Radioactive substances are fundamental tools in modern science and industry, with applications ranging from medical diagnostics and cancer treatment to energy production, food safety, and archaeological dating. Their utility comes from the predictable and detectable energy they release as they decay.
The power of radioactive substances lies in their unique properties: their emitted radiation can be used as a tracer to "see" inside systems, as a tool to sterilize or destroy targeted cells, and as an immense source of energy, while their predictable rate of decay serves as a natural clock for measuring time.

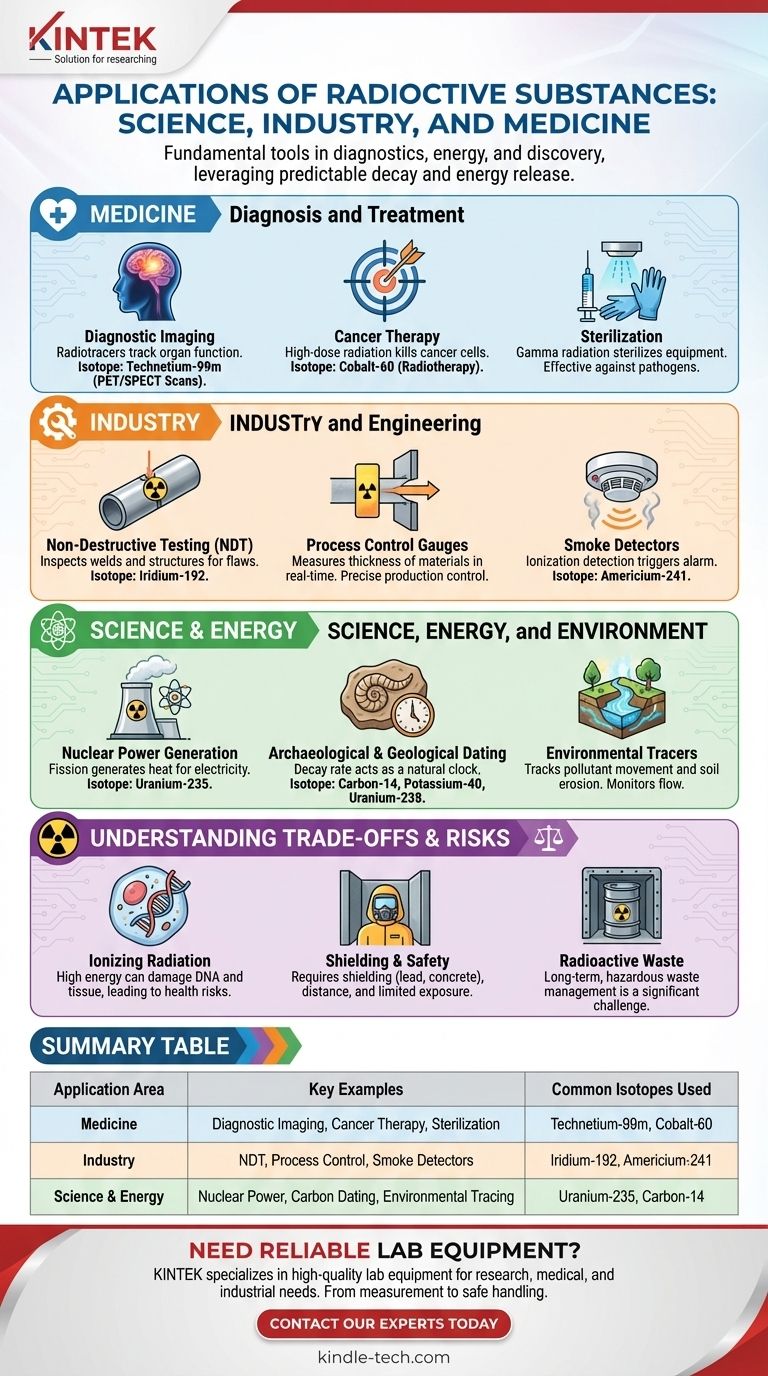
Medicine: Diagnosis and Treatment
The most well-known applications of radioactivity are often in the medical field, where it is used to both diagnose and combat disease. The key is using specific isotopes with properties tailored to the task.
Diagnostic Imaging
Radioactive tracers, or radiopharmaceuticals, are compounds that include a radioactive isotope. These are introduced into the body, and their movement is tracked by a detector, like a PET or SPECT scanner.
Because different chemical compounds concentrate in different parts of the body, doctors can "tag" a specific compound to see how an organ is functioning. For example, Technetium-99m is a common isotope used for imaging the brain, bones, and other organs.
Cancer Therapy (Radiotherapy)
While diagnostic uses involve very low doses of radiation, therapeutic uses involve high doses. The goal of radiotherapy is to use high-energy radiation to damage the DNA of cancer cells, killing them or stopping their growth.
This is often done using a focused external beam from a source like Cobalt-60. The energy is carefully targeted at the tumor to minimize damage to surrounding healthy tissue.
Sterilization of Medical Equipment
Gamma radiation is extremely effective at killing bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. This makes it an ideal method for sterilizing heat-sensitive medical equipment like syringes, surgical gloves, and implants after they have been packaged.
Industry and Engineering
In industrial settings, radioactive sources provide a reliable way to inspect, measure, and control processes without physical contact.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
Industrial radiography functions much like a medical X-ray but for materials. A gamma radiation source, such as Iridium-192, is used to inspect welds, pipes, and structural components for hidden cracks or flaws.
The radiation passes through the object and creates an image on a film, revealing internal defects that would otherwise be invisible.
Process Control Gauges
Radioactive sources are used in manufacturing to measure the thickness of materials like paper, plastic film, or sheet metal. A source is placed on one side and a detector on the other.
The amount of radiation that passes through is inversely proportional to the material's thickness, allowing for precise, real-time adjustments to the production process.
Smoke Detectors
One of the most common household applications is in ionization-type smoke detectors. These contain a tiny amount of Americium-241, an alpha-particle emitter.
The alpha particles ionize the air in a small chamber, creating a steady electrical current. When smoke particles enter the chamber, they disrupt this current, which triggers the alarm.
Science, Energy, and Environment
From powering cities to uncovering the history of ancient artifacts, radioactivity is a critical tool for discovery and innovation.
Nuclear Power Generation
Nuclear reactors use the process of fission, most commonly of Uranium-235. When a U-235 atom is struck by a neutron, it splits, releasing an immense amount of energy (as heat) and more neutrons.
This creates a controlled chain reaction that generates heat. The heat is used to boil water, creating steam that turns turbines to produce electricity without releasing greenhouse gases.
Archaeological and Geological Dating
The constant, predictable decay rate (half-life) of radioactive isotopes makes them perfect clocks. Carbon-14 dating is used to determine the age of organic materials (like wood or bone) up to about 50,000 years old.
For dating rocks and determining the age of the Earth, scientists use isotopes with much longer half-lives, such as Potassium-40 or Uranium-238.
Environmental Tracers
Scientists can use specific isotopes to track the movement of substances through the environment. For example, radioactive tracers can be used to monitor the flow of pollutants in groundwater or to study the rate of soil erosion.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Risks
The same energy that makes radioactive substances useful also makes them hazardous if not handled correctly. This is the central trade-off of nuclear technology.
The Nature of Ionizing Radiation
The radiation emitted—alpha particles, beta particles, and gamma rays—is "ionizing," meaning it has enough energy to knock electrons out of atoms and molecules. In living tissue, this can damage DNA and lead to health risks, including cancer.
Shielding and Safe Handling
Because of this risk, the use of radioactive materials is highly regulated. Safe handling requires appropriate shielding (like lead or concrete), distance from the source, and limiting the time of exposure.
Radioactive Waste
A significant challenge, particularly for the nuclear power industry, is the management of radioactive waste. Spent nuclear fuel remains hazardous for thousands of years and must be securely stored in deep geological repositories to isolate it from the environment.
How to Apply This Knowledge
Understanding the diverse applications of radioactivity becomes simpler when you connect them to the core properties of the isotopes being used.
- If your primary goal is imaging or tracing: You are leveraging the penetrating power and detectability of radiation to "see" inside an object or system, from medical scans to industrial inspections.
- If your primary goal is destruction or sterilization: You are using the destructive, ionizing energy of high-dose radiation to kill targeted cells or microorganisms, as in cancer therapy or equipment sterilization.
- If your primary goal is measurement over time: You are relying on the predictable decay rate (half-life) of an isotope, using it as a clock for applications like carbon dating and geological studies.
- If your primary goal is generating massive amounts of energy: You are harnessing the incredible power released during nuclear fission in a controlled chain reaction for electricity generation.
By grasping these fundamental principles, you can see the common scientific thread that connects this wide array of powerful and transformative technologies.
Summary Table:
| Application Area | Key Examples | Common Isotopes Used |
|---|---|---|
| Medicine | Diagnostic Imaging, Cancer Therapy, Sterilization | Technetium-99m, Cobalt-60 |
| Industry | Non-Destructive Testing, Process Control, Smoke Detectors | Iridium-192, Americium-241 |
| Science & Energy | Nuclear Power, Carbon Dating, Environmental Tracing | Uranium-235, Carbon-14 |
Need reliable lab equipment for working with radioactive materials or other scientific applications? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your research, medical, or industrial needs. From precise measurement tools to safe handling equipment, we ensure your laboratory operates efficiently and safely. Contact our experts today to find the perfect solutions for your laboratory's challenges!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Optical Window Glass Substrate Wafer Barium Fluoride BaF2 Substrate Window
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Evaporation
- Optical Ultra-Clear Glass Sheet for Laboratory K9 B270 BK7
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
People Also Ask
- What are the factors affecting optical properties? Master the Atomic and Microstructural Influences
- What is the alternative to KBr in IR? Choosing the Right Sample Matrix for Accurate Spectroscopy
- Why you should avoid water contamination when performing FTIR measurements using NaCl or KBr plates? Protect Your Equipment & Data Integrity
- How does concentration affect IR? Master Quantitative Analysis and Spectral Interpretation
- Why is KBr used for IR? Create Transparent Pellets for Accurate Solid Sample Analysis










