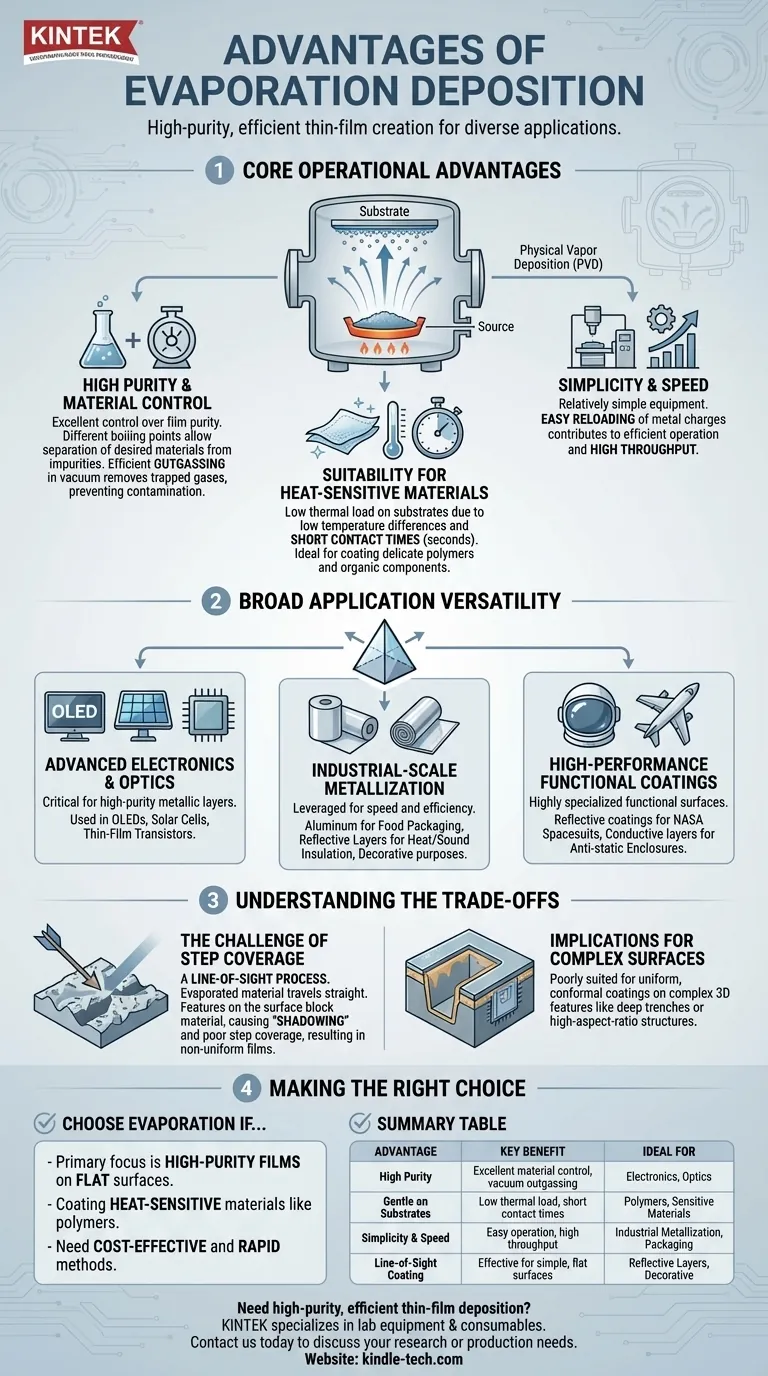
At its core, evaporation deposition offers a straightforward and efficient method for creating high-purity thin films. Its key advantages are the ability to maintain material purity, its gentle handling of heat-sensitive substrates, and its operational simplicity, which makes it suitable for a wide range of applications from advanced electronics to industrial packaging.
While often valued for its speed and purity, the defining characteristic of evaporation deposition is its line-of-sight nature. This makes it an exceptional tool for coating simple, flat surfaces but presents significant challenges for complex topographies.
Core Operational Advantages
Evaporation deposition is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique where a source material is heated in a vacuum until it evaporates, travels through the vacuum chamber, and condenses onto a substrate as a thin film. The primary benefits stem directly from this simple mechanism.
High Purity and Material Control
The process allows for excellent control over the purity of the final film. Because different materials have different boiling points, the source can be heated to a temperature that evaporates the desired material while leaving less volatile impurities behind.
Furthermore, efficient outgassing in the vacuum environment removes trapped gases from the source material before deposition begins, preventing them from being incorporated into the film as contaminants.
Suitability for Heat-Sensitive Materials
Evaporation can be performed with very low temperature differences between the heating source and the boiling liquid. This, combined with short product contact times (often just a few seconds), minimizes the thermal load on the substrate.
This characteristic makes it an ideal choice for depositing metals onto delicate materials like polymers or organic electronic components that would be damaged by higher-temperature processes.
Simplicity and Speed
Compared to other deposition methods, the equipment for thermal evaporation can be relatively simple. The ability to easily reload metal charges into the evaporation filament or boat contributes to efficient operation and high throughput.
Broad Application Versatility
The advantages of evaporation deposition have led to its adoption across numerous fields, from high-tech research to large-scale industrial manufacturing.
Advanced Electronics and Optics
The ability to create high-purity metallic layers is critical for manufacturing devices. It is commonly used to create metal bonding layers and electrodes in OLEDs, solar cells, and thin-film transistors.
Industrial-Scale Metallization
The speed and efficiency of the process are leveraged for creating thin films on polymers. This includes depositing aluminum for food packaging, creating reflective layers for heat and sound insulation, and for various decorative purposes.
High-Performance Functional Coatings
The technique is used to create highly specialized functional surfaces. Examples include reflective coatings for NASA spacesuits and emergency blankets, as well as conductive layers for anti-static enclosures in aircraft.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single technique is perfect for every scenario. The primary limitation of evaporation deposition is a direct consequence of its fundamental mechanism.
The Challenge of Step Coverage
Evaporation is a line-of-sight process. The evaporated material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. If the substrate has a rough or patterned surface with protruding features, those features can block the material from reaching other areas.
This phenomenon, known as "shadowing," results in poor step coverage. The film will be non-uniform, with thinner or non-existent layers in the "shadowed" regions of the topography.
Implications for Complex Surfaces
This limitation makes evaporation deposition poorly suited for applications that require a uniform, conformal coating over substrates with complex 3D features, such as deep trenches or high-aspect-ratio structures found in advanced microchips.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the right deposition method requires matching the technique’s strengths and weaknesses to your specific requirements.
- If your primary focus is high-purity films on flat or simple surfaces: Evaporation deposition is an excellent, cost-effective, and rapid method.
- If your primary focus is coating heat-sensitive materials like polymers: The low thermal load of evaporation makes it a standout choice to prevent substrate damage.
- If your primary focus is uniformly coating complex, non-flat topographies: You must account for the "shadowing" effect and will likely need to explore alternative methods like sputtering, which offers better step coverage.
Ultimately, evaporation deposition is a powerful and versatile tool when applied to the right problem.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| High Purity | Excellent material control and outgassing in vacuum | Electronics, optics |
| Gentle on Substrates | Low thermal load, short contact times | Polymers, sensitive materials |
| Simplicity & Speed | Easy operation and high throughput | Industrial metallization, packaging |
| Line-of-Sight Coating | Effective for flat or simple surfaces | Reflective layers, decorative coatings |
Need high-purity, efficient thin-film deposition for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing reliable evaporation deposition solutions tailored to your research or production needs. Whether you're working with advanced electronics, sensitive polymers, or industrial coatings, our expertise ensures optimal performance and results. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Evaporation Boat for High Temperature Applications
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Oxygen-Free Copper Crucible and Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is the process of evaporation coating? A Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What materials are used in vacuum evaporation? A Guide to Metals, Alloys, and Dielectrics
- What is the basic working principle of e-beam evaporation process? Achieve High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- What is the electron beam evaporation technique? Achieve High-Purity Thin Film Deposition
- Is deposition the same as evaporation? Unraveling the Hierarchy of Thin-Film Technology
- How do you evaporate metal? Mastering Thermal vs. E-beam Evaporation for Thin Films
- What is the difference between e-beam evaporation and thermal evaporation? A Guide to Choosing the Right PVD Method
- How thin film is prepared using thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to High-Purity Deposition



















