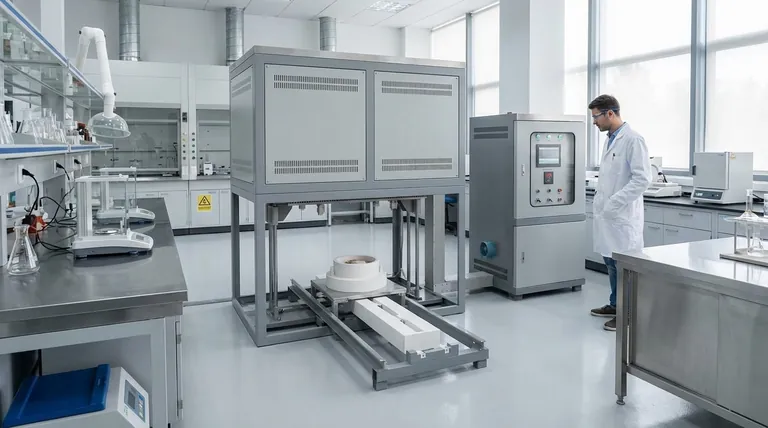
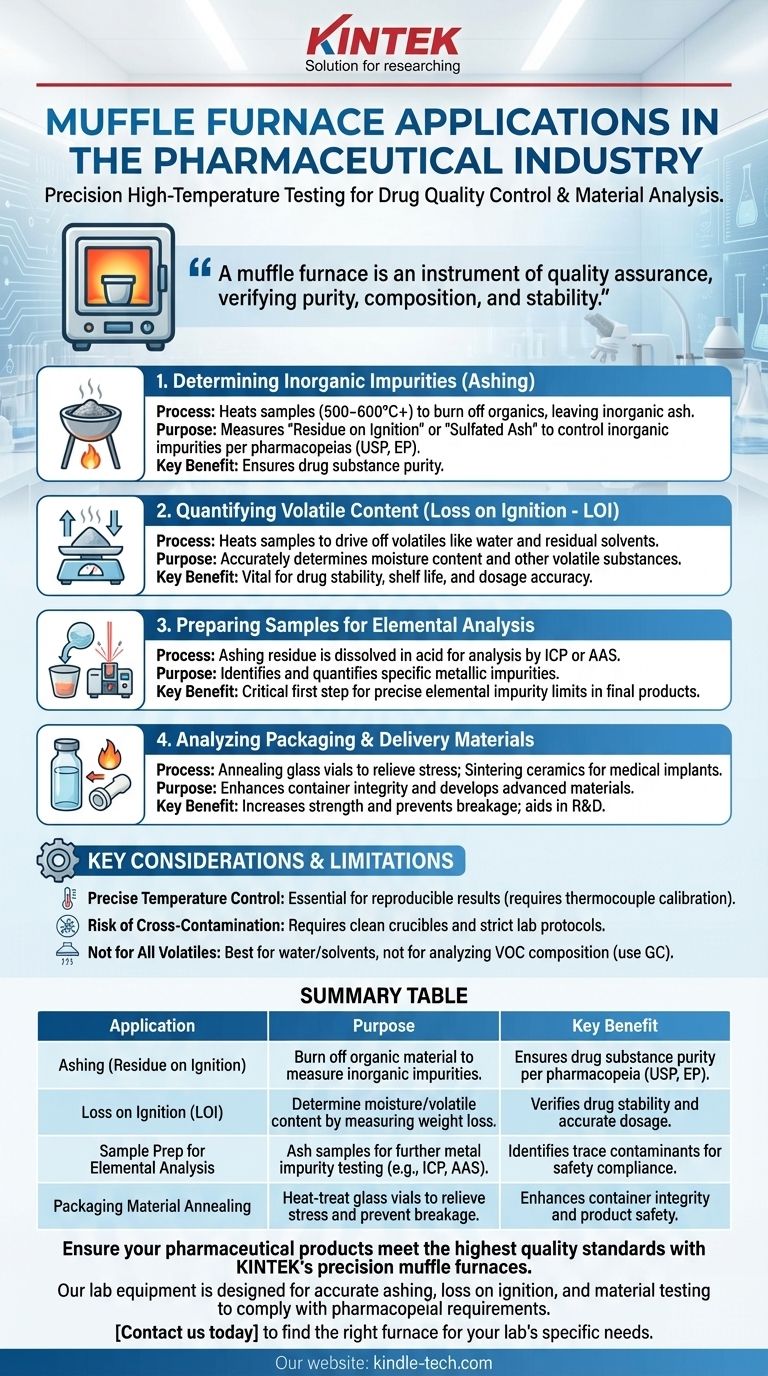
In the pharmaceutical industry, a muffle furnace is a fundamental tool used for high-temperature testing that is critical for drug quality control and material analysis. Its primary applications involve the pretreatment of medical and drug samples to perform essential tests like ashing, which determines the total amount of inorganic impurities in a substance.
A muffle furnace is not just a high-temperature oven; in pharmaceuticals, it is an instrument of quality assurance. It enables chemists and technicians to verify the purity, composition, and stability of drug substances and packaging materials by thermally decomposing samples under controlled conditions.

The Role of High-Temperature Testing in Pharma
The core function of a muffle furnace in a pharmaceutical setting is to provide a precise, high-temperature environment free from contaminants. This capability is essential for several analytical tests mandated by regulatory bodies to ensure drug safety and efficacy.
Determining Inorganic Impurities (Ashing)
One of the most common applications is ashing. This process involves heating a sample to a high temperature, typically 500-600°C or higher, to burn off all organic material.
What remains is the ash, which consists of non-volatile inorganic compounds. The weight of this residue is a critical measure of the purity of a drug substance or excipient.
This procedure is often referred to as "Residue on Ignition" or "Sulfated Ash" testing and is a standard requirement in most pharmacopeias (e.g., USP, EP) to control the level of inorganic impurities.
Quantifying Volatile Content (Loss on Ignition)
A related application is Loss on Ignition (LOI). In this test, a sample is heated to a specific temperature to drive off volatile components, such as water or residual solvents.
By measuring the weight loss of the sample, analysts can accurately determine its moisture content or the amount of other volatile substances. This is vital for ensuring drug stability and dosage accuracy.
Preparing Samples for Elemental Analysis
After ashing, the inorganic residue can be dissolved in acid and further analyzed using techniques like Atomic Absorption Spectroscopy (AAS) or Inductively Coupled Plasma (ICP).
This allows for the precise identification and quantification of specific metallic impurities, which are often strictly limited in final drug products. The muffle furnace serves as the crucial first step in this analytical workflow.
Analyzing Packaging and Delivery Materials
The furnace's role extends beyond the drug itself to its packaging. For instance, annealing glass vials or containers at controlled high temperatures helps relieve internal stresses, increasing their strength and preventing breakage.
It can also be used in the research and development of novel materials, such as the sintering of ceramics for use in medical implants or advanced drug delivery systems.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While invaluable, a muffle furnace must be operated with a clear understanding of its requirements and limitations, especially within a regulated pharmaceutical environment (GMP).
The Need for Precise Temperature Control
Accurate and repeatable results depend entirely on the furnace's ability to maintain a uniform and stable temperature. Any deviation can lead to incomplete combustion or sample degradation, invalidating the test.
Thermocouple calibration and regular furnace validation are therefore non-negotiable procedures in a pharmaceutical quality control lab.
Risk of Cross-Contamination
Because testing often involves trace amounts of residue, preventing cross-contamination between samples is paramount.
This requires using scrupulously clean crucibles (often ceramic or platinum) and maintaining strict laboratory protocols to ensure the integrity of each analysis.
Not Suitable for All Volatiles
While excellent for water and some solvents, a muffle furnace is not designed to analyze the specific composition of volatile organic compounds. For that, techniques like Gas Chromatography (GC) are used. The furnace's role is simply to remove them.
Applying This to Your Objective
Your choice of application will depend entirely on your specific analytical goal.
- If your primary focus is drug substance purity: Your key application will be ashing (Residue on Ignition) to quantify total inorganic impurities according to pharmacopeial standards.
- If your primary focus is material stability and composition: Your key application will be Loss on Ignition (LOI) to determine moisture and volatile content, which directly impacts shelf life and dosage.
- If your primary focus is container or device integrity: Your key applications will be annealing for stress-relieving glass or sintering for developing new ceramic-based medical materials.
Ultimately, the muffle furnace serves as a gatekeeper for quality, ensuring that pharmaceutical products are free from harmful impurities and perform as expected.
Summary Table:
| Application | Purpose | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Ashing (Residue on Ignition) | Burn off organic material to measure inorganic impurities. | Ensures drug substance purity per pharmacopeia (USP, EP). |
| Loss on Ignition (LOI) | Determine moisture/volatile content by measuring weight loss. | Verifies drug stability and accurate dosage. |
| Sample Prep for Elemental Analysis | Ash samples for further metal impurity testing (e.g., ICP, AAS). | Identifies trace contaminants for safety compliance. |
| Packaging Material Annealing | Heat-treat glass vials to relieve stress and prevent breakage. | Enhances container integrity and product safety. |
Ensure your pharmaceutical products meet the highest quality standards with KINTEK's precision muffle furnaces.
Our lab equipment is designed for accurate ashing, loss on ignition, and material testing—helping you comply with pharmacopeial requirements (USP, EP) and maintain drug purity.
Contact us today to find the right furnace for your lab's specific needs in drug quality control and material analysis.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What controls melting point? The Hierarchy of Forces from Ionic Bonds to Intermolecular Attractions
- How is melting point affected by heating rate? Avoid Inaccurate Measurements in Your Lab
- What is the principle working and use of muffle furnace? Achieve Precise, Contamination-Free Heating
- Why is the melting point different for different substances? The Key Role of Bond Strength
- What is the theory of muffle furnace? Achieve Pure, Controlled High-Temperature Processing



















