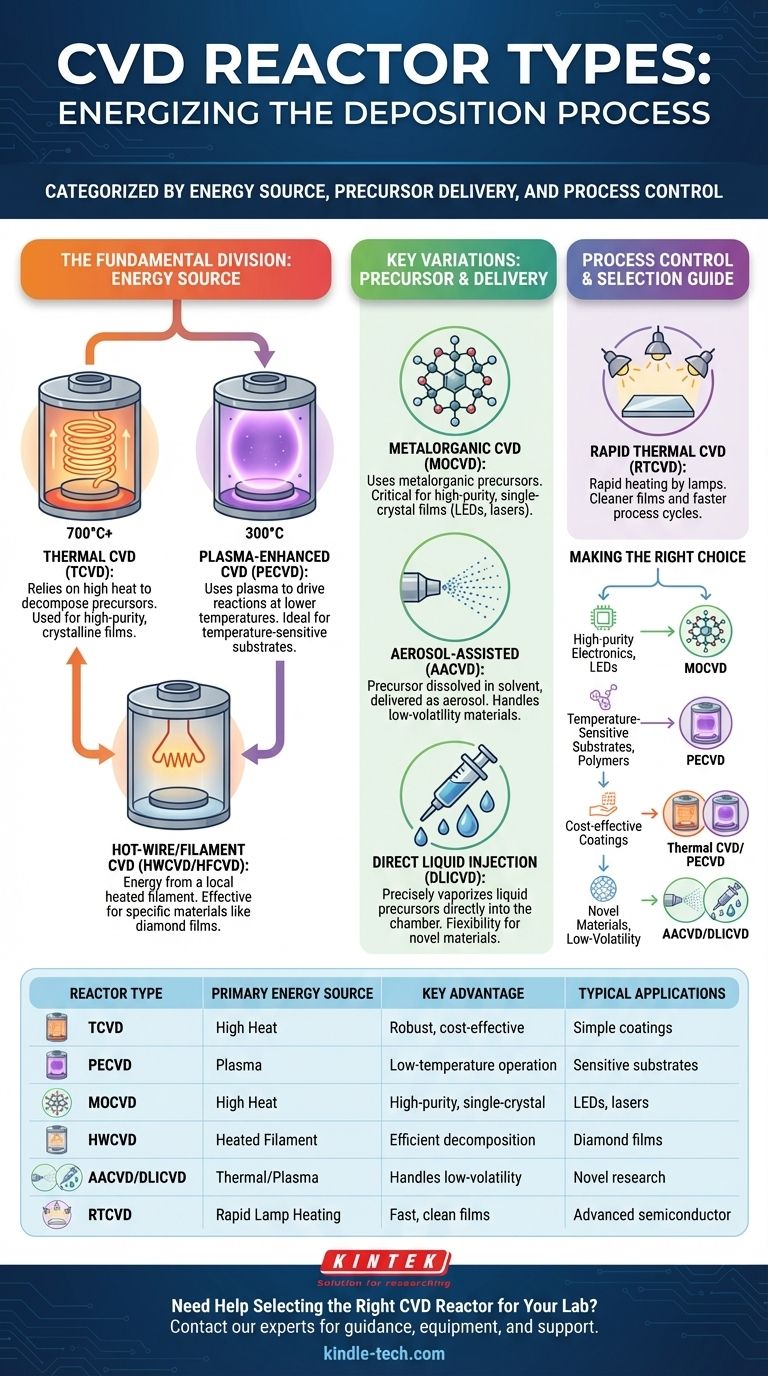
The primary types of Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) reactors are categorized by the method used to provide energy for the chemical reaction. The two most fundamental categories are Thermal CVD, which relies on high heat, and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), which uses a plasma to drive reactions at lower temperatures. From these, numerous specialized variations have been developed to handle different precursor materials and achieve specific film properties.
The choice of a CVD reactor is not about finding the "best" one, but about matching the reactor's energy source, operating pressure, and precursor delivery system to the specific requirements of the material you want to deposit and the substrate you are using.
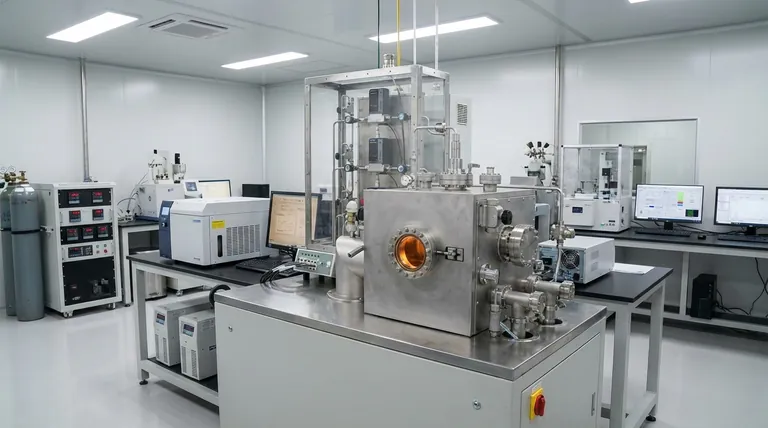

The Fundamental Division: How is the Reaction Energized?
The core difference between CVD reactor designs lies in how they supply the energy needed to break down the precursor gases and initiate film deposition on the substrate.
Thermal CVD (TCVD)
Thermal CVD is the classic approach, using high heat to energize the chemical reaction. The entire reaction chamber, including the substrate, is typically heated to temperatures often exceeding 700°C.
This high thermal energy causes the precursor gases to decompose and react on the heated substrate surface, forming the desired solid film.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
PECVD reactors operate at much lower temperatures, typically around 300°C. Instead of relying solely on heat, they generate a plasma (an ionized gas) within the chamber.
This plasma creates highly reactive chemical species (ions and radicals) that can deposit as a film without requiring extreme heat. This makes PECVD ideal for depositing on temperature-sensitive substrates like plastics or complex integrated circuits.
Hot-Wire/Filament CVD (HWCVD/HFCVD)
This method is a variation of thermal CVD where energy is supplied locally by a heated metal filament (like tungsten or tantalum) placed near the substrate.
The hot filament efficiently decomposes the precursor gases, which then deposit onto the nearby, often cooler, substrate. This technique is highly effective for specific materials, such as amorphous silicon or diamond films.
Key Variations Based on Precursor and Delivery
Beyond the energy source, reactors are also specialized to handle different types of precursor materials—the chemical building blocks of the film.
Metalorganic CVD (MOCVD)
MOCVD is a highly precise form of thermal CVD that uses metalorganic precursors, which are complex molecules containing both metal and organic components.
This method is critical for manufacturing high-purity, single-crystal thin films, making it the cornerstone technology for producing modern LEDs, lasers, and high-performance transistors.
Aerosol-Assisted and Direct Liquid Injection CVD (AACVD/DLICVD)
These specialized systems are designed to use precursors that are liquids or solids with low volatility, making them difficult to turn into a gas by simple heating.
In AACVD, the precursor is dissolved in a solvent and turned into a fine aerosol mist that is carried into the reaction chamber. DLICVD uses high-pressure injectors to vaporize a precise amount of liquid precursor directly into the chamber.
Variations for Process Control and Speed
Some reactor designs are optimized for specific process outcomes, such as deposition speed or film purity.
Rapid Thermal CVD (RTCVD)
In an RTCVD system, the substrate is heated very quickly using high-intensity lamps. The chamber walls remain cool.
This rapid heating minimizes the time for unwanted chemical reactions to occur in the gas phase before the precursors reach the substrate, resulting in cleaner films and faster process cycles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD method involves balancing competing factors. There is no single solution that is superior for all applications.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
High-temperature processes like Thermal CVD often produce higher-quality, more crystalline films. However, these temperatures can damage or destroy sensitive substrates.
Low-temperature PECVD enables deposition on a wide variety of materials but can sometimes result in films with lower density or impurities (like hydrogen) incorporated from the plasma.
Complexity vs. Capability
Simple thermal CVD reactors are robust and cost-effective. However, they are limited to thermally stable substrates and precursors that vaporize easily.
More complex systems like MOCVD and DLICVD are more expensive and require sophisticated control systems but unlock the ability to deposit a vast range of advanced materials with exceptional purity.
Conformal Coverage vs. Line-of-Sight
A key advantage of CVD is its multidirectional deposition, allowing it to uniformly coat complex, three-dimensional surfaces. This is a significant advantage over line-of-sight processes like Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD).
However, achieving perfect uniformity inside deep trenches or complex topographies remains a challenge that depends heavily on reactor design, pressure, and gas flow dynamics.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Your application's specific needs will dictate the most appropriate CVD reactor technology.
- If your primary focus is high-purity crystalline films for electronics (e.g., LEDs): MOCVD is the industry standard due to its unmatched precision and material quality.
- If your primary focus is depositing films on temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., polymers): PECVD is the definitive choice because of its low-temperature operation.
- If your primary focus is cost-effective, simple oxide or nitride coatings: A standard Thermal CVD or PECVD system is likely the most practical and economical solution.
- If your primary focus is exploring novel materials with low-volatility precursors: AACVD or DLICVD provides the essential flexibility to work with a wider chemical palette.
Ultimately, understanding these core reactor types empowers you to select the process that best balances performance, material compatibility, and cost for your specific objective.
Summary Table:
| Reactor Type | Primary Energy Source | Key Advantage | Typical Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD (TCVD) | High Heat | Robust, cost-effective | Simple oxide/nitride coatings |
| Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) | Plasma | Low-temperature operation | Temperature-sensitive substrates (e.g., polymers) |
| Metalorganic CVD (MOCVD) | High Heat | High-purity, single-crystal films | LEDs, lasers, high-performance transistors |
| Hot-Wire CVD (HWCVD) | Heated Filament | Efficient precursor decomposition | Amorphous silicon, diamond films |
| Aerosol-Assisted/DLI CVD | Thermal/Plasma | Handles low-volatility precursors | Novel materials research |
| Rapid Thermal CVD (RTCVD) | Rapid Lamp Heating | Fast process cycles, clean films | Advanced semiconductor manufacturing |
Need Help Selecting the Right CVD Reactor for Your Lab?
Choosing the correct CVD reactor is critical for achieving your desired film properties and substrate compatibility. The experts at KINTEK specialize in matching laboratory equipment to your specific research and production goals.
We provide:
- Expert Guidance: Our team will help you navigate the trade-offs between temperature, material compatibility, and process complexity to select the ideal CVD system.
- High-Quality Equipment: From robust Thermal CVD systems to advanced MOCVD and PECVD reactors, we supply reliable equipment for depositing everything from simple coatings to high-purity electronic films.
- Ongoing Support: We ensure your lab operates at peak efficiency with comprehensive service and consumables support.
Ready to enhance your thin-film deposition capabilities? Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and find the perfect CVD solution for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
People Also Ask
- What is the difference between PECVD and APCVD? Choose the Right CVD Method for Your Application
- What are the process capabilities of ICPCVD systems? Achieve Low-Damage Film Deposition at Ultra-Low Temperatures
- Why is a Matching Network Indispensable in RF-PECVD for Siloxane Films? Ensure Stable Plasma and Uniform Deposition
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition



















