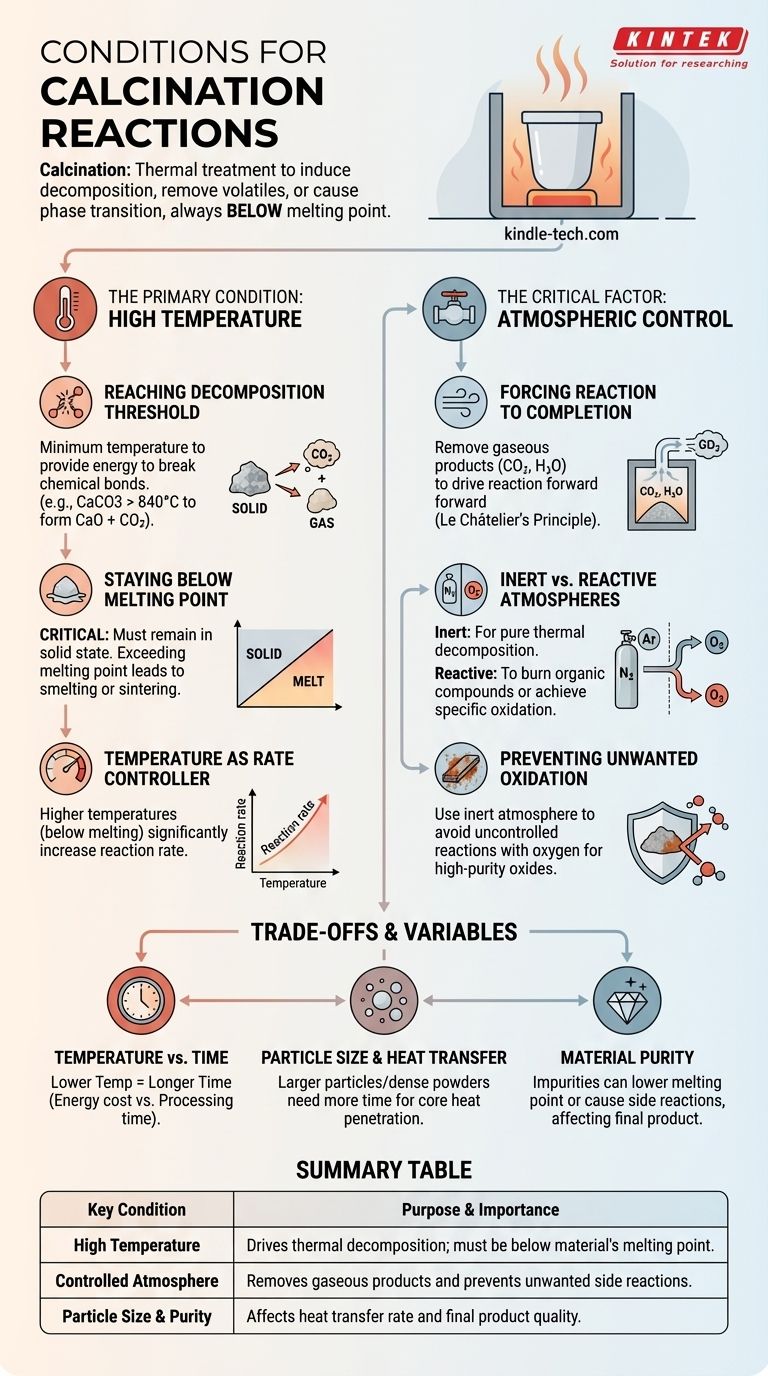
Calcination reactions are driven by high temperatures, typically below a material's melting point, and are conducted within a specifically controlled atmosphere. The goal is to induce thermal decomposition, remove volatile substances, or trigger a phase transition in a solid material without melting it.
Calcination is fundamentally a thermal treatment process where high heat is applied to a solid to achieve a specific chemical or physical change. Success depends not just on reaching a target temperature, but on precisely controlling the surrounding atmosphere to drive the desired reaction and prevent unwanted side effects.

The Primary Condition: High Temperature
The application of heat is the most fundamental condition for calcination. However, the specific temperature range is critical and is governed by two opposing constraints.
Reaching the Decomposition Threshold
Every calcination reaction has a minimum temperature required to provide the energy needed to break chemical bonds. For example, calcium carbonate (limestone) must be heated to above 840°C (1544°F) to overcome its bond energy and decompose into calcium oxide (lime) and carbon dioxide.
Staying Below the Melting Point
This is a defining characteristic of calcination. The process must occur while the material is in a solid state. If the temperature exceeds the material's melting point, the process is no longer calcination; it becomes smelting or sintering, fundamentally changing the outcome and structure of the product.
Temperature as a Rate Controller
While there is a minimum temperature for decomposition, increasing the temperature (while still staying below melting) will significantly increase the rate of the reaction. Industrial processes often operate at higher temperatures to ensure the reaction completes quickly and efficiently.
The Critical Factor: Atmospheric Control
The gas surrounding the material during heating is just as important as the temperature itself. The atmosphere can be either a passive or an active participant in the reaction.
Forcing the Reaction to Completion
Many calcination reactions release a gas, such as CO₂ or H₂O. According to Le Châtelier's principle, the accumulation of this gas can slow or even reverse the reaction. Therefore, a key condition is often an airflow or vacuum that continuously removes the gaseous product, forcing the decomposition to proceed to completion.
Inert vs. Reactive Atmospheres
The choice of atmosphere prevents unwanted side reactions. An inert atmosphere, such as nitrogen or argon, is used when the goal is pure thermal decomposition without oxidation. A reactive atmosphere, such as air or pure oxygen, is intentionally used to burn off organic compounds or achieve a specific oxidation state in the final material.
Preventing Unwanted Oxidation
When creating high-purity metal oxides, heating the precursor material in open air can lead to uncontrolled reactions with oxygen. Using an inert atmosphere ensures that the only reaction taking place is the intended thermal decomposition, yielding a purer product.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variables
Achieving the perfect calcination conditions involves balancing several competing factors.
Temperature vs. Time
A lower temperature can still achieve calcination, but it will take a significantly longer time. This creates a practical trade-off between the energy cost of maintaining high temperatures and the processing time required for a complete reaction.
Particle Size and Heat Transfer
Heat must penetrate to the core of every particle for the reaction to be complete. Larger particles or a densely packed powder require more time, as heat transfer to the center is slower. Incomplete calcination is a common issue resulting from insufficient heating time for the given particle size.
Material Purity
Impurities in the starting material can have a significant impact. They can lower the material's melting point, leading to accidental sintering, or cause unintended side reactions that contaminate the final product. The purity of the raw material is a critical initial condition.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal calcination conditions are entirely dependent on the desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is producing a bulk chemical like lime: The main conditions are a temperature well above the decomposition point and a strong airflow to remove CO₂ efficiently.
- If your primary focus is activating a catalyst or adsorbent: Precise temperature control and a specific atmosphere (e.g., dry air) are critical to remove water or other volatiles without destroying the material's delicate porous structure.
- If your primary focus is preparing a high-purity ceramic powder: The key conditions are a highly pure starting material, precise temperature control to avoid sintering, and an atmosphere tailored to prevent unwanted oxidation.
Ultimately, mastering calcination lies in understanding that temperature and atmosphere are precise tools to control a material's chemical destiny.
Summary Table:
| Key Condition | Purpose & Importance |
|---|---|
| High Temperature | Drives thermal decomposition; must be below material's melting point. |
| Controlled Atmosphere | Removes gaseous products and prevents unwanted side reactions. |
| Particle Size & Purity | Affects heat transfer rate and final product quality. |
Ready to perfect your calcination process? KINTEK specializes in high-performance lab furnaces and equipment that deliver precise temperature control and atmospheric management. Whether you're developing catalysts, synthesizing ceramics, or processing minerals, our solutions ensure your reactions are efficient and repeatable. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific calcination needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a rotary heat type furnace? The Ultimate Guide to Uniform Heating & Mixing
- What is the purpose of pre-treating coal samples? Ensure Accurate Pyrolysis with Nitrogen Drying
- What are the advantages of a rotary furnace? Achieve Superior Homogeneity & Efficiency for Powders & Granules
- What is modified chemical vapour deposition method? The Inside-Out Process for Ultra-Pure Optical Fibers
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic



















