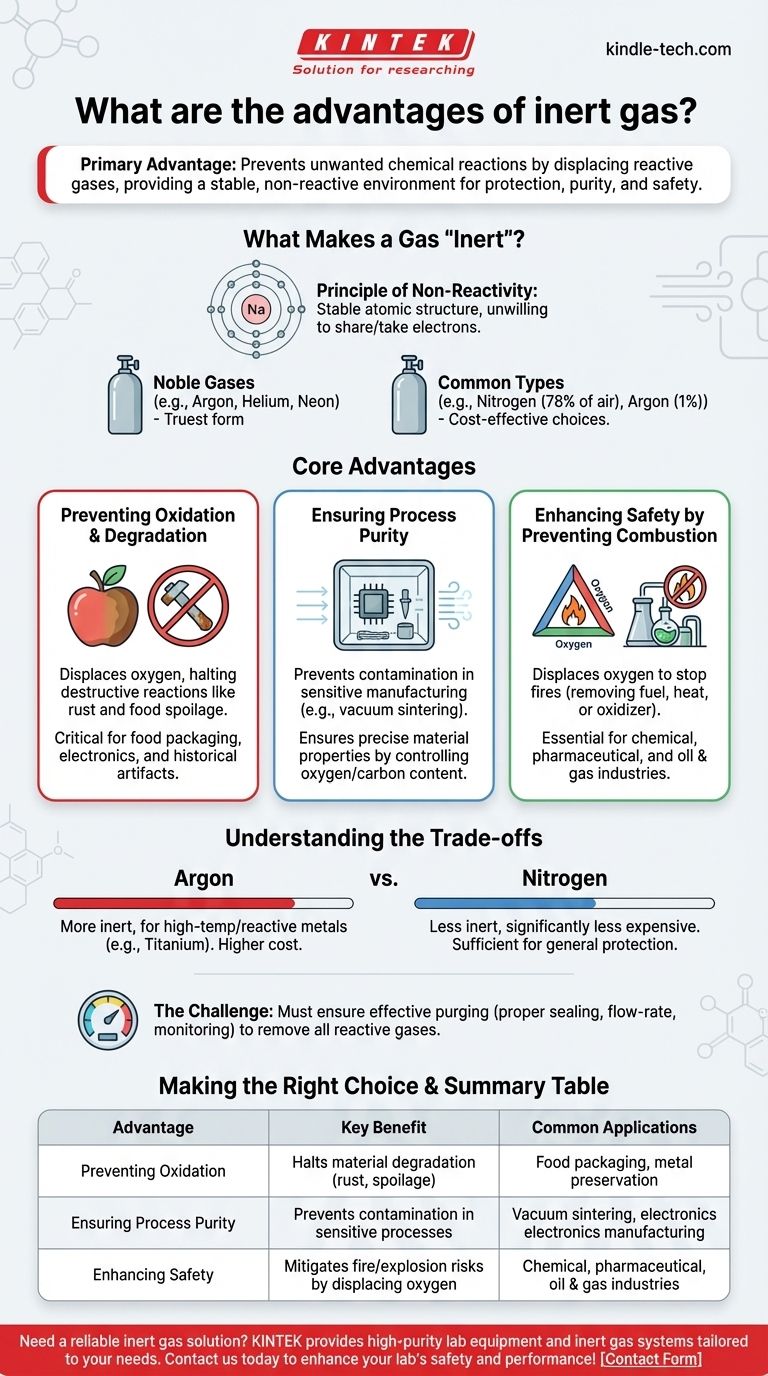
In essence, the primary advantage of an inert gas is its ability to prevent unwanted chemical reactions. By displacing chemically reactive gases like oxygen, an inert gas provides a stable environment that protects materials, ensures process purity, and enhances safety by mitigating the risk of fire or explosions.
The fundamental value of an inert gas is its ability to create a controlled, non-reactive environment. This prevents oxidation, contamination, and combustion, allowing sensitive processes to occur safely and materials to maintain their integrity.

What Makes a Gas "Inert"?
The Principle of Non-Reactivity
An inert gas is one that does not easily participate in chemical reactions. This stability is due to its atomic structure, typically a full outer shell of electrons, which makes it unwilling to share or take electrons from other substances.
The noble gases (like argon, helium, and neon) are the most chemically inert elements and serve as the textbook example of inert gases.
Common Types of Inert Gases
While noble gases are the truest form of inert gas, other gases can behave inertly under specific conditions.
The most common gases used for this purpose are nitrogen (N₂) and argon (Ar). Nitrogen makes up approximately 78% of the Earth's atmosphere, and argon makes up about 1%. This abundance, particularly for nitrogen, makes it a very cost-effective choice for many applications.
Core Advantages in Industrial and Scientific Applications
Preventing Oxidation and Degradation
Many materials degrade when exposed to oxygen and moisture in the air. This process, called oxidation, is responsible for everything from metal rusting to food spoilage.
By purging an area with an inert gas, you displace the oxygen, effectively halting or dramatically slowing down these destructive reactions. This is critical in food packaging, electronics manufacturing, and the preservation of historical artifacts.
Ensuring Process Purity
In high-precision manufacturing, such as the vacuum sintering of metal parts, even tiny amounts of reactive gas can ruin the final product.
An inert atmosphere prevents the depletion of key alloying elements, helps remove binding agents, and gives operators precise control over the final oxygen and carbon content of the material. This ensures the finished part has the exact mechanical properties required.
Enhancing Safety by Preventing Combustion
Fire requires three components: fuel, heat, and an oxidizer (typically oxygen). Removing any one of these stops a fire from starting or continuing.
Inert gas is used to displace oxygen in environments where flammable liquids or combustible dusts are present. This "inerting" of the atmosphere is a critical safety measure in the chemical, pharmaceutical, and oil and gas industries to prevent catastrophic fires and explosions.
Understanding the Trade-offs
True Inertness vs. Cost: Argon vs. Nitrogen
While often used interchangeably, argon and nitrogen have key differences. Argon is more inert than nitrogen and is the required choice for very high-temperature processes or reactions involving metals that can react with nitrogen (like titanium or lithium).
However, nitrogen is significantly less expensive than argon. For a vast range of applications where extreme reactivity is not a concern, nitrogen provides sufficient protection at a fraction of the cost.
The Challenge of Purity and Displacement
Simply introducing an inert gas is not enough. You must ensure that it has effectively purged the container or environment of all reactive gases.
This requires proper sealing, flow-rate calculations, and sometimes monitoring equipment to confirm that oxygen levels are below the required threshold. Improper purging can lead to a false sense of security and failed processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct inert gas strategy depends entirely on your specific objective, budget, and tolerance for risk.
- If your primary focus is maximum protection for highly sensitive materials: Use a noble gas like purified argon, as it offers the highest degree of non-reactivity for demanding applications like TIG welding or semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, general-purpose inerting: Nitrogen is often the most practical and economical choice for broad applications like food packaging, tire inflation, or preventing general oxidation.
- If your primary focus is safety and fire suppression: The main goal is oxygen displacement, making nitrogen or specialized inert gas mixtures a highly effective solution for protecting personnel and facilities.
By understanding these principles, you can strategically implement an inert gas atmosphere to protect your process, product, and personnel.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Preventing Oxidation | Halts material degradation (rust, spoilage) | Food packaging, metal preservation |
| Ensuring Process Purity | Prevents contamination in sensitive processes | Vacuum sintering, electronics manufacturing |
| Enhancing Safety | Mitigates fire/explosion risks by displacing oxygen | Chemical, pharmaceutical, oil & gas industries |
Need to protect your processes and materials with a reliable inert gas solution? KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity lab equipment and consumables, including inert gas systems tailored for your laboratory's unique needs. Whether you require cost-effective nitrogen for general use or ultra-pure argon for sensitive applications, our experts can help you design a safe and efficient setup. Contact us today to discuss how we can enhance your lab's safety and performance!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Platinum Auxiliary Electrode for Laboratory Use
- Variable Speed Peristaltic Pump
- Platinum Sheet Electrode for Laboratory and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapour deposition method? A Low-Temperature Solution for Advanced Coatings













