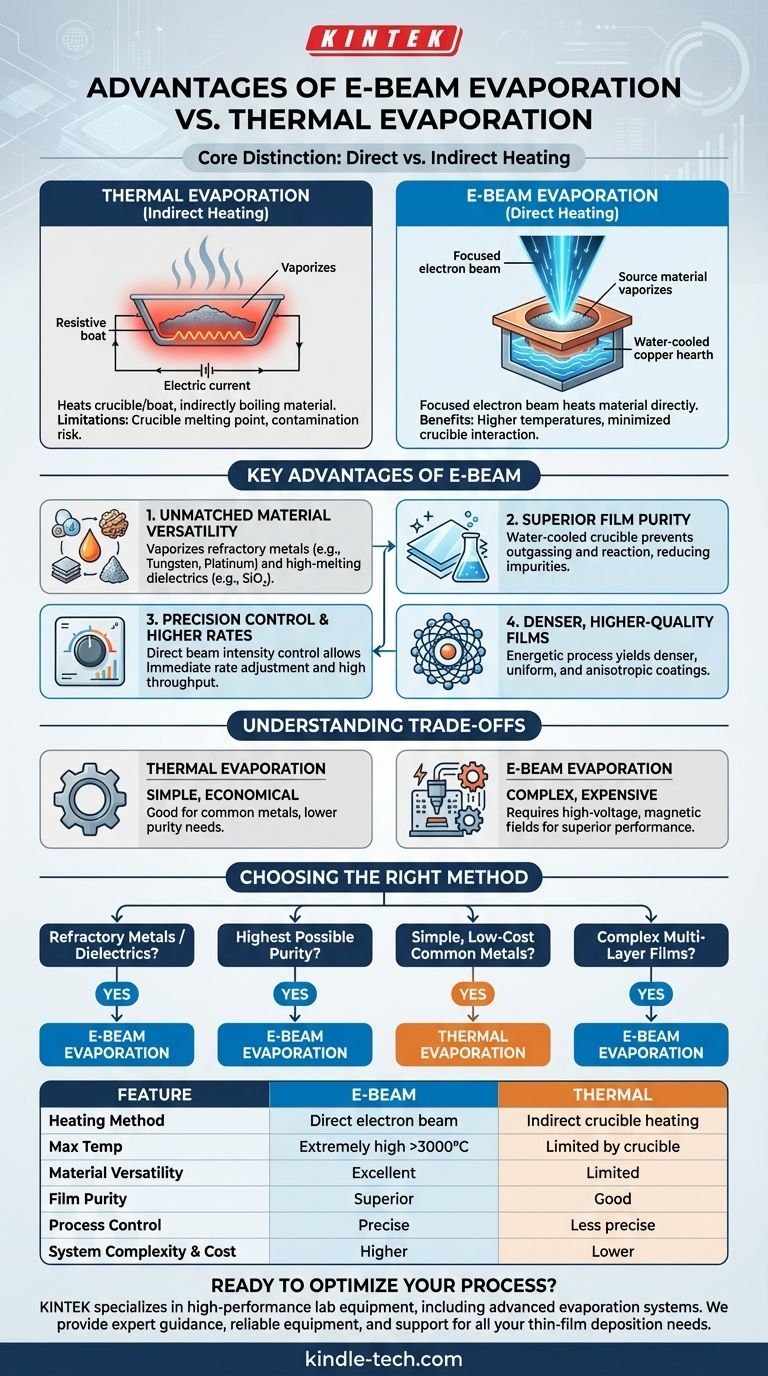
In short, electron-beam (e-beam) evaporation offers significant advantages over thermal evaporation, primarily delivering higher film purity, the ability to deposit a much wider range of materials, and superior control over the deposition process. These benefits stem from its fundamentally different method of heating the source material.
The core distinction is this: Thermal evaporation heats a crucible to indirectly boil the material within it, introducing potential impurities and temperature limitations. E-beam evaporation uses a focused beam of electrons to heat the material directly, bypassing the crucible and enabling a purer, more versatile, and more controlled process.
The Fundamental Difference: Direct vs. Indirect Heating
To understand the advantages of e-beam evaporation, you must first grasp the core difference in how each method generates vapor. The choice between them directly impacts the quality of your final thin film.
How Thermal Evaporation Works
In thermal evaporation, an electric current is passed through a resistive boat or crucible containing the source material.
This boat heats up significantly, and that heat is transferred to the source material, causing it to melt and eventually evaporate. This is an indirect heating method.
The primary limitations are the melting point of the crucible itself and the risk of the hot crucible material reacting with or contaminating the source material.
How E-Beam Evaporation Works
In e-beam evaporation, a high-energy beam of electrons is generated from a charged tungsten filament and magnetically guided to strike the source material directly.
This focused energy heats a very small area of the material to extremely high temperatures, causing it to evaporate. The material is typically held in a water-cooled copper hearth, which remains cool during the process. This is a direct heating method.
Key Advantages of E-Beam Evaporation Explained
This direct heating mechanism is the source of e-beam's primary advantages in thin-film deposition.
Unmatched Material Versatility
Because the energy is delivered directly to the source, e-beam evaporation can achieve much higher temperatures than thermal methods.
This allows it to vaporize materials with very high melting points, including refractory metals (like tungsten, platinum, tantalum) and dielectrics (like silicon dioxide, SiO₂), which are impossible to deposit with standard thermal evaporation.
Superior Film Purity
In an e-beam system, the water-cooled crucible remains relatively cool, confining the intense heat only to the source material.
This prevents the crucible from outgassing or reacting with the source, significantly reducing the risk of impurities being incorporated into the deposited film. Thermal evaporation's hot crucible is a common source of contamination.
Precision Control and Higher Deposition Rates
The intensity of the electron beam can be precisely controlled, which provides direct and immediate control over the evaporation rate. This is critical for managing film properties.
Furthermore, the high energy density of the electron beam enables much higher deposition rates than thermal evaporation, increasing process throughput.
Denser, Higher-Quality Films
The direct and energetic nature of e-beam evaporation often results in thin films that are denser and more uniform compared to those produced by thermal evaporation. The line-of-sight nature of the process also produces highly directional, or anisotropic, coatings, which is beneficial for certain applications like lift-off patterning.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, e-beam evaporation is not always the best choice. The advantages come with increased complexity.
The Simplicity of Thermal Evaporation
Thermal evaporation systems are mechanically simpler, less expensive, and easier to operate. For materials with lower melting points where ultra-high purity is not the primary concern, it is an extremely effective and economical choice.
The Complexity of E-Beam Systems
E-beam evaporators are more complex and expensive systems. They require high-voltage power supplies and magnetic fields to guide the beam, adding to the cost and maintenance requirements. This complexity is the trade-off for its superior performance and versatility.
Choosing the Right Method for Your Application
Your material requirements and performance goals should dictate your choice of deposition technology.
- If your primary focus is depositing refractory metals or dielectrics: E-beam evaporation is your only viable option due to its high-temperature capabilities.
- If your primary focus is achieving the highest possible film purity: E-beam evaporation is the superior choice because it minimizes contamination from the crucible.
- If your primary focus is simple, low-cost deposition of common metals (e.g., aluminum, gold, chromium): Thermal evaporation is often the most practical and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is creating complex, multi-layer films in a single process: E-beam systems with multi-pocket carousels provide unmatched flexibility for depositing different materials sequentially.
By understanding the core heating mechanism, you can confidently select the deposition technique that aligns with your material, purity, and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Feature | E-Beam Evaporation | Thermal Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Direct electron beam | Indirect crucible heating |
| Max Temperature | Extremely high (>3000°C) | Limited by crucible |
| Material Versatility | Excellent (refractory metals, dielectrics) | Limited (lower melting point materials) |
| Film Purity | Superior (minimized crucible contamination) | Good (risk of crucible reaction) |
| Process Control | Precise rate control | Less precise |
| System Complexity & Cost | Higher | Lower |
Ready to Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process?
KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab equipment, including advanced evaporation systems. Whether your research demands the ultimate purity of e-beam evaporation or the cost-effective simplicity of thermal evaporation, our experts can help you select the perfect solution for your specific materials and application requirements.
We provide:
- Expert guidance to match the right technology to your goals.
- Reliable equipment for depositing everything from common metals to high-temperature dielectrics.
- Support to ensure you achieve dense, high-quality films with maximum efficiency.
Don't let equipment limitations compromise your results. Contact our team today to discuss how we can advance your laboratory's capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Circulating Water Vacuum Pump for Laboratory and Industrial Use
People Also Ask
- What is vacuum thermal evaporation? A Guide to High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the evaporation process in semiconductors? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is thermal evaporation technique thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD



















