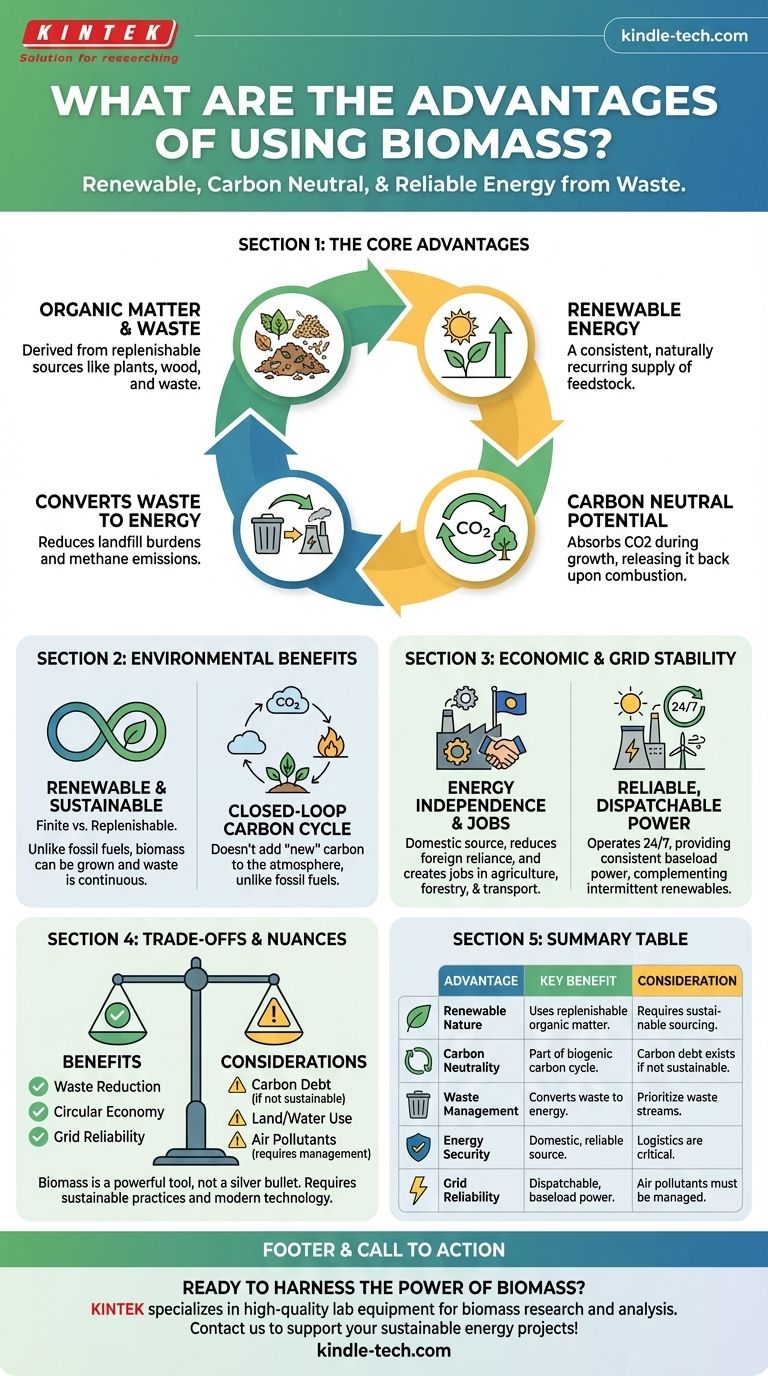
The primary advantages of biomass are its renewable nature, potential for carbon neutrality, and ability to convert waste into a reliable energy source. Unlike finite fossil fuels, biomass is derived from organic matter such as plants, wood, and waste, which can be replenished. This positions it as a key component in diversifying energy portfolios and enhancing energy security.
Biomass is more than just a renewable fuel; it's a versatile energy solution that leverages organic waste streams to create reliable power, reduce landfill burdens, and bolster domestic energy security.

The Environmental Case for Biomass
Understanding the environmental benefits requires looking at the entire lifecycle of biomass, from its growth to its conversion into energy.
A Renewable Energy Source
Biomass energy comes from organic material, which is a naturally recurring resource.
As long as plants can be grown and waste is generated, a consistent supply of feedstock can be maintained. This stands in stark contrast to fossil fuels like coal, oil, and natural gas, which are finite and being depleted.
The Principle of Carbon Neutrality
In theory, biomass is carbon neutral. The carbon dioxide (CO2) released when biomass is burned is part of the natural biogenic carbon cycle.
The plants that form the biomass absorbed that same amount of CO2 from the atmosphere during their growth. This closed-loop system means it doesn't add new carbon to the atmosphere, unlike the combustion of fossil fuels.
A Solution for Waste Management
A significant advantage of biomass is its ability to utilize materials that would otherwise be discarded.
This includes agricultural crop residues, forestry byproducts, and the organic component of municipal solid waste. Using this waste for energy generation reduces the volume sent to landfills, which in turn cuts down on methane, a potent greenhouse gas released from decomposing organic matter.
Economic and Grid Stability Benefits
Beyond the environmental arguments, biomass offers tangible benefits for national economies and the stability of the power grid.
Enhancing Energy Independence
Biomass is a domestic energy source. It can be grown and harvested locally, reducing a nation's dependence on foreign oil and gas.
This insulates the economy from the price volatility and geopolitical instability often associated with the global energy market.
Creating Domestic Jobs
The biomass industry supports jobs across several sectors, particularly in rural communities.
Employment is generated in agriculture and forestry for feedstock cultivation and collection, in transportation for logistics, and at biomass conversion facilities for operations and maintenance.
Providing Reliable, Dispatchable Power
Unlike intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind, which only produce power under specific conditions, biomass is dispatchable.
Biomass power plants can operate 24/7, providing a consistent and reliable baseload power to the grid. This makes it an excellent complement to other renewables, ensuring the lights stay on when the sun isn't shining or the wind isn't blowing.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Nuances
To make an informed decision, it's critical to acknowledge that biomass is not a perfect solution. Its benefits come with important considerations.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate
The concept of carbon neutrality is an ideal. In practice, there is a "carbon debt" if, for example, mature forests are harvested for fuel, as it takes decades for new trees to reabsorb that released carbon.
Furthermore, emissions from harvesting, processing, and transporting biomass must be factored into its total carbon footprint. The most sustainable biomass comes from waste streams that require minimal processing and transport.
Land and Water Use Concerns
Large-scale cultivation of dedicated energy crops can compete with food crops for arable land and water resources.
This raises concerns about food security and the ecological impact of converting natural habitats into energy farms. Prioritizing waste-based biomass over dedicated energy crops helps mitigate this issue.
Air Pollutant Emissions
Burning biomass releases air pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), sulfur oxides (SOx), and particulate matter.
While modern biomass plants use advanced filtration and combustion technologies to minimize these emissions, they are not zero-emission at the point of combustion and must be managed carefully to protect air quality.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The suitability of biomass depends entirely on your strategic objectives.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction and circular economy: Biomass is an excellent solution for converting agricultural, forestry, or municipal waste streams into valuable energy.
- If your primary focus is grid stability and energy security: Biomass provides a reliable, dispatchable renewable power source that complements intermittent sources like solar and wind.
- If your primary focus is purely carbon reduction: Evaluate the specific biomass feedstock carefully, as sustainably sourced waste materials offer a much better carbon profile than dedicated energy crops or old-growth forests.
Understanding these core advantages and trade-offs allows you to see biomass not as a silver bullet, but as a powerful tool for a diversified and sustainable energy future.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit | Consideration |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Nature | Uses replenishable organic matter (plants, waste) | Requires sustainable sourcing to avoid resource depletion |
| Carbon Neutrality | Part of the biogenic carbon cycle; doesn't add new CO2 | Carbon debt exists if not sourced sustainably (e.g., old-growth forests) |
| Waste Management | Converts agricultural, forestry, and municipal waste into energy | Prioritizing waste streams minimizes land-use competition |
| Energy Security | Domestic energy source reducing reliance on foreign fuels | Logistics and supply chain efficiency are critical |
| Grid Reliability | Provides dispatchable, baseload power (unlike solar/wind) | Air pollutants (NOx, SOx) must be managed with modern technology |
Ready to harness the power of biomass for your energy or laboratory needs? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for biomass research, analysis, and conversion processes. Whether you're developing new biofuels, analyzing feedstock, or optimizing conversion efficiency, our solutions ensure precision and reliability. Contact us today to learn how we can support your sustainable energy projects!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Battery Lab Equipment Battery Capacity and Comprehensive Tester
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Non Consumable Vacuum Arc Induction Melting Furnace
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What is the function of an in-situ spectro-electrochemical cell? Unlocking Li-CO2 Battery Reaction Insights
- What core data does a multi-channel battery test system monitor? Enhance Zinc Anode Cycling Stability Analysis
- What problems do high-pressure split electrolytic cells address in anode-free batteries? Optimizing Testing Stability
- How does an electrochemical testing system evaluate mesoporous oxide electrodes? Precision Analysis for Battery Research
- What technical support does a multi-channel battery test system provide? Optimize All-Solid-State Battery Performance







