The primary challenges in using carbon nanotubes (CNTs) for biomedical applications center on their potential toxicity, poor solubility in biological systems, and the uncertainty of their long-term fate within the body. These hurdles stem directly from their unique physical and chemical properties, such as their needle-like shape, inherent water-repellence, and biopersistence.
While carbon nanotubes offer revolutionary potential for applications like targeted drug delivery and advanced diagnostics, their inherent material properties create significant biocompatibility and safety obstacles that must be systematically addressed before they can be considered for widespread clinical use.
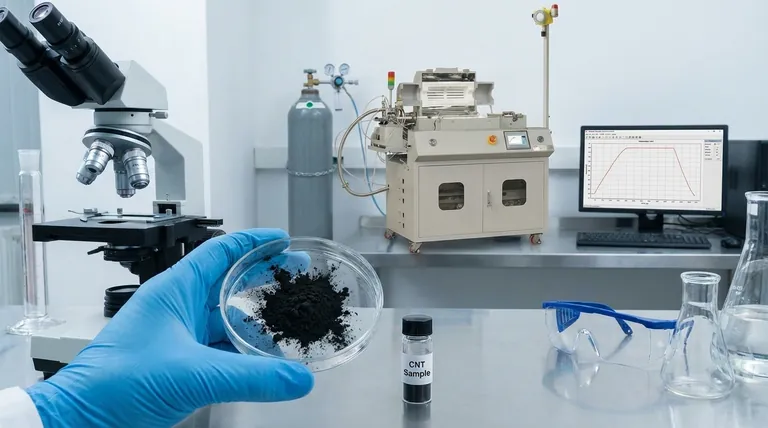

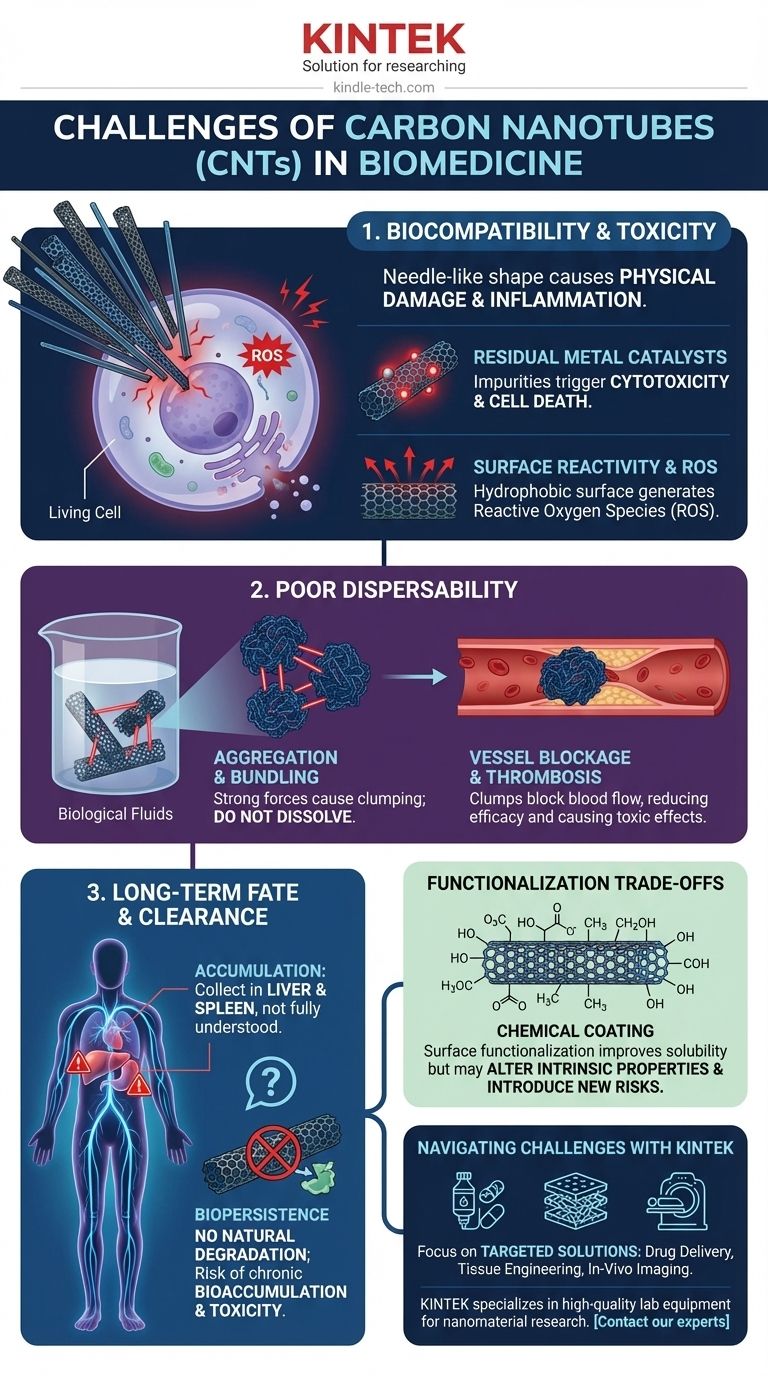
The Core Challenge: Biocompatibility and Toxicity
The interaction between a nanotube and a living cell is complex and fraught with potential risks. The very features that make CNTs unique also make them potentially harmful if not properly controlled.
The Problem of Shape and Size
The high aspect ratio (long and thin) of many CNTs gives them a fiber-like or needle-like structure. This can lead to physical damage, where the nanotubes pierce cell membranes, disrupting cellular function and potentially causing inflammatory responses similar to those seen with asbestos fibers.
Impurities from Synthesis
The processes used to manufacture CNTs often rely on residual metal catalysts, such as iron, nickel, or cobalt. If not meticulously removed, these metallic impurities can leach out and are a primary source of cytotoxicity, triggering cell death through oxidative stress.
Surface Chemistry and Reactivity
Pristine, unmodified carbon nanotubes are hydrophobic, meaning they repel water. When introduced into the aqueous environment of the body, they can trigger the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), a key driver of cellular damage and inflammation.
The Practical Hurdle: Poor Dispersibility
Before a CNT can perform its function, it must be able to travel through the body effectively. Its natural tendency to clump together in liquids is a major barrier.
Aggregation in Biological Fluids
Due to powerful intermolecular (van der Waals) forces, CNTs have an extremely strong tendency to bundle and agglomerate in water-based solutions like blood or saline. They do not dissolve or disperse easily.
Impact on Efficacy and Safety
These large aggregates are not useful for targeted applications at a cellular level. More dangerously, they can become trapped in and block small blood vessels, potentially leading to thrombosis or accumulating in organs like the lungs, liver, and spleen, where they can cause toxic effects.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Functionalization
The most common solution to the problems of toxicity and dispersibility is surface functionalization—chemically attaching other molecules to the surface of the CNT. However, this solution introduces its own set of complexities.
Solving One Problem, Creating Another
Functionalization makes CNTs water-soluble and can reduce their toxicity. However, the process can also alter the desirable intrinsic properties of the nanotube, such as its electrical conductivity or mechanical strength, which may have been the original reason for its selection.
Unpredictable Biological Interactions
The body no longer interacts with the carbon nanotube itself, but with the chemical coating on its surface. This new surface can have its own unforeseen toxicological profile or trigger an immune response, requiring a completely new round of safety and biocompatibility testing.
The Long-Term Question: Biodistribution and Clearance
Perhaps the greatest unknown is what happens to carbon nanotubes inside the body over months or years. This uncertainty is a major obstacle to regulatory approval and clinical adoption.
Where Do They Go?
Once administered, it is difficult to fully track where CNTs accumulate. Studies show they often collect in the organs of the reticuloendothelial system, primarily the liver and spleen, but their precise long-term distribution is not fully understood.
How Do They Leave?
The human body has no natural enzymes or metabolic pathways to degrade or break down carbon nanotubes. Their biopersistence raises serious concerns about long-term bioaccumulation and the potential for chronic, low-level toxicity that may only become apparent after many years.
Navigating CNT Challenges in Your Research
To move forward, research must be targeted at solving these specific challenges based on the intended application.
- If your primary focus is drug delivery: Prioritize developing stable surface functionalization methods that prevent aggregation in blood and minimize recognition by the immune system.
- If your primary focus is tissue engineering: Concentrate on rigorous purification techniques to eliminate catalytic impurities and conduct long-term studies on local inflammation and material degradation.
- If your primary focus is in-vivo imaging: Your first priority must be to clearly characterize the biodistribution, accumulation, and clearance pathways for your specific CNT formulation.
Successfully harnessing the power of carbon nanotubes in biomedicine depends entirely on meticulously engineering solutions to these fundamental safety and stability challenges.
Summary Table:
| Challenge | Key Issue | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Biocompatibility & Toxicity | Needle-like shape, residual metal catalysts, reactive surface | Cell damage, inflammation, cytotoxicity |
| Poor Dispersibility | Hydrophobicity and strong aggregation in fluids | Reduced efficacy, potential vessel blockage |
| Functionalization Trade-offs | Coating alters intrinsic properties, creates new biological interactions | Unpredictable safety profile, loss of desired functionality |
| Long-Term Fate | Biopersistence, accumulation in organs (e.g., liver, spleen), lack of degradation pathways | Chronic toxicity risks, regulatory hurdles |
Ready to overcome the challenges of advanced materials in your lab? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment and consumables to support your research into nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes. Whether you need precise synthesis tools, purification systems, or analytical instruments to characterize material safety and performance, we have the solutions to help you navigate complex biomedical applications.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can equip your laboratory for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What function does CVD equipment serve in rhodium-modified coatings? Achieve Deep Diffusion and Microstructural Precision
- What is the floating catalyst method? A Guide to High-Yield CNT Production
- What are the main advantages of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)? Achieve Precision Coating for Complex Geometries
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit
- Why are carbon nanotubes important in industry? Unlocking Next-Generation Material Performance



















