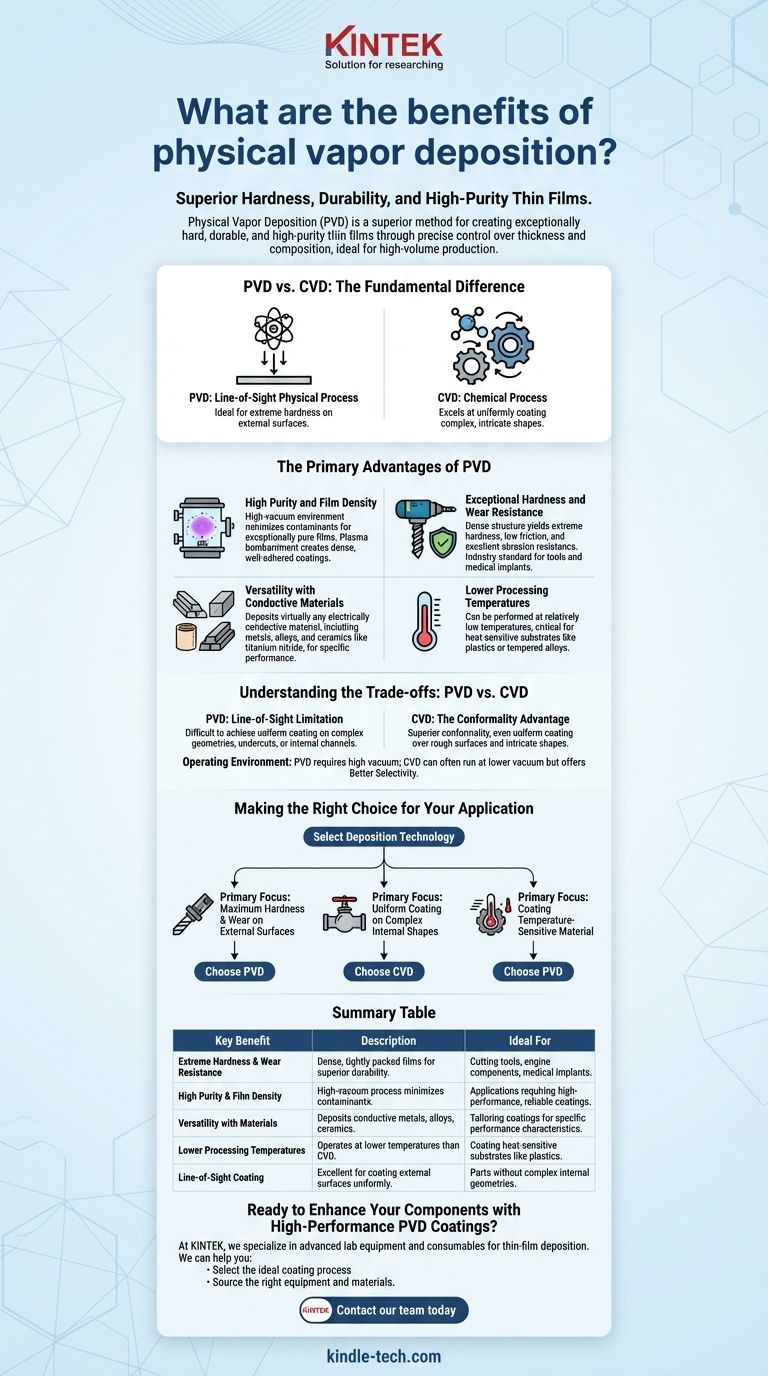
At its core, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is a superior method for creating exceptionally hard, durable, and high-purity thin films. The process excels due to its precise control over film thickness and composition, making it highly efficient for high-volume production of performance-critical coatings on a wide range of materials.
While both PVD and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) create powerful thin-film coatings, the fundamental difference lies in their application method. PVD is a line-of-sight physical process, making it ideal for extreme hardness on external surfaces, whereas CVD is a chemical process that excels at uniformly coating complex, intricate shapes.

The Primary Advantages of PVD
Physical Vapor Deposition encompasses several methods, like sputtering and arc deposition, that physically transfer material from a source onto a substrate in a vacuum. This physical mechanism is the source of its key benefits.
High Purity and Film Density
PVD processes occur in a high vacuum, which minimizes the inclusion of contaminants and results in exceptionally pure films. Techniques like cathodic arc deposition use plasma to ionize the coating material, accelerating it toward the substrate with high energy. This bombardment creates coatings that are extremely dense and well-adhered.
Exceptional Hardness and Wear Resistance
The dense, tightly packed structure of PVD coatings translates directly into superior performance. These films are known for their extreme hardness, excellent abrasion resistance, and low friction, making them the industry standard for cutting tools, engine components, and medical implants.
Versatility with Conductive Materials
A significant advantage of many PVD methods is the ability to deposit virtually any electrically conductive material, including metals, alloys, and ceramics like titanium nitride. This gives engineers a vast palette of materials to choose from to achieve specific performance characteristics.
Lower Processing Temperatures
Compared to many high-temperature CVD processes, PVD can be performed at relatively low temperatures. This is a critical advantage when coating substrates that are sensitive to heat, such as plastics, certain metal alloys, or components with precise tempering.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PVD vs. CVD
To truly understand PVD's benefits, you must compare it to its primary alternative, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD). The choice between them depends entirely on the application's geometry and performance needs.
The Line-of-Sight Limitation
PVD is a line-of-sight process. The coating material travels in a straight line from the source to the substrate. This makes it perfect for coating external surfaces but makes it difficult to achieve a uniform coating on parts with complex geometries, undercuts, or internal channels.
The CVD Conformality Advantage
CVD, by contrast, uses precursor gases that react chemically on the substrate's surface. Because the gas can flow into and around complex features, CVD offers superior conformality, meaning it provides an even, uniform coating over rough surfaces and intricate shapes.
Operating Environment and Selectivity
PVD requires a high-vacuum environment to operate effectively, which can add to equipment complexity. CVD can often run at lower vacuum levels. Furthermore, because CVD is based on chemical reactions, it can sometimes offer better selectivity, depositing material only on specific regions of a substrate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct deposition technology requires a clear understanding of your end goal.
- If your primary focus is maximum hardness and wear resistance on external surfaces: PVD is almost always the superior choice for applications like cutting tools, drills, and decorative finishes.
- If your primary focus is uniform coating on complex internal shapes: CVD's non-line-of-sight nature makes it the definitive solution for parts like valves, pipes, or intricate machinery components.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material: PVD's lower processing temperature provides a significant advantage and prevents damage to the underlying substrate.
Ultimately, choosing the right method is about matching the unique physical or chemical strengths of the process to your specific material, geometry, and performance requirements.
Summary Table:
| Key Benefit | Description | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Extreme Hardness & Wear Resistance | Creates dense, tightly packed films for superior durability. | Cutting tools, engine components, medical implants. |
| High Purity & Film Density | High-vacuum process minimizes contaminants for pure, well-adhered coatings. | Applications requiring high-performance, reliable coatings. |
| Versatility with Materials | Can deposit a wide range of electrically conductive metals, alloys, and ceramics. | Tailoring coatings for specific performance characteristics. |
| Lower Processing Temperatures | Operates at lower temperatures than many CVD processes. | Coating heat-sensitive substrates like plastics or certain metal alloys. |
| Line-of-Sight Coating | Excellent for coating external surfaces uniformly. | Parts without complex internal geometries or deep undercuts. |
Ready to Enhance Your Components with High-Performance PVD Coatings?
Choosing the right coating technology is critical for the performance and longevity of your parts. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced lab equipment and consumables, including solutions for thin-film deposition.
We can help you:
- Select the ideal coating process (PVD, CVD, or other methods) for your specific material, geometry, and performance requirements.
- Source the right equipment and materials to achieve superior hardness, wear resistance, and purity in your lab or production facility.
Let our expertise in laboratory needs guide you to the optimal solution. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your project and deliver the durable, high-quality coatings your work demands.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- How does plasma vapor deposition work? A Low-Temperature Coating Solution for Sensitive Materials
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is plasma enhanced? A Guide to Low-Temperature, High-Precision Manufacturing



















