The primary defects in aluminum brazing stem directly from two core challenges: the rapid formation of a stubborn oxide layer and the extremely narrow temperature window between the filler metal and the base aluminum. This oxide layer prevents the filler metal from properly wetting the joint, leading to incomplete bonds and voids. Simultaneously, even minor deviations in temperature can either melt the parent material or fail to activate the filler, both resulting in a failed joint.
Success in aluminum brazing is not just about technique, but about precise process control. The fundamental challenge is managing aluminum's reactive nature and its unforgiving thermal properties, which are the root cause of nearly all common brazing defects.
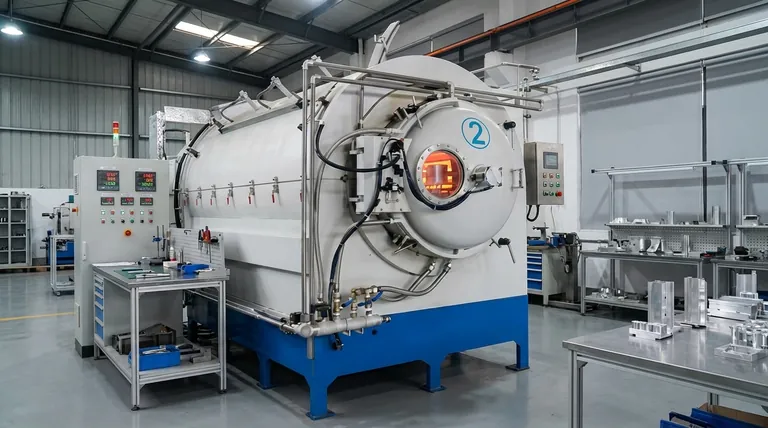

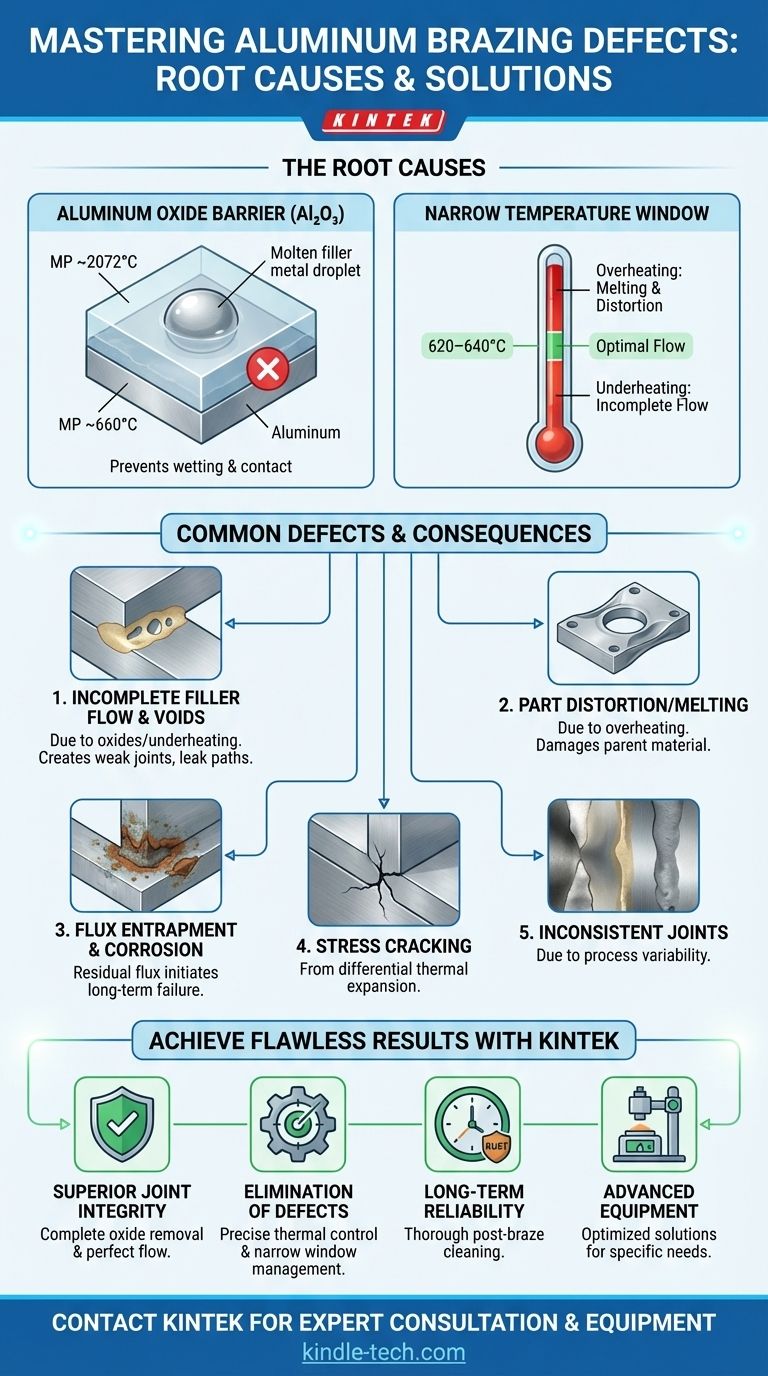
The Root Causes of Aluminum Brazing Defects
To troubleshoot or prevent defects, you must understand the underlying material science that makes aluminum brazing uniquely challenging. The most common failures are direct consequences of these properties.
The Aluminum Oxide (Al₂O₃) Barrier
Aluminum is highly reactive and instantly forms a tough, transparent layer of aluminum oxide (Al₂O₃) when exposed to air.
This oxide layer has a melting point of approximately 2072°C (3762°F), which is far higher than the melting point of the base aluminum itself, around 660°C (1220°F).
Because the oxide does not melt during the brazing cycle, it acts as a physical barrier. This prevents the molten filler metal from making contact with and flowing across the base metal, a phenomenon known as wetting. This is the single greatest challenge in aluminum brazing.
The Narrow Temperature Processing Window
Aluminum brazing alloys are designed to melt at a temperature only slightly below that of the base material—often with a gap of just 20-40°C.
This creates an extremely narrow and unforgiving processing window. Overheating by a small margin will cause the parent components to melt, sag, or distort.
Conversely, underheating will prevent the filler metal from becoming fully liquid. This inhibits its ability to flow via capillary action, which is necessary to completely fill the gap in the joint. Uniform thermal distribution across the entire assembly is critical.
Incomplete Filler Flow and Voids
The direct result of failing to manage oxides or temperature is an incomplete joint. These defects manifest as voids, skips, or unwetted areas.
When the filler metal encounters an un-fluxed patch of oxide or a cold spot, its flow is arrested. It may "ball up" on the surface instead of being drawn into the joint.
These voids act as stress concentrators, drastically reducing the mechanical strength of the joint. They also create potential leak paths in applications requiring a hermetic seal.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Complications
Beyond the core challenges, several other factors can introduce defects or complicate the brazing process, particularly regarding material selection and post-process reliability.
Differential Thermal Expansion
When brazing aluminum to a different material, such as copper or steel, their different rates of thermal expansion become a major concern.
As the assembly cools from the brazing temperature, one material will contract more or faster than the other. This generates significant internal stress on the newly formed brazed joint.
This stress can be strong enough to cause cracks in the filler metal or even in the base material, leading to immediate or delayed joint failure.
The Challenge of Repairing Defects
While defective joints can often be repaired by re-brazing, the process is not as simple as reheating the part.
During the initial brazing cycle, the filler alloy's chemical composition changes slightly, which increases its re-melt temperature.
Simply reheating the assembly will likely not be sufficient to re-flow the existing filler. A successful repair almost always requires the application of additional new filler alloy to the defective area.
Flux Entrapment and Corrosion
To break down the aluminum oxide layer, chemical fluxes are used in many brazing processes. These fluxes are typically highly corrosive.
If the flux is not completely removed after brazing, residue can become trapped within the joint.
This entrapped flux will attract moisture and initiate corrosion over time, compromising the long-term integrity and reliability of the joint.
Achieving a Successful Aluminum Braze
Based on these challenges, the success of your project depends on precisely controlling your process variables. Your strategy should directly address the root causes of failure.
- If your primary focus is joint integrity: Prioritize meticulous cleaning and the correct application of flux (or a flux-free vacuum environment) to completely remove the oxide layer before heating.
- If your primary focus is avoiding part distortion: Implement precise, uniform temperature control with calibrated equipment to stay within the narrow processing window.
- If your primary focus is long-term reliability: Ensure a thorough post-braze cleaning process to remove all corrosive flux residue from the assembly.
- If you are brazing dissimilar materials: Design the joint with features that can accommodate for differential thermal expansion to prevent stress-induced cracking upon cooling.
Mastering aluminum brazing is a matter of respecting the material's properties and implementing rigorous process discipline.
Summary Table:
| Defect Type | Root Cause | Primary Consequence |
|---|---|---|
| Aluminum Oxide Barrier | Rapid formation of a high-melting-point oxide layer (Al₂O₃) | Prevents filler metal wetting, leading to incomplete bonds |
| Incomplete Filler Flow & Voids | Improper temperature control or insufficient oxide removal | Creates weak joints and potential leak paths |
| Part Distortion/Melting | Overheating beyond the narrow 20-40°C processing window | Melts or warps the base aluminum components |
| Flux Entrapment & Corrosion | Failure to remove corrosive flux residue post-braze | Initiates long-term corrosion, compromising joint integrity |
| Stress Cracking | Differential thermal expansion when brazing dissimilar materials | Causes immediate or delayed joint failure upon cooling |
Achieve Flawless Aluminum Brazing with KINTEK
Struggling with oxide barriers, inconsistent joints, or part distortion? Your lab's success depends on precise thermal management and process control. KINTEK specializes in the advanced lab equipment and consumables necessary to master the challenges of aluminum brazing.
We provide solutions that deliver:
- Superior Joint Integrity: Ensure complete oxide removal and perfect filler metal flow for strong, reliable bonds.
- Elimination of Defects: Maintain the critical narrow temperature window to prevent base metal melting and distortion.
- Long-Term Reliability: Achieve thorough post-braze cleaning to prevent flux-induced corrosion.
Let our experts help you optimize your brazing process. Contact KINTEK today for a consultation and discover the right equipment for your laboratory's specific needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is a vacuum furnace used for? Unlock Purity in High-Temperature Processing
- What is the cost of a vacuum brazing furnace? A guide to key factors and investment strategy
- What are vacuum furnaces used for? Unlock Ultimate Material Purity and Performance
- What is vacuum brazing? The Ultimate Guide to High-Purity, Flux-Free Metal Joining
- What is the process of a vacuum furnace? Achieve Purity and Precision in High-Temp Processing



















