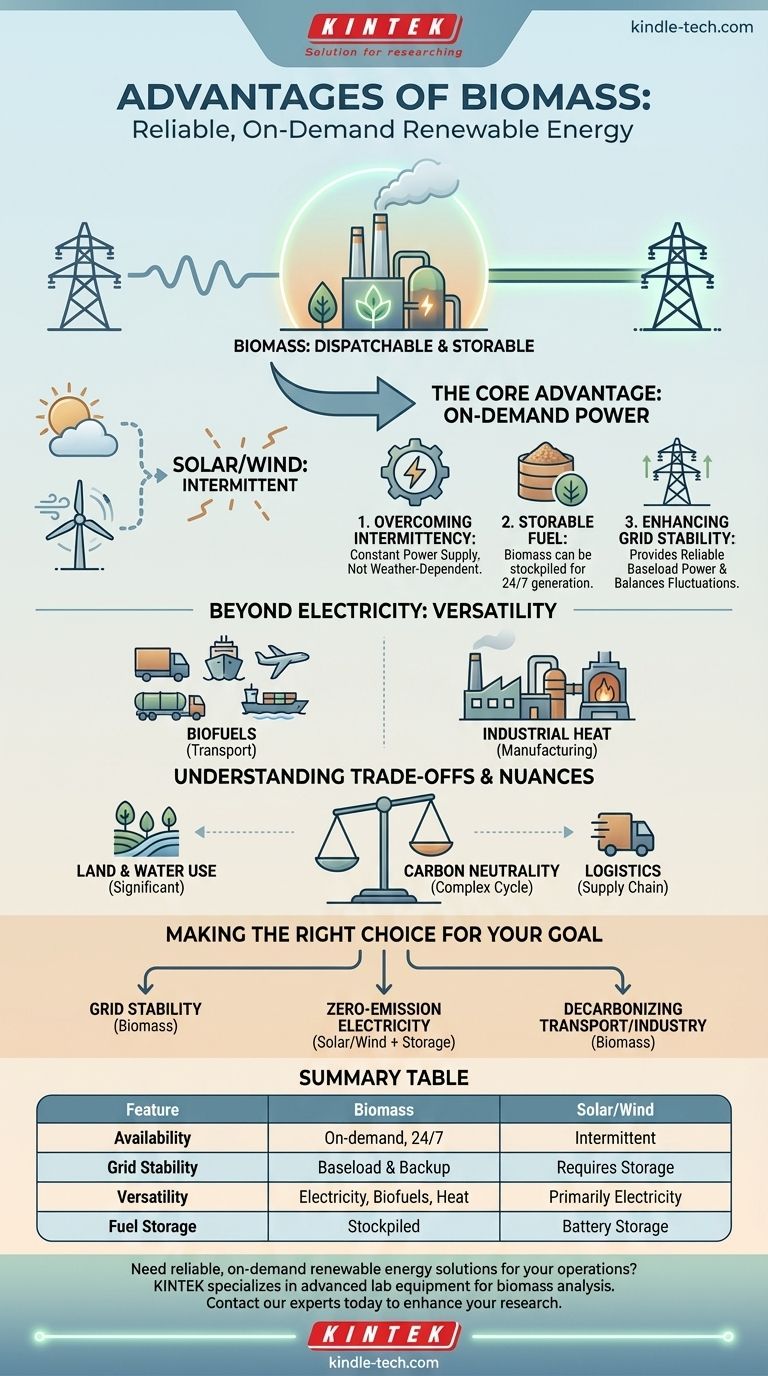
The single greatest advantage of biomass over other major renewables like solar and wind is its reliability and dispatchability. While solar and wind are intermittent, dependent on weather conditions, biomass acts as a storable, on-demand energy source. This allows it to generate power consistently, much like a traditional fossil fuel power plant, but with a renewable fuel source.
While many renewables produce energy when nature allows, biomass produces energy when we demand it. This fundamental difference makes it a critical tool for ensuring grid stability and providing a consistent power supply that intermittent sources alone cannot guarantee.

The Core Advantage: On-Demand Renewable Power
The primary challenge with integrating sources like solar and wind into the power grid is their variability. Biomass directly addresses this core problem.
Overcoming Intermittency
Solar panels only generate electricity when the sun is shining, and wind turbines only spin when the wind is blowing. This is known as intermittency.
Power grids require a constant, stable balance between electricity supply and demand. The intermittent nature of solar and wind can strain this balance, requiring backup power sources to fill the gaps.
Biomass as a Storable Fuel
Unlike sunlight or wind, biomass—in forms like wood pellets, agricultural residue, or dedicated energy crops—is a physical, storable fuel.
This fuel can be stockpiled at a power plant and used to generate electricity whenever it is needed, day or night, regardless of the weather. This makes biomass a dispatchable power source.
Enhancing Grid Stability
Because it is dispatchable, biomass can provide reliable baseload power—the minimum level of electricity demand on a grid over a 24-hour period.
It can also be ramped up or down to meet fluctuations in demand or to compensate for a sudden drop in generation from intermittent renewables, thereby enhancing the overall stability and reliability of the grid.
Beyond Electricity: The Versatility of Biomass
Biomass's advantages extend beyond just generating dispatchable electricity. Its physical nature as a carbon-based fuel opens up applications where solar and wind cannot compete.
Production of Biofuels
Biomass can be converted into liquid biofuels such as ethanol and biodiesel.
These biofuels are a crucial tool for decarbonizing the transportation sector, particularly for aviation, shipping, and heavy-duty trucking where direct electrification is currently challenging.
A Source for Industrial Heat
Many industrial processes, such as cement or steel manufacturing, require extremely high temperatures that are difficult and inefficient to achieve with electricity.
Biomass can be burned directly to produce this high-grade heat, offering a renewable alternative to natural gas or coal for these hard-to-abate industrial sectors.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
To make an informed decision, it is crucial to recognize that the advantages of biomass come with significant trade-offs that are not present with solar or wind.
Land and Water Use
Growing dedicated energy crops for biomass requires significant amounts of land and water. This can create competition with agriculture for food production and put pressure on natural ecosystems if not managed sustainably.
The Question of Carbon Neutrality
Burning biomass releases carbon dioxide at the point of combustion. The claim of carbon neutrality rests on the assumption that the carbon released is reabsorbed by new plant growth.
This cycle is only truly neutral if the biomass is sourced from sustainably managed forests or from waste streams that would have decomposed and released methane anyway. Poorly managed biomass can lead to deforestation and a net increase in atmospheric carbon.
Logistical and Supply Chain Complexity
Unlike a solar panel that captures energy on-site, biomass requires a complex supply chain. This involves harvesting, collecting, drying, processing, and transporting the fuel to the power facility, which adds cost, energy consumption, and logistical hurdles.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" renewable energy source depends entirely on the specific problem you are trying to solve. Biomass is not a universal replacement for solar or wind, but a complementary technology with unique strengths.
- If your primary focus is grid stability and reliable, on-demand power: Biomass is a powerful option because it is a dispatchable renewable that can provide baseload energy.
- If your primary focus is zero-emission electricity with minimal land use per unit of energy: Utility-scale solar and wind are superior choices, especially when their intermittency is managed with battery storage.
- If your primary focus is decarbonizing transportation or heavy industry: Biomass is uniquely suited for producing the liquid biofuels and high-grade heat these sectors require.
Ultimately, building a resilient and clean energy system requires leveraging a diverse portfolio of technologies for their specific strengths.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Biomass | Solar/Wind |
|---|---|---|
| Availability | On-demand, 24/7 | Intermittent, weather-dependent |
| Grid Stability | Provides baseload & backup power | Requires storage for stability |
| Versatility | Can produce electricity, biofuels, & industrial heat | Primarily produces electricity |
| Fuel Storage | Fuel can be stockpiled for later use | Energy must be stored in batteries |
Need reliable, on-demand renewable energy solutions for your operations? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for biomass analysis, biofuel development, and renewable energy research. Our expertise helps you accurately test fuel properties, optimize conversion processes, and ensure the sustainability of your biomass projects. Contact our experts today to enhance your renewable energy capabilities with precision equipment tailored to your laboratory's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
- Battery Lab Equipment Battery Capacity and Comprehensive Tester
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- How does PECVD work? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition







