In industrial chemistry, calcination is a foundational thermal process used to induce chemical and physical changes in solid materials. Its most common application is in the manufacturing of cement, where limestone is heated to produce lime (calcium oxide), the primary component of cement. The process is also widely used to remove bound water from materials, drive off volatile substances like carbon dioxide from ores, and alter a material's crystalline structure for specific uses.
Calcination is fundamentally a purification and preparation step. It uses high heat, below a material's melting point, to drive off volatile substances like water and CO₂, fundamentally altering the material's chemical and physical state for a specific industrial purpose.
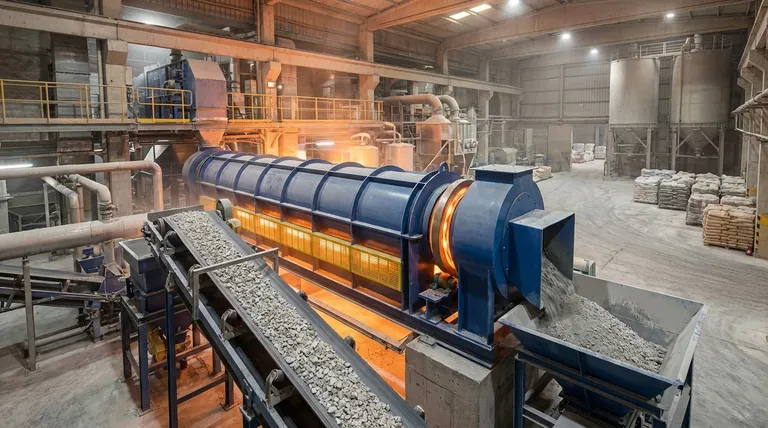

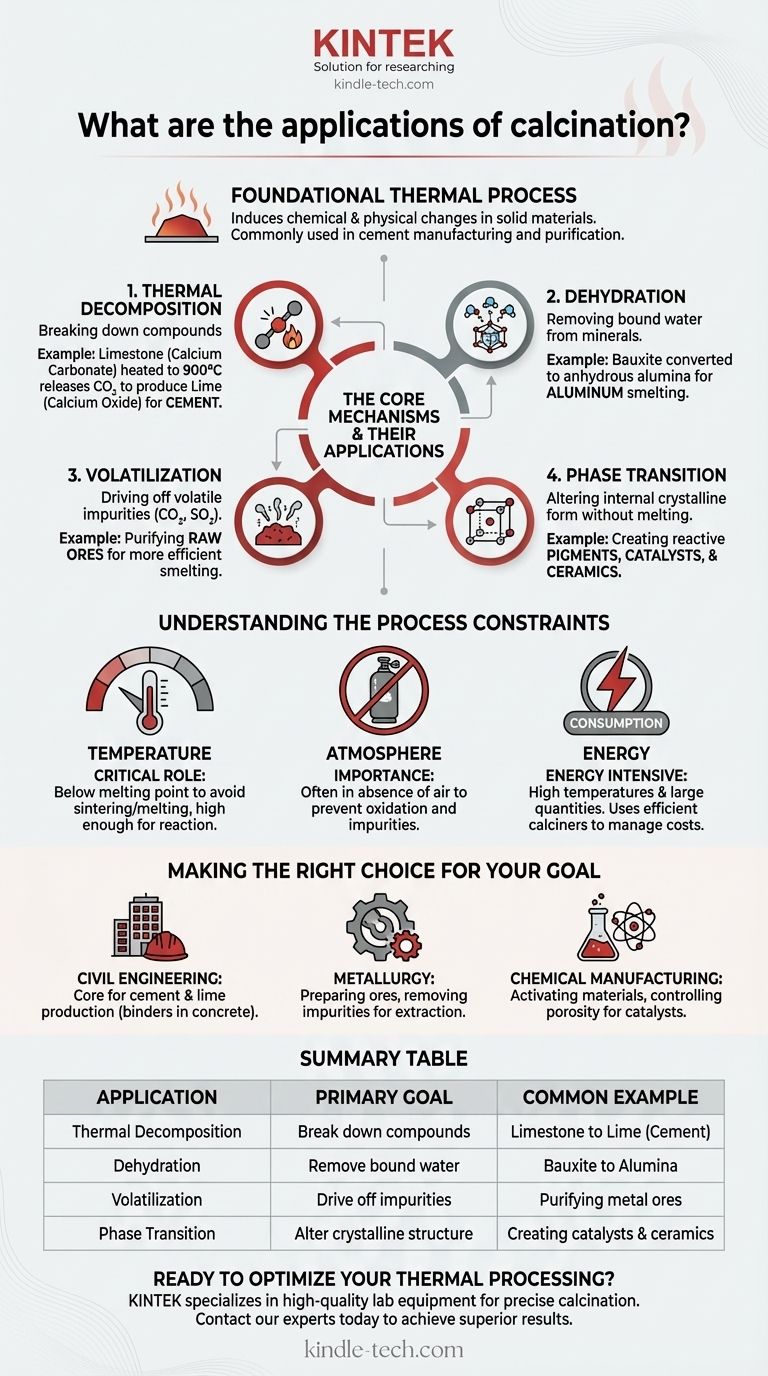
The Core Mechanisms and Their Applications
Calcination is not a single process but a category of thermal treatments. Its applications are best understood by looking at the specific transformation it is designed to achieve.
Thermal Decomposition: Breaking Down Compounds
This is the most significant application of calcination, where heat is used to break a chemical compound into simpler substances.
The quintessential example is the production of lime (calcium oxide) from limestone (calcium carbonate). When heated to around 900°C, the limestone decomposes, releasing carbon dioxide gas and leaving behind lime.
This reaction is the cornerstone of the global cement industry. The resulting lime is the critical binding agent in concrete and mortar.
Dehydration: Removing Bound Water
Many minerals exist as hydrates, meaning water molecules are chemically bound within their crystalline structure.
Calcination provides the energy needed to break these bonds and drive off the water as vapor. This is essential in processes like the production of alumina from bauxite ore, where hydrated aluminum oxide is converted to anhydrous alumina for smelting into aluminum.
Volatilization: Driving Off Impurities
Raw ores and other solid materials often contain volatile impurities that must be removed before further processing.
Calcination heats the material to a temperature where these volatiles (such as carbon dioxide or sulfur dioxide) are driven off as gas. This purifies the material and increases the concentration of the desired element, making subsequent steps like smelting more efficient.
Phase Transition: Altering Crystalline Structure
Heat can be used to change the internal crystalline form (phase) of a material without melting it.
This is a more subtle but critical application. For example, it can be used to convert a material into a more reactive or stable form, which is crucial in the production of pigments, catalysts, and certain ceramics. The final product has the same chemical formula but different physical properties.
Understanding the Process Constraints
The effectiveness of calcination hinges on precise control over its parameters. Mismanaging these variables can lead to an incomplete reaction or a ruined product.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The process temperature must be carefully managed. It needs to be high enough to initiate the desired decomposition or phase change but remain below the material's melting point.
If the temperature is too low, the reaction will be incomplete. If it is too high, the material may melt or sinter (fuse into a solid mass), destroying the desired powdered or porous structure.
The Importance of the Atmosphere
Calcination is typically performed in the absence or with a limited supply of air. This is to prevent unwanted side reactions, most notably oxidation.
In some specific applications, a controlled amount of an oxidizing agent is intentionally introduced. However, for most uses, like lime production, an uncontrolled atmosphere would lead to impurities and a lower-quality product.
Energy Consumption and Throughput
Heating vast quantities of solid material to high temperatures is extremely energy-intensive, representing a significant operational cost for industries like cement manufacturing.
The equipment used, typically a large, rotating cylindrical kiln called a calciner, is designed to maximize heat transfer and material throughput while managing these high energy costs.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The relevance of calcination depends entirely on your industrial context. Its value lies in its ability to prepare a raw solid for its final purpose.
- If your primary focus is civil engineering or construction: You will encounter calcination as the core process for producing cement and lime, the fundamental binders in concrete and mortar.
- If your primary focus is metallurgy or materials science: You will use calcination to prepare ores by removing volatile impurities and water, making downstream extraction processes more efficient.
- If your primary focus is chemical manufacturing: Calcination is key for creating catalysts and desiccants by activating materials and controlling their porosity and crystalline structure through precise heating.
Ultimately, understanding calcination is understanding how to purposefully transform raw solids into refined, functional materials.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Goal | Common Example |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Decomposition | Break down compounds | Limestone to Lime (Cement) |
| Dehydration | Remove bound water | Bauxite to Alumina |
| Volatilization | Drive off impurities | Purifying metal ores |
| Phase Transition | Alter crystalline structure | Creating catalysts & ceramics |
Ready to Optimize Your Thermal Processing?
Calcination is a critical step for achieving the precise material properties required in modern industry. Whether you are developing catalysts, purifying ores, or manufacturing advanced ceramics, the right equipment is fundamental to your success.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for all your thermal processing needs. Our solutions are designed to provide the precise temperature control and atmosphere management essential for effective calcination.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific applications and help you achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the industrial applications of pyrolysis? Transform Waste into Energy and Valuable Products
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What is the purpose of a calciner? Boost Efficiency in High-Temperature Processing
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What equipment is used in pyrolysis? Choosing the Right Reactor for Your Feedstock and Products



















