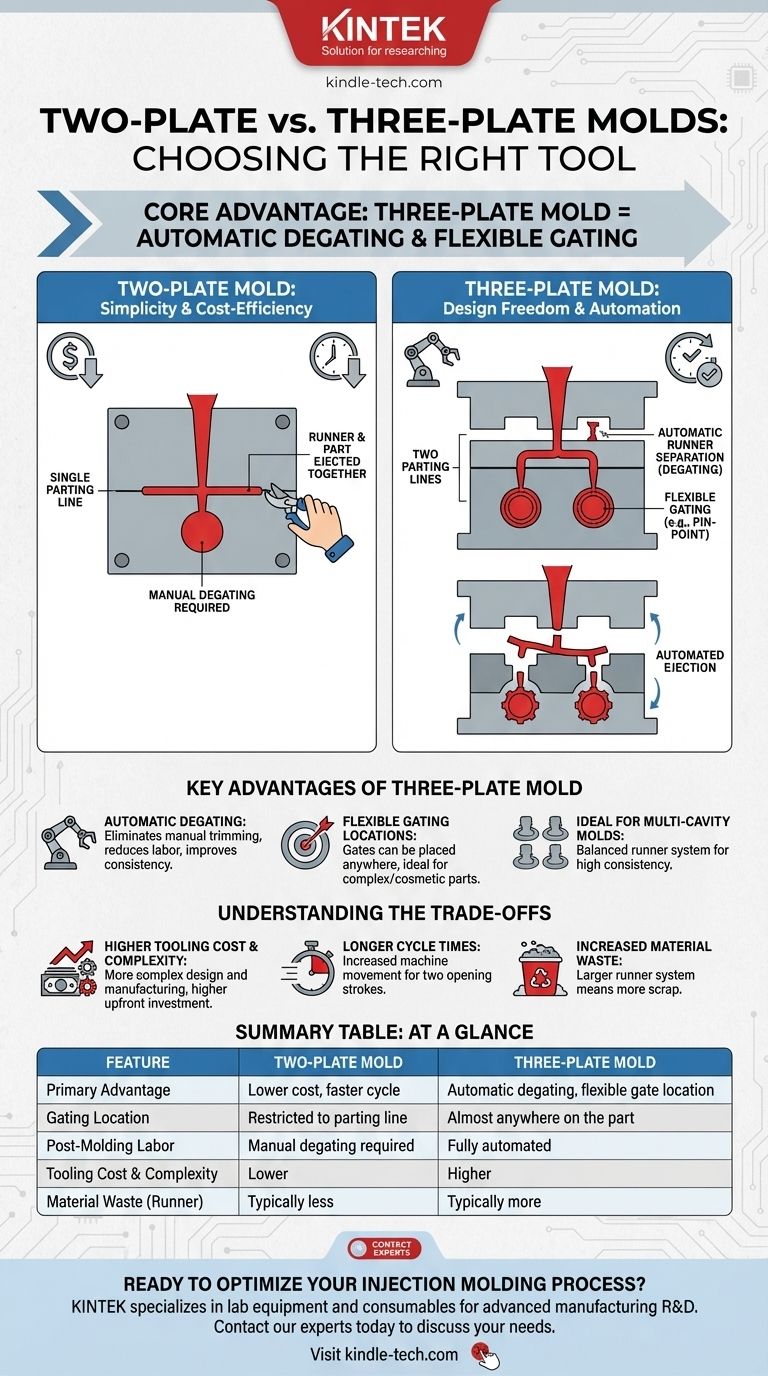
At its core, the primary advantage of a three-plate mold is its ability to automatically separate the runner system from the molded part, offering significant flexibility in gate location. While a simpler two-plate mold is cheaper and often faster, a three-plate mold enables more complex part designs and reduces post-molding labor costs.
The decision between a two-plate and a three-plate mold is a strategic trade-off. You are choosing between the upfront simplicity and low cost of a two-plate mold versus the enhanced design freedom and downstream automation of a three-plate system.
The Fundamental Difference: How They Manage Plastic Flow
The key distinction between these two mold types lies in how they handle the runner—the channel that delivers molten plastic from the machine's nozzle to the part cavity. This structural difference dictates their primary functions and applications.
How a Two-Plate Mold Works
A two-plate mold is the most common and straightforward design in injection molding. It consists of two main plates, a cavity side and a core side, which meet at a single parting line.
The runner system and the gate (the opening into the part cavity) are located on this same parting line. When the mold opens, the part and the attached runner are ejected together. This requires a secondary operation, either manual or robotic, to separate the runner from the final part.
How a Three-Plate Mold Works
A three-plate mold introduces an additional "runner plate" between the top clamping plate and the cavity plate. This creates two parting lines.
The runner system is contained between the top plate and the runner plate. As the mold opens, the first parting line separates the runner from the part, automatically shearing the plastic at the gate. The second parting line then opens to eject the finished part, leaving the runner to be ejected separately.
Key Advantages of the Three-Plate Mold
The more complex structure of a three-plate mold unlocks several critical capabilities that are impossible to achieve with a standard two-plate design.
Automatic Degating
This is the most significant advantage. The runner is automatically sheared from the part during the mold's opening sequence.
This eliminates the need for a manual trimming process, which reduces labor costs, improves cycle consistency, and prevents potential cosmetic damage to the part from manual cutting.
Flexible Gating Locations
Because the runner is on a separate plate, the gate can be placed almost anywhere on the part's surface, not just along the parting line.
This is ideal for pin-point gating directly into the center of a round part to ensure uniform filling and reduce warpage. It also allows for gating on cosmetically important surfaces where a gate vestige would be unacceptable.
Ideal for Multi-Cavity Molds
Three-plate molds excel at producing multiple small parts in a single cycle. The design allows for a balanced runner system that feeds each cavity evenly from a central sprue, ensuring higher part-to-part consistency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The advantages of a three-plate mold come with clear and important trade-offs that must be considered.
Higher Tooling Cost and Complexity
The addition of a third plate and the associated mechanisms makes the mold significantly more complex to design, manufacture, and maintain.
This directly translates to a higher upfront tooling cost and a longer lead time to produce the mold compared to a simpler two-plate design.
Longer Cycle Times
While it saves time by eliminating manual degating, the mechanical action of a three-plate mold often results in a longer cycle time.
The mold requires a longer opening stroke to separate the two parting lines and eject both the part and the runner. This added machine movement increases the time for each complete cycle.
Increased Material Waste
The runner system in a three-plate mold is typically larger and more complex than in a two-plate mold. This results in more plastic material being used for the runner, which is often reground or discarded as scrap, increasing the material cost per part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Choosing the correct mold type is not about which is universally "better," but which is right for your specific part, production volume, and budget.
- If your primary focus is minimizing upfront tooling cost and achieving the fastest machine cycle: A two-plate mold is the definitive choice, provided you can accommodate manual degating and its parting-line gate locations.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production with minimal labor: A three-plate mold's automatic degating can deliver a significant return on investment by eliminating a costly secondary operation.
- If your part design demands a central gate for structural integrity or aesthetics: A three-plate mold provides the necessary gating flexibility that a standard two-plate mold simply cannot offer.
Ultimately, your choice requires balancing the upfront investment in tooling complexity against the long-term gains in automation and design freedom.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Two-Plate Mold | Three-Plate Mold |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Advantage | Lower cost, faster cycle | Automatic degating, flexible gate location |
| Gating Location | Restricted to parting line | Almost anywhere on the part |
| Post-Molding Labor | Manual degating required | Fully automated |
| Tooling Cost & Complexity | Lower | Higher |
| Material Waste (Runner) | Typically less | Typically more |
Ready to optimize your injection molding process?
Choosing the right mold is critical for your project's success, balancing upfront cost against long-term efficiency. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and consumables needed to support advanced manufacturing R&D, including prototyping and material testing for applications like injection molding.
Our expertise can help you validate your mold design decisions and ensure your production runs smoothly. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Polygon Press Mold for Lab
- Special Shape Press Mold for Lab
- Multi-Punch Rotary Tablet Press Mold Ring for Rotating Oval and Square Molds
- Cylindrical Press Mold with Scale for Lab
- Special Heat Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of using high-strength graphite molds in the hot press sintering of Ti6Al4V-based composites?
- What are the primary functions of graphite molds in NiCr powder metallurgy? Optimize Your Composite Material Density
- How do custom graphite molds contribute to Al-20% Si/graphite flake composites? Optimize Microstructure & Conductivity
- What are the advantages of using PEEK molds for sulfide all-solid-state batteries? High Performance and Insulation
- What is the lifespan of a mold? It's Immortal Unless You Control Moisture



















