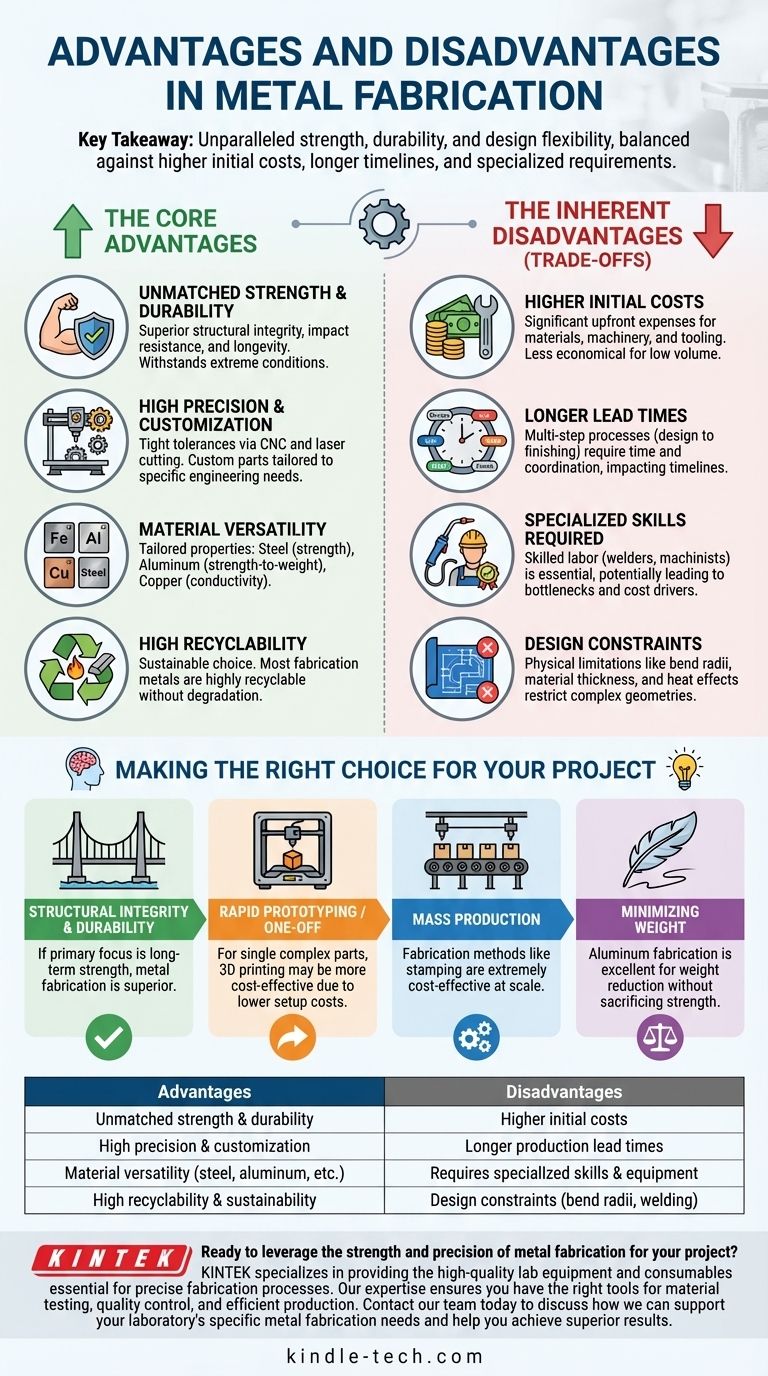
In essence, metal fabrication's key advantages are its unparalleled strength, durability, and design flexibility. This makes it the go-to process for creating robust, long-lasting components for nearly any application. The primary disadvantages, however, are the higher initial costs, potentially longer production timelines, and the requirement for specialized equipment and skilled labor.
The core takeaway is not to view metal fabrication's challenges as inherent failures, but as necessary trade-offs for achieving a level of strength, precision, and longevity that other materials and processes simply cannot match.

The Core Advantages of Metal Fabrication
Metal fabrication is the foundational process behind countless industries, from aerospace to construction. Its benefits are rooted in the fundamental properties of the materials and the precision of modern techniques.
Unmatched Strength and Durability
The most significant advantage of metal is its inherent strength. Fabricated metal components offer superior structural integrity, impact resistance, and longevity compared to materials like plastic or wood.
Metals like steel and aluminum can withstand extreme temperatures, high pressures, and harsh environmental conditions, ensuring reliability in critical applications.
High Precision and Customization
Modern fabrication techniques, such as CNC machining and laser cutting, allow for the creation of complex parts with extremely tight tolerances.
This precision ensures that components fit together perfectly in assemblies and perform reliably. It gives engineers immense freedom to design custom parts and structures tailored to a specific need, rather than being limited by off-the-shelf options.
Material Versatility
The term "metal" covers a vast range of materials, each with unique properties. This allows for a tailored approach to solving engineering challenges.
Common choices include carbon steel for raw strength, stainless steel for corrosion resistance, aluminum for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, and copper for its electrical conductivity.
High Recyclability
Most metals used in fabrication are highly recyclable without degrading their fundamental properties. Steel, for example, is one of the most recycled materials on earth. This makes metal fabrication a more sustainable choice over the entire lifecycle of a product.
Understanding the Inherent Disadvantages (The Trade-offs)
The challenges associated with metal fabrication are directly linked to the same properties that make it so advantageous. The strength and durability of metal mean it requires more energy, time, and expertise to work with.
Higher Initial Costs
Metal fabrication often involves significant upfront costs. This is driven by several factors: the cost of the raw material itself, the investment in heavy machinery, and the setup or "tooling" required for a specific job.
For low-volume or one-off parts, these initial costs can make fabrication less economical than alternatives like 3D printing.
Longer Lead Times
A typical fabrication project is a multi-step process: design, material sourcing, cutting, forming, welding, finishing, and quality inspection.
Each of these stages takes time and coordination, often resulting in longer lead times compared to single-step manufacturing processes like injection molding (once the mold is made).
The Need for Specialized Skills
Proper metal fabrication is a craft that requires highly skilled and often certified labor. Welders, machine operators, and quality control inspectors need extensive training and experience to produce safe and reliable parts.
This demand for expertise can be a cost driver and a potential production bottleneck if skilled labor is in short supply.
Design Constraints
While highly customizable, metal fabrication is not without limitations. The physical properties of metal impose certain design rules.
Factors like minimum bend radii, material thickness, and the heat effects from welding can all place constraints on the final design. Overly complex geometries can become difficult or prohibitively expensive to produce.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing metal fabrication depends entirely on your project's non-negotiable requirements. Use these points to guide your decision.
- If your primary focus is structural integrity and long-term durability: Metal fabrication is almost always the superior choice, as its material strength is unparalleled.
- If your primary focus is rapid prototyping or one-off complex parts: Consider 3D printing first, as fabrication's setup costs and lead times may be prohibitive for a single unit.
- If your primary focus is mass production of identical parts: Fabrication methods like stamping can be extremely cost-effective at scale, but require a significant upfront tooling investment.
- If your primary focus is minimizing weight without sacrificing strength: Aluminum fabrication provides an excellent solution, though the material cost is typically higher than steel.
Understanding these trade-offs empowers you to leverage metal fabrication not just as a manufacturing process, but as a strategic engineering decision.
Summary Table:
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| Unmatched strength & durability | Higher initial costs |
| High precision & customization | Longer production lead times |
| Material versatility (steel, aluminum, etc.) | Requires specialized skills & equipment |
| High recyclability & sustainability | Design constraints (bend radii, welding) |
Ready to leverage the strength and precision of metal fabrication for your project? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for precise fabrication processes. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for material testing, quality control, and efficient production. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific metal fabrication needs and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Ten-Body Horizontal Jar Mill for Lab Use
- Warm Isostatic Press WIP Workstation 300Mpa for High Pressure Applications
- Automatic Laboratory Heat Press Machine
- Warm Isostatic Press for Solid State Battery Research
- Laboratory Disc Rotary Mixer for Efficient Sample Mixing and Homogenization
People Also Ask
- What role does the ball milling process play in RP-LYCB composite anodes? Essential Tips for Superior Battery Materials
- Why is secondary ball milling necessary for sulfur cathodes? Master Solid-State Electrolyte Composite Preparation
- How does a ball mill facilitate the integration of MOFs with glass matrices? Achieve Precision Material Synthesis
- How does a laboratory ball mill prepare catalysts like CuAlO2? Enhancing Efficiency with Mechanical Alloying
- Why is mechanical alloying equipment used for nickel-based alloys? Enhance Powder Activity & Precision



















