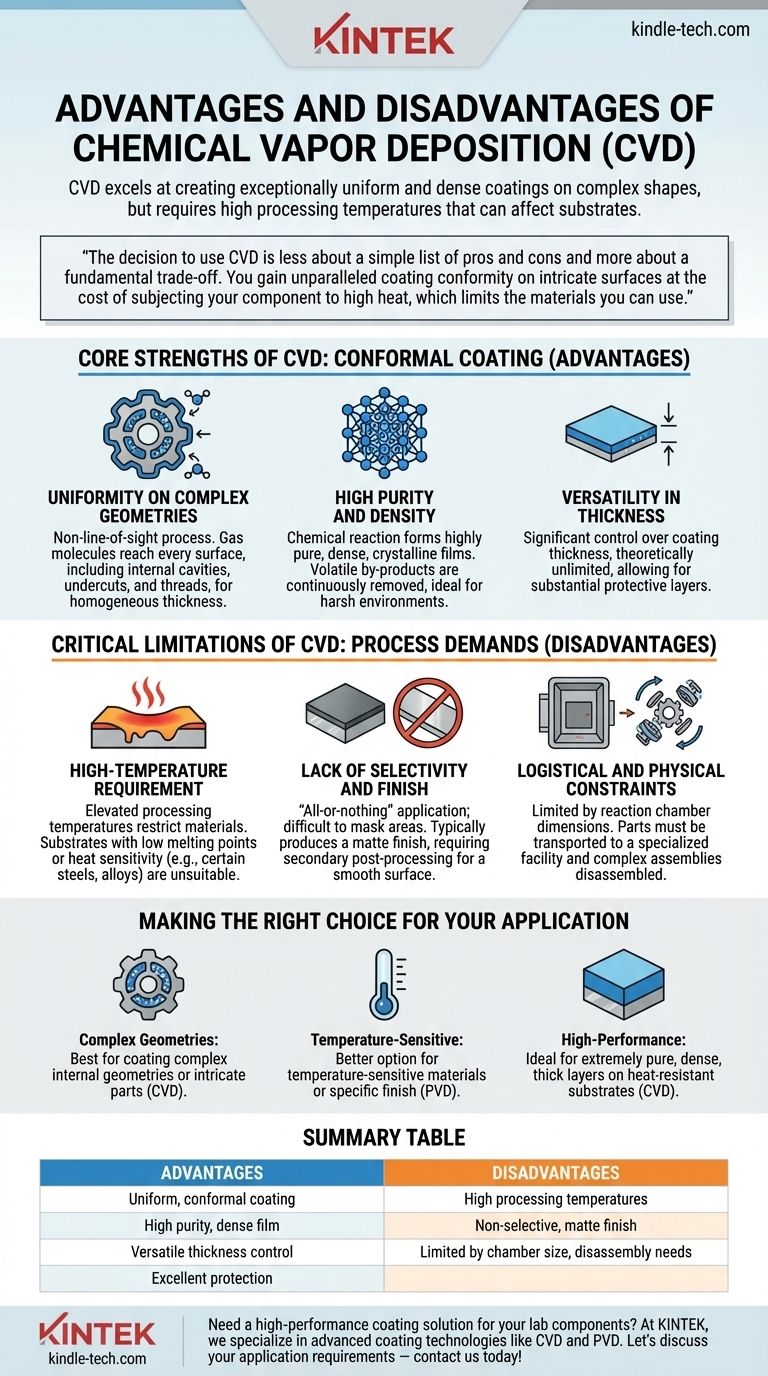
The primary advantage of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is its ability to create exceptionally uniform and dense coatings on complex shapes, a feat difficult for line-of-sight methods. Its main disadvantage, however, is the high processing temperature required, which can damage or alter the properties of the substrate material being coated.
The decision to use CVD is less about a simple list of pros and cons and more about a fundamental trade-off. You gain unparalleled coating conformity on intricate surfaces at the cost of subjecting your component to high heat, which limits the materials you can use.

The Core Strengths of CVD: Conformal Coating
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process where a heated substrate is exposed to precursor gases that react or decompose on its surface, forming a solid film. This chemical reaction, rather than a physical spray, is the source of its unique advantages.
Uniformity on Complex Geometries
Because the process relies on a precursor gas filling the entire reaction chamber, CVD is a non-line-of-sight process.
The gas molecules can reach every exposed surface of a component, including internal cavities, undercuts, and screw threads. This results in a homogenous and uniform coating thickness across even the most intricate parts.
High Purity and Density
The nature of the chemical reaction allows for the creation of highly pure and dense coatings.
Volatile by-products from the reaction are continuously removed from the chamber, leaving behind a solid, crystalline structure with excellent material properties, ideal for extending the life of components in harsh environments.
Versatility in Thickness
CVD offers significant control over the final coating thickness. By managing the process time and conditions, the thickness is theoretically unlimited, allowing for the creation of very substantial protective layers when required.
The Critical Limitations of CVD: Process Demands
The strengths of CVD are directly tied to its demanding process requirements, which also create its most significant disadvantages.
The High-Temperature Requirement
CVD processes operate at elevated temperatures, often many hundreds of degrees Celsius, which is necessary to drive the chemical reaction on the substrate's surface.
This high heat fundamentally restricts the types of materials that can be coated. Substrates with low melting points or materials that could be structurally compromised by heat (like certain steels or aluminum alloys) are not suitable candidates.
Lack of Selectivity and Finish
It is very difficult to mask off specific areas during the CVD process. As a result, the coating is applied to all exposed surfaces, making it an "all-or-nothing" application.
Additionally, CVD typically produces a matte surface finish. If a polished or smooth finish is required, a secondary processing step is necessary after coating.
Logistical and Physical Constraints
The size of the components that can be coated is limited by the dimensions of the reaction chamber.
Furthermore, the process is not portable and requires parts to be shipped to a specialized facility. Complex assemblies must also be broken down into individual components before they can be coated.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct coating technology requires a clear-eyed assessment of your material properties and performance goals.
- If your primary focus is coating complex internal geometries or intricate parts: CVD is likely the superior choice due to its non-line-of-sight deposition that ensures complete coverage.
- If your primary focus is coating temperature-sensitive materials or maintaining a specific surface finish: A lower-temperature process like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is almost certainly the better option.
- If your primary focus is creating an extremely pure, dense, and thick protective layer on a robust substrate that can withstand heat: CVD offers exceptional control and quality for high-performance applications.
Ultimately, choosing the right coating technology depends on a clear understanding of your substrate's limitations and your component's geometric demands.
Summary Table:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Uniform, conformal coating on complex geometries | High processing temperatures can damage substrates |
| High purity and dense film quality | Coating is applied to all surfaces (non-selective) |
| Versatile control over coating thickness | Matte surface finish may require post-processing |
| Excellent for harsh environment protection | Limited by chamber size and part disassembly needs |
Need a high-performance coating solution for your lab components? At KINTEK, we specialize in lab equipment and consumables, including advanced coating technologies like CVD and PVD. Whether you're working with intricate parts or temperature-sensitive materials, our expertise ensures you get the right solution for durability and precision. Let's discuss your application requirements — contact us today to enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What is the vapor phase deposition technique? A Guide to PVD & CVD Thin-Film Coating Methods
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings



















