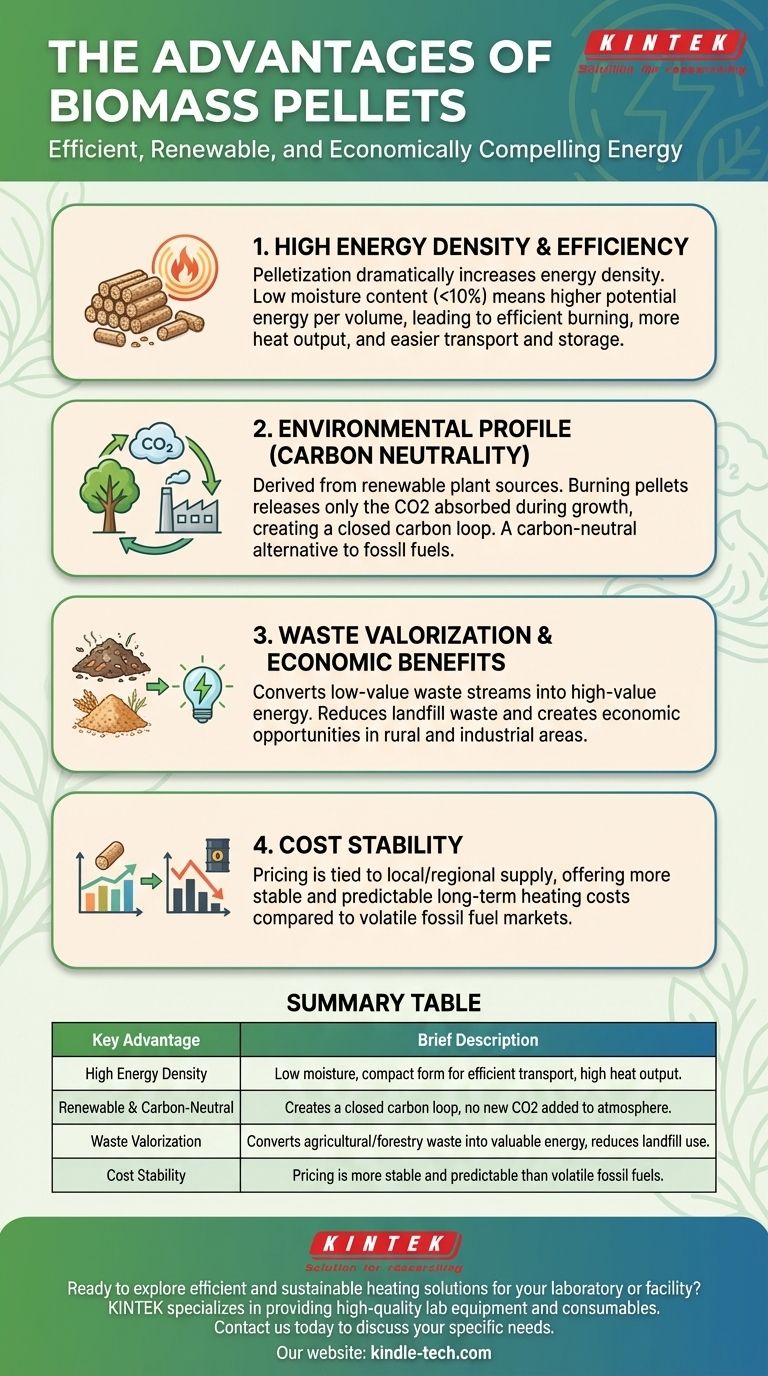
The primary advantages of biomass pellets are their high energy density, status as a renewable and carbon-neutral fuel source, and their ability to convert waste materials into a valuable product. This combination makes them an economically and environmentally compelling alternative to traditional fossil fuels for both residential and industrial heating.
The core value of biomass pellets is not just that they are "green," but that they standardize a renewable fuel. By compressing organic waste into a dense, uniform format, pellets become an efficient, automatable, and more predictable energy source than raw biomass.

The Core Advantages of Pellet Fuel
Biomass pellets derive their strengths from the process that creates them. Raw materials like sawdust, agricultural residue, or forest waste are dried, pulverized, and compressed under intense pressure, resulting in a superior fuel.
Advantage 1: High Energy Density and Efficiency
Raw biomass, like wood chips or straw, is bulky and contains significant moisture, making it inefficient to transport and burn.
The pelletization process dramatically increases the energy density of the material. By removing moisture and compressing the fibers, you get a fuel that contains more potential energy per unit of volume, making it easier and cheaper to store and transport.
This low moisture content (typically under 10%) also means pellets burn more completely and efficiently than raw firewood, producing more heat and less smoke and ash.
Advantage 2: Environmental Profile (Carbon Neutrality)
Biomass is considered a renewable resource because it is derived from plants that can be regrown in a relatively short time.
When burned, pellets release the same amount of carbon dioxide that the original plant absorbed from the atmosphere during its growth. This creates a closed carbon loop, meaning it doesn't add new carbon to the atmosphere, unlike fossil fuels. This is why it is often referred to as a carbon-neutral fuel.
Advantage 3: Waste Valorization and Economic Benefits
A significant portion of biomass pellets are produced from waste streams. This includes sawdust from sawmills, leftover crops from farms, and managed forest thinnings.
This process, known as waste valorization, turns a low-value or disposal-cost material into a high-value energy product. This not only reduces landfill waste but also creates economic opportunities in rural and industrial areas.
Advantage 4: Cost Stability
While the price of fossil fuels like heating oil and natural gas can be highly volatile, the cost of biomass pellets is often more stable.
Pellet pricing is tied to local and regional supply of raw materials, insulating it from the geopolitical factors that frequently impact global fossil fuel markets. This can lead to more predictable heating costs over the long term.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
No fuel source is without its complexities. The advantages of biomass pellets are powerful, but they are dependent on responsible sourcing and proper use.
The Myth of "Perfectly Green" Fuel
The term "environmentally friendly" requires context. The process of producing pellets—drying, compressing, and transporting them—consumes energy, which can have its own carbon footprint.
Furthermore, burning pellets still produces particulate matter and other emissions. To minimize this, it is critical to use a modern, high-efficiency pellet stove or boiler that is properly maintained.
Sourcing Is Everything
The carbon-neutral claim hinges entirely on sustainable sourcing. If pellet production drives deforestation or relies on whole trees from poorly managed forests, its environmental benefits are severely compromised.
True sustainability comes from using genuine waste products or biomass from forests certified for responsible management practices. Always inquire about the source of your pellet supply.
Handling and Storage Requirements
Compared to oil or natural gas, pellets require more hands-on management. They are delivered in bags or bulk and must be stored in a completely dry location to prevent them from degrading.
Users must also manually load pellets into a hopper and perform regular cleaning of the burn pot and ash pan, making them less "set and forget" than fossil fuel systems.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Biomass pellets offer a compelling set of benefits, but whether they are the right choice depends entirely on your priorities.
- If your primary focus is reducing your carbon footprint: Pellets are an excellent choice, provided you verify they are produced from sustainable waste streams and not from deforestation.
- If your primary focus is long-term cost stability: Pellets can shield you from volatile fossil fuel prices, but you must account for the initial investment in a specialized stove or boiler.
- If your primary focus is convenience and automation: A modern pellet stove offers significant automation, but it still requires more user involvement for loading and cleaning than a natural gas furnace.
Ultimately, choosing biomass pellets is a decision to adopt a renewable fuel that requires a clear understanding of both its significant advantages and its practical responsibilities.
Summary Table:
| Key Advantage | Brief Description |
|---|---|
| High Energy Density | Low moisture content and compact form for efficient transport and high heat output. |
| Renewable & Carbon-Neutral | Creates a closed carbon loop, not adding new CO2 to the atmosphere. |
| Waste Valorization | Converts agricultural/forestry waste into valuable energy, reducing landfill use. |
| Cost Stability | Pricing is often more stable and predictable than volatile fossil fuels. |
Ready to explore efficient and sustainable heating solutions for your laboratory or facility? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables. Whether you are researching biomass properties or require reliable heating systems, our expertise can help you achieve your goals efficiently and sustainably. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customizable Fuel Cell Stack Components for Diverse Applications
- FS Electrochemical Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Diverse Applications
- Customizable PEM Electrolysis Cells for Diverse Research Applications
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Hollow Cleaning Basket and Rack Carrier
- Custom Machined and Molded PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer for Laboratory ITO FTO Conductive Glass Cleaning Flower Basket
People Also Ask
- What criteria are used during the visual inspection of electrodes? Essential Quality Assessment for Your Lab
- What is the proper way to handle the glass components of the electrolytic cell? Ensure Safe and Accurate Experiments
- What are the procedures for handling a proton exchange membrane after use? Ensure Longevity and Performance
- What is a proton exchange membrane? The Selective Heart of Hydrogen Energy Systems
- How should carbon paper used in a fuel cell be maintained? Prevent PTFE Degradation for Peak Performance













