In essence, compression molding is a foundational process for creating strong, durable, and dimensionally stable parts, particularly from thermoset plastics and composite materials. Its applications span numerous industries, from producing high-performance automotive body panels and aerospace components to everyday items like electrical sockets and kitchenware handles. The process is chosen when material strength, heat resistance, and durability are paramount.
The true value of compression molding lies not just in the parts it creates, but in its unique ability to process high-performance thermoset materials and long-fiber reinforcements. It is the definitive choice when part strength and heat resistance are non-negotiable design requirements.

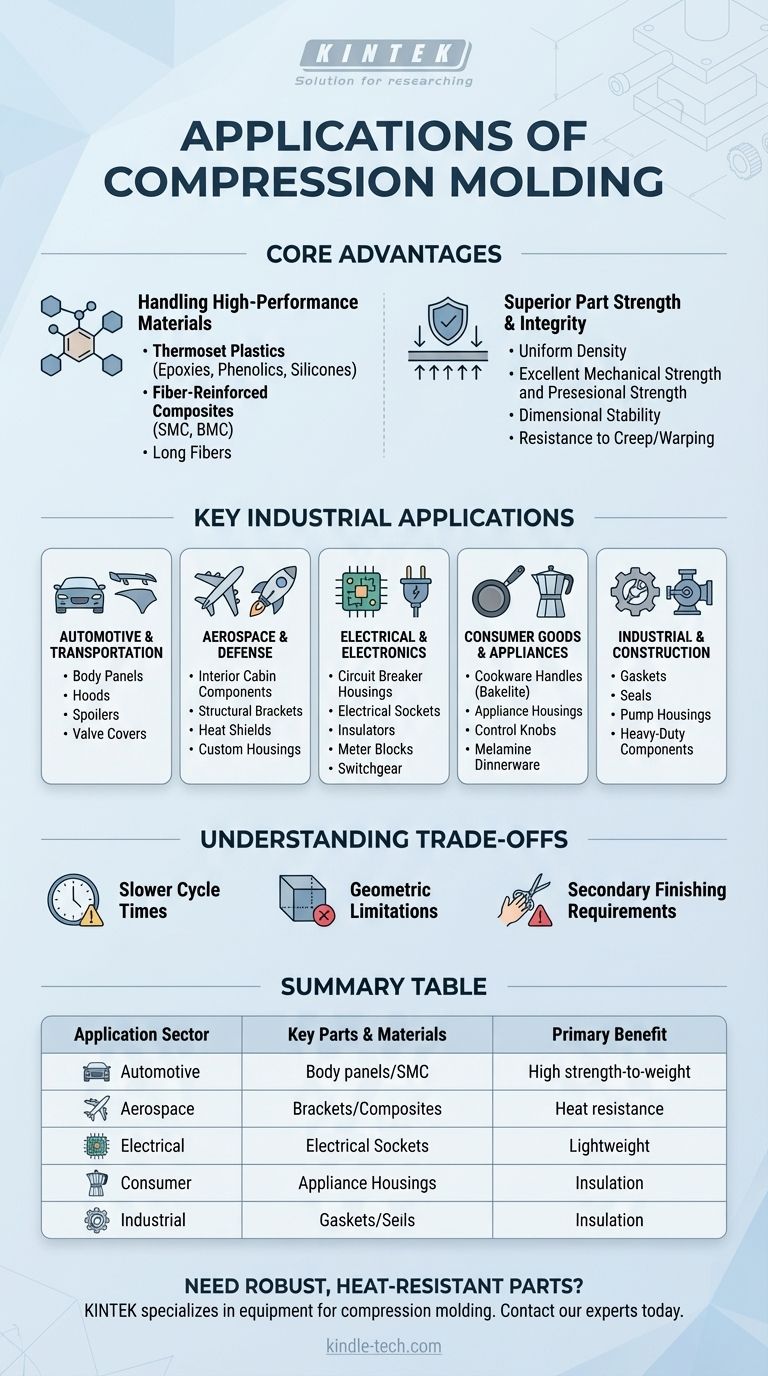
Why Compression Molding is Chosen for Demanding Applications
To understand the applications of compression molding, you must first understand its core advantages. The decision to use this method is almost always driven by material requirements and the desired physical properties of the final part.
Handling High-Performance Materials
Compression molding excels with thermoset plastics like epoxies, phenolics, and silicones. Unlike the thermoplastics used in injection molding, thermosets undergo an irreversible chemical reaction (curing) when heated, forming a strong, cross-linked molecular structure.
This process is also the primary method for molding fiber-reinforced composites, such as Sheet Molding Compound (SMC) and Bulk Molding Compound (BMC). These materials integrate long glass or carbon fibers, which cannot be processed effectively by other molding techniques without damaging the fibers and compromising strength.
Superior Part Strength and Integrity
The high pressure applied during the molding process forces the material into every part of the mold cavity. This ensures a uniform density and minimizes the residual stress common in other processes.
The result is parts with excellent mechanical strength, dimensional stability, and resistance to creep or warping over time, even under significant load or high temperatures.
Cost-Effectiveness for Specific Scales
Tooling for compression molding is often simpler and therefore less expensive than the complex, high-pressure molds required for injection molding.
This makes it an economically viable choice for low-to-medium volume production runs and for manufacturing very large parts (like vehicle hoods or satellite dishes) where injection molding tooling would be prohibitively costly.
Key Industrial Applications in Detail
The unique capabilities of compression molding make it indispensable across several key sectors where performance is critical.
The Automotive and Transportation Sector
This is one of the largest markets for compression molding. It is used to produce parts where a high strength-to-weight ratio is essential for fuel efficiency and performance.
Common applications include body panels, hoods, spoilers, valve covers, and other under-the-hood components that require both structural integrity and heat resistance.
Aerospace and Defense
In aerospace, every gram matters. Compression-molded composites provide the strength of metal at a fraction of the weight.
The process is used for interior cabin components, structural brackets, heat shields, and custom housings for sensitive equipment where dimensional stability under extreme temperature shifts is vital.
Electrical and Electronics
Thermoset materials have outstanding electrical insulating properties and high heat resistance, making them ideal for the electrical industry.
You will find compression-molded parts in circuit breaker housings, electrical sockets, insulators, meter blocks, and switchgear components.
Consumer Goods and Appliances
Many durable consumer goods rely on the heat resistance and sturdiness of compression-molded parts.
Classic examples include cookware handles (Bakelite), appliance housings, control knobs, and famously durable dinnerware made from melamine resin.
Industrial and Construction
For heavy-duty applications, compression molding is used to create robust components that can withstand harsh chemical and physical environments.
This includes industrial gaskets, seals, pump housings, heavy-duty equipment components, and various protective casings.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No manufacturing process is perfect for every situation. Being a trusted advisor means acknowledging the limitations.
Slower Cycle Times
The chemical curing process for thermoset materials takes significantly longer than the simple cooling of thermoplastics in injection molding. This results in longer cycle times, making it less suitable for high-volume, rapid production of small parts.
Geometric Limitations
Compression molding is best suited for parts with relatively simple geometries. Highly intricate features, sharp internal corners, and undercuts can be difficult or impossible to produce effectively without complex and costly mold designs.
Secondary Finishing Requirements
The process creates "flash," which is excess material squeezed out at the mold's parting line. This flash must be manually or automatically trimmed in a secondary operation, adding a step and cost to the production process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Project
Selecting the right manufacturing process depends entirely on your project's core requirements for material, scale, and complexity.
- If your primary focus is maximum strength and heat resistance: Compression molding is the superior choice, especially when designing with high-performance thermoset composites.
- If your primary focus is high-volume production of complex parts: You should investigate injection molding, as its rapid cycle times are purpose-built for mass production.
- If your primary focus is producing very large, strong components cost-effectively: Compression molding offers a significant advantage due to its relatively lower tooling costs for large-scale parts.
By understanding its strengths in material capability and structural integrity, you can leverage compression molding to produce robust parts that other processes simply cannot match.
Summary Table:
| Application Sector | Key Parts & Materials | Primary Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Body panels, hoods, valve covers (SMC) | High strength-to-weight ratio, heat resistance |
| Aerospace & Defense | Structural brackets, heat shields (Composites) | Lightweight, dimensional stability under extreme temps |
| Electrical & Electronics | Circuit breaker housings, sockets (Thermosets) | Excellent electrical insulation, heat resistance |
| Consumer Goods | Cookware handles, appliance housings (BMC, Melamine) | Durability, heat resistance |
| Industrial | Gaskets, seals, pump housings | Robustness for harsh environments |
Need robust, heat-resistant parts for your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing the equipment and expertise for compression molding processes. Whether you're working with high-performance thermoset composites for automotive applications or durable components for consumer goods, we can help you achieve superior part strength and integrity.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can meet your laboratory and production needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Integrated Manual Heated Plates for Lab Use
- Double Plate Heating Press Mold for Lab
- Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates Split Manual Laboratory Hot Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- 24T 30T 60T Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What are filter presses used for? Mastering Solid-Liquid Separation from Lab to Industry
- What is a laboratory press? Achieve Precise Sample Preparation for Reliable Analysis
- What precautions should be taken when using hydraulic forming or cutting equipment to prepare stainless steel corrosion specimens? Ensure Accuracy.
- Why Use a Laboratory Hydraulic Press for LLZTO Ceramic Electrolytes? Achieving High-Density Green Pellets
- What is a wood pellet mill? Turn Waste Biomass into High-Density Fuel
- What is the alternative to XRF? Choose the Right Elemental Analysis for Your Lab
- How hot is too hot for hydraulics? Protect Your System from Costly Heat Damage
- What is the maintenance on a hydraulic press? Ensure Safety and Prevent Costly Downtime



















