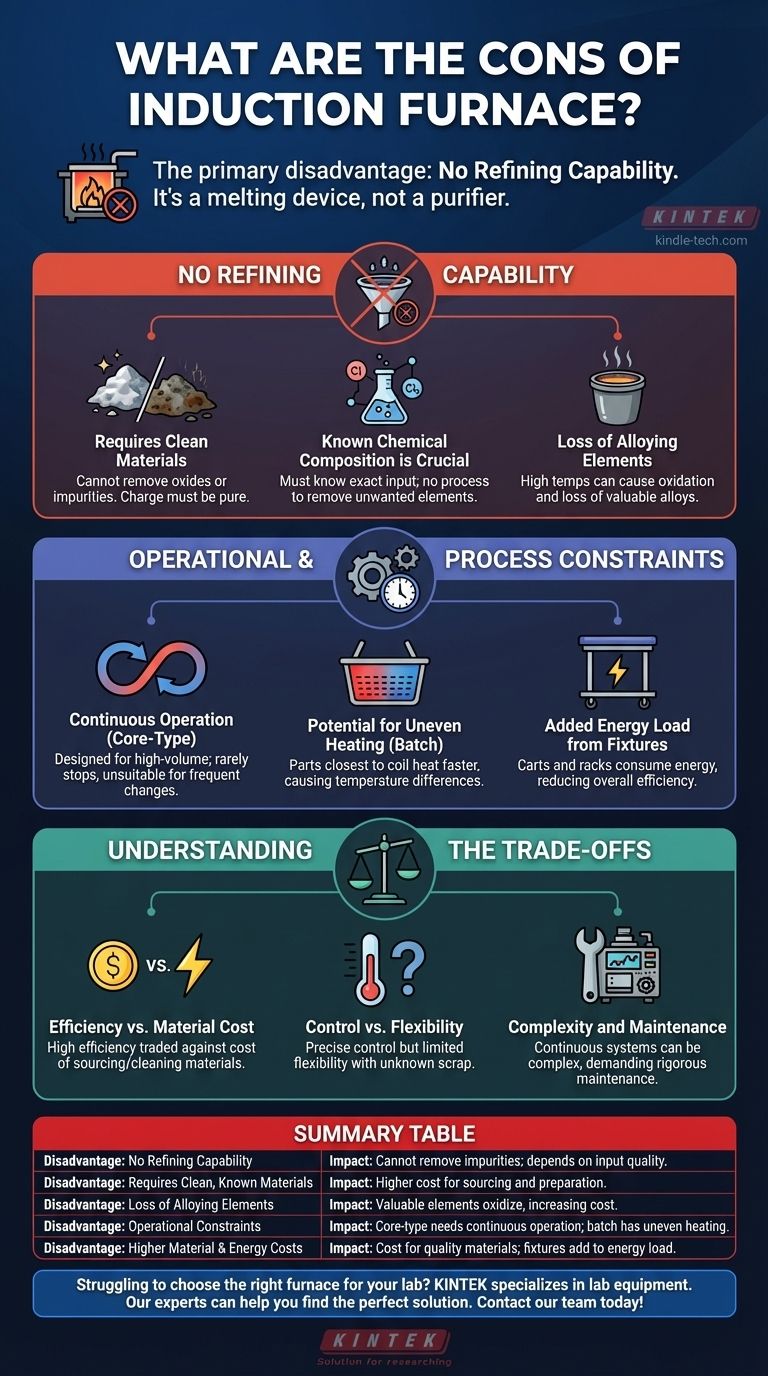
The primary disadvantage of an induction furnace is its lack of refining capability. Unlike furnaces that can purify raw materials, an induction furnace is fundamentally a melting device, meaning the quality of the output metal is almost entirely dependent on the quality of the materials you put in.
While prized for their speed, efficiency, and cleanliness, induction furnaces cannot remove impurities from the charge material. This core limitation dictates strict requirements for the raw materials used, which can impact cost and operational flexibility.

The Primary Limitation: No Refining Capability
The most significant constraint of an induction furnace is its inability to purify metal. This characteristic creates several operational requirements that must be carefully managed.
Requirement for Clean Materials
Because the furnace cannot remove oxides (like rust) or other non-metallic impurities, the charge materials must be clean. Any contaminants in the initial charge will remain in the final molten bath, potentially compromising the quality and integrity of the finished product.
Known Chemical Composition is Crucial
The furnace is a melter, not a converter. You must know the exact composition of the metals being loaded. Without this knowledge, achieving the precise chemical specifications for the final alloy is impossible, as there is no process to remove unwanted elements.
Loss of Alloying Elements
While induction heating is precise, the high temperatures can still cause some valuable alloying elements to be lost through oxidation. These elements must then be measured and re-added to the melt to meet specifications, adding a layer of complexity and cost to the process.
Operational and Process Constraints
Beyond material quality, the design and function of induction furnaces introduce specific operational challenges that can affect their suitability for certain applications.
Continuous Operation for Core-Type Furnaces
The highly efficient core-type induction furnace is designed for high-volume, continuous production. It is rarely allowed to cool down and requires constant maintenance of its molten metal loop, making it unsuitable for operations with frequent stops, startups, or diverse alloy changes.
Potential for Uneven Heating in Batch Processes
In batch-style induction furnaces, parts loaded into baskets or fixtures can heat unevenly. The pieces closest to the induction coil will heat faster than those in the center of the load. This can create an undesirable temperature difference across the batch, impacting metallurgical consistency.
Added Energy Load from Fixtures
Any carts, baskets, or racks used to hold the charge material inside a batch furnace must also be heated. This increases the total heat load and overall energy consumption, slightly reducing the system's acclaimed efficiency.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing an induction furnace involves balancing its distinct advantages against these practical limitations.
Efficiency vs. Material Cost
The high energy efficiency and clean operation are major benefits. However, this is traded against the potentially higher cost of sourcing, sorting, and cleaning charge materials to meet the furnace's strict input requirements.
Control vs. Flexibility
The furnace offers precise temperature control, which is excellent for maintaining alloy integrity. This comes at the cost of flexibility; it cannot easily handle dirty scrap or a wide variety of unknown raw materials the way a refining furnace can.
Complexity and Maintenance
While cleaner than combustion furnaces, some designs, particularly continuous systems, can be mechanically complex and expensive. They demand a rigorous and consistent maintenance schedule to ensure reliability and performance.
Is an Induction Furnace Right for Your Application?
Your decision should be based on a clear understanding of your materials, process, and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is melting clean, pre-alloyed metals with high precision: An induction furnace is the ideal tool, as its "con" of not refining becomes a feature that preserves your known alloy composition.
- If your primary focus is processing raw, contaminated scrap or refining ore: An induction furnace is fundamentally the wrong choice; you require a furnace with active refining capabilities, such as an Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) or a Basic Oxygen Furnace (BOF).
- If you require intermittent production with varied alloys: A coreless batch-type induction furnace is more suitable than a core-type, but you must still manage clean materials and account for potential heating inconsistencies.
Ultimately, an induction furnace is an exceptional tool for remelting and holding applications, provided you can control the quality of the materials you feed it.
Summary Table:
| Disadvantage | Impact on Operation |
|---|---|
| No Refining Capability | Cannot remove impurities; final metal quality depends entirely on input material quality. |
| Requires Clean, Known Materials | Higher cost for sourcing and preparing clean scrap or pre-alloyed metals. |
| Loss of Alloying Elements | Valuable elements can oxidize and be lost, requiring re-addition and increasing cost. |
| Operational Constraints | Core-type furnaces require continuous operation; batch types can have uneven heating. |
| Higher Material & Energy Costs | Increased cost for high-quality materials; fixtures in batch furnaces add to energy load. |
Struggling to choose the right furnace for your lab's melting needs? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate the pros and cons of different furnace technologies to find the perfect solution for your specific materials and processes. Contact our team today to discuss your application and ensure you get the performance and reliability your research demands!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Lab-Scale Vacuum Induction Melting Furnace
- 600T Vacuum Induction Hot Press Furnace for Heat Treat and Sintering
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a vacuum induction melting furnace? Melt High-Purity Metals with Precision
- What is vacuum arc melting technique? Discover the Precision of Vacuum Induction Melting
- What is the difference between induction melting and vacuum induction melting? Choosing the Right Process for Purity
- What types of metals are typically processed in a vacuum induction melting furnace? High-Purity Alloys for Critical Applications
- What principle is used to generate heat in a vacuum induction melting furnace? Achieve Clean, Efficient Metal Melting



















