At their core, industrial furnaces are used for any process that requires precise, high-temperature heating to fundamentally change a material. Their applications span nearly every manufacturing sector, from melting raw metals and firing ceramics to enabling complex chemical reactions and treating hazardous waste.
An industrial furnace is not simply an oven; it is a highly engineered tool for manipulating matter at a molecular level. The true purpose is to use thermal energy to alter a material's physical properties (like hardness or shape) or its chemical composition.
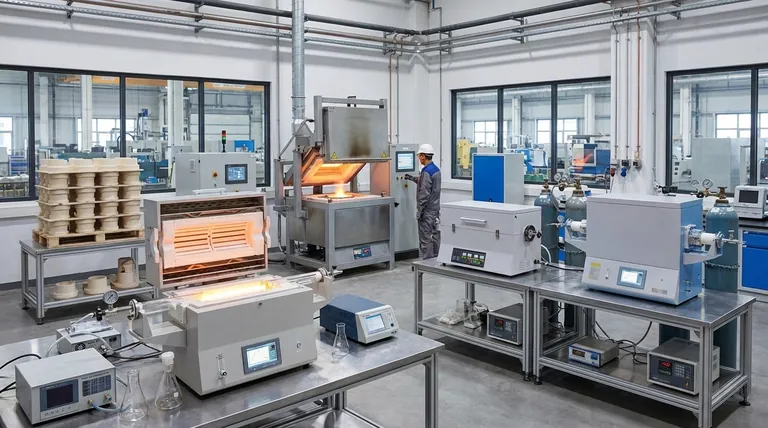

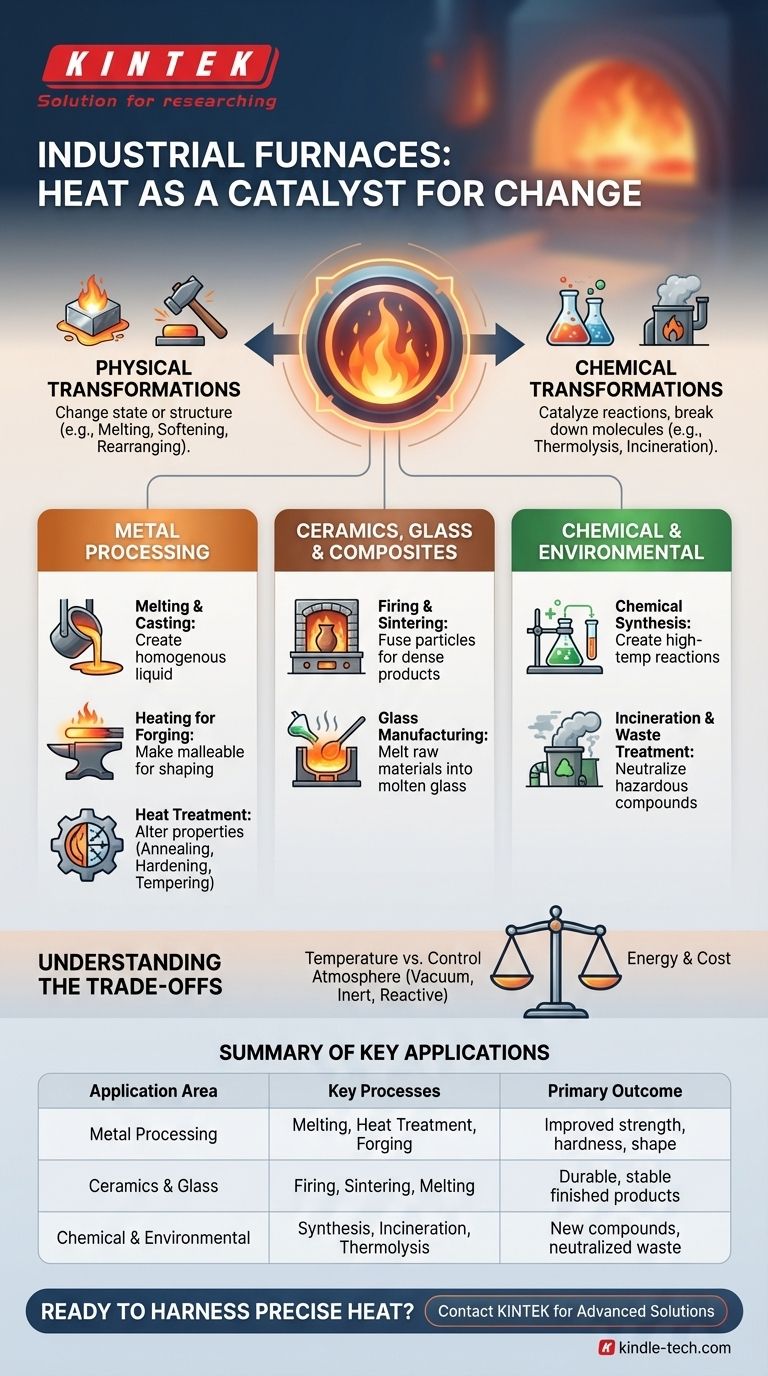
The Principle: Using Heat as a Catalyst for Change
The fundamental job of any furnace is to deliver controlled thermal energy. This energy overcomes the bonds holding a material together, allowing for intentional and predictable transformations.
Physical Transformations
Furnaces provide the energy needed to change a material's physical state or internal structure without altering its chemical makeup. This includes melting a solid into a liquid, softening it for forming, or rearranging its crystalline structure to change its mechanical properties.
Chemical Transformations
Heat also acts as a catalyst for chemical reactions. In a furnace, this can mean breaking down complex molecules (thermolysis), driving impurities out of a substance, or providing the activation energy for new compounds to form.
Core Applications in Metal Processing
The most widely recognized use of industrial furnaces is in metallurgy. Here, heat is used to both create and refine metal products from raw materials.
Melting and Casting
This is the most basic application. Furnaces melt raw materials like scrap metal, ore concentrates, and alloying agents to create a homogenous liquid metal. This molten metal is then poured into molds to create parts in a process called casting.
Heating for Forging and Forming
To make metals like steel or aluminum easier to shape, they are heated to a specific temperature range where they become plastic and malleable. This allows them to be forged, rolled, or extruded into desired shapes with less force and without cracking.
Heat Treatment for Performance
This is a more subtle but critical application. Heat treatment uses carefully controlled heating and cooling cycles to alter a metal's internal microstructure, thereby changing its mechanical properties. Key processes include:
- Annealing: Softens metal to make it more ductile and easier to work with.
- Hardening: Heats and then rapidly cools (quenches) steel to increase its hardness and wear resistance.
- Tempering: A secondary, lower-temperature heating process that reduces the brittleness of hardened steel, increasing its toughness.
Beyond Metals: Ceramics, Glass, and Composites
Furnace technology is equally essential for non-metallic materials, where heat is used to create durable, finished products from raw powders or mixtures.
Firing and Sintering Ceramics
Raw ceramic materials, like clay or advanced technical ceramics, are heated in a furnace in a process called firing or sintering. The heat fuses the individual particles together, driving out water and creating a dense, hard, and stable final product.
Glass Manufacturing
The production of glass begins in a furnace. Raw materials, primarily silica sand, soda ash, and limestone, are melted together at extremely high temperatures to form molten glass. This liquid can then be molded, blown, or floated into sheets.
Enabling Chemical and Environmental Processes
Furnaces also serve as contained reactors for chemical and environmental applications, using heat to drive specific reactions or destroy unwanted materials.
Chemical Synthesis
As seen in specialized laboratory and industrial settings, furnaces can create the high-temperature environment needed for certain chemical reactions. Processes like thermolysis use heat to break down compounds into simpler substances, such as in the preparation of ketenes for organic synthesis.
Incineration and Waste Treatment
High-temperature furnaces are a primary method for the safe disposal of hazardous waste. The extreme heat breaks down toxic organic compounds into less harmful substances like carbon dioxide and water, effectively neutralizing them and reducing waste volume.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing or operating a furnace involves balancing competing priorities. The "best" furnace is determined by the specific requirements of the process.
Temperature vs. Control
Reaching ultra-high temperatures often comes at the expense of precise control. A melting furnace is optimized for maximum heat input, while a heat-treating furnace is designed for extremely precise temperature ramps and holds, even if its maximum temperature is lower.
Atmosphere Control
The gas inside the furnace chamber is a critical variable. Some processes require a vacuum or an inert gas (like argon) to prevent oxidation. Others use reactive atmospheres to intentionally cause a surface reaction, like in carburizing, where carbon is diffused into the surface of steel to harden it.
Energy Consumption and Cost
Furnaces are significant energy consumers, making operational cost a major factor. The choice between electric, gas, or induction heating depends on utility costs, process requirements for speed and control, and environmental regulations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The application dictates the technology. To determine the right process, identify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is changing a material's shape: You need a process like melting for casting or high-temperature heating for forging.
- If your primary focus is improving a material's intrinsic properties: You require a precise heat treatment process like annealing, hardening, or tempering.
- If your primary focus is creating a new chemical substance or destroying an old one: Your application involves chemical synthesis or high-temperature incineration.
Ultimately, the industrial furnace is one of the foundational tools that enables the conversion of raw resources into the finished, high-performance materials that define our modern world.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Processes | Primary Material Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Metal Processing | Melting, Heat Treatment, Forging | Improved strength, hardness, shape |
| Ceramics & Glass | Firing, Sintering, Melting | Durable, stable finished products |
| Chemical & Environmental | Synthesis, Incineration, Thermolysis | New compounds, neutralized waste |
Ready to harness the power of industrial furnaces for your manufacturing needs? KINTEK specializes in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including industrial furnaces tailored for precise temperature control and process efficiency. Whether you're in metalworking, ceramics, or chemical processing, our solutions are designed to enhance your material transformations and boost productivity. Contact us today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and industrial heating requirements!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
People Also Ask
- How do I choose a tube furnace? A Guide to Matching Your Process Needs
- Why is an Alumina Ceramic Tube Support Necessary for 1100°C Experiments? Ensure Data Accuracy and Chemical Inertness
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What is the pressure on a tube furnace? Essential Safety Limits for Your Lab
- How does a tube furnace work? Master Precise Thermal and Atmospheric Control



















