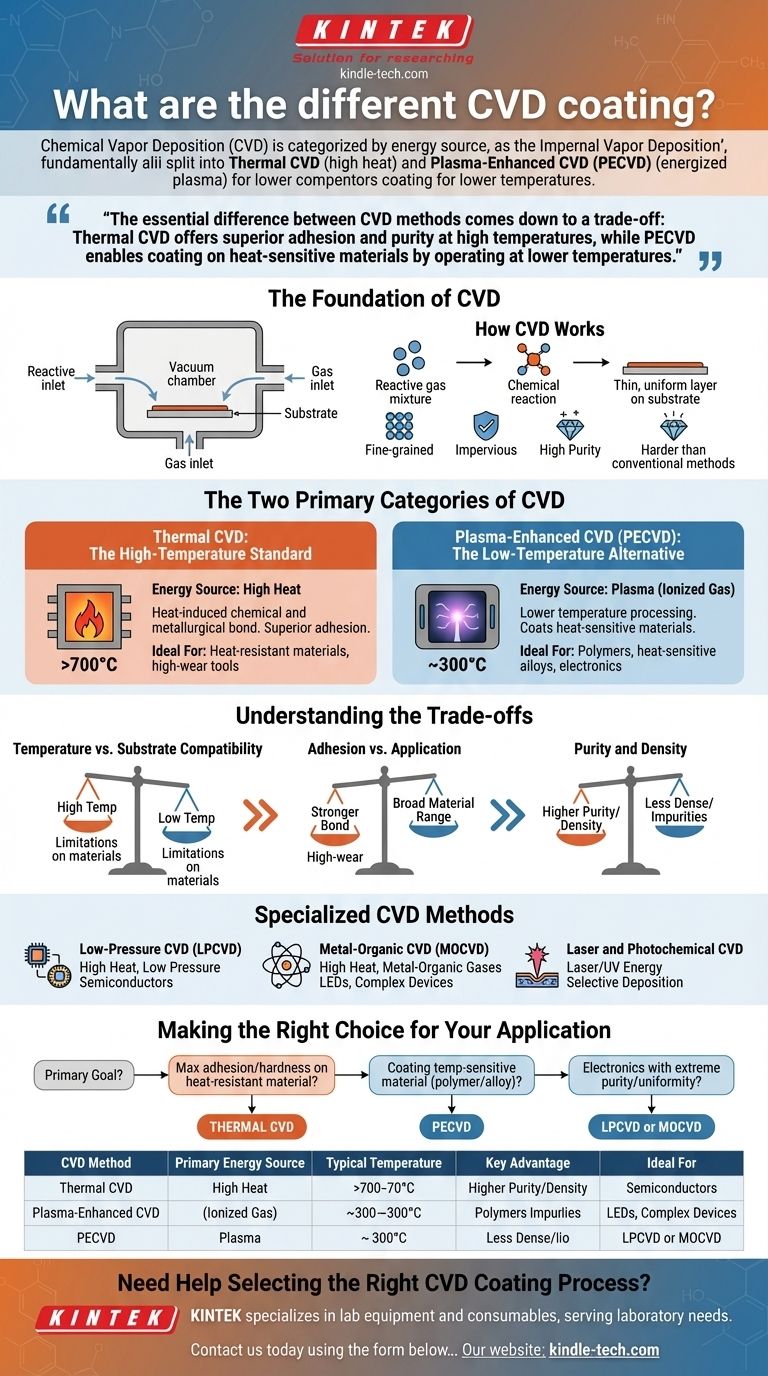
At its core, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is categorized by the energy source used to initiate the chemical reaction. The two fundamental types are Thermal CVD, which relies on high heat to deposit films, and Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), which uses an energized plasma to achieve deposition at much lower temperatures. Other specialized variations exist for highly specific applications.
The essential difference between CVD methods comes down to a trade-off: Thermal CVD offers superior adhesion and purity at high temperatures, while PECVD enables coating on heat-sensitive materials by operating at lower temperatures.

The Foundation of CVD: What It Is and Why It's Used
How CVD Works
Chemical Vapor Deposition is a process where a thin film is applied to a material's surface, known as a substrate. This occurs inside a vacuum chamber where a reactive gas mixture is introduced. The gases undergo a chemical reaction, causing a solid material to deposit as a very thin, uniform layer onto the substrate.
Key Characteristics of CVD Coatings
The resulting coatings are known for their exceptional qualities. They are typically fine-grained, impervious, and possess high purity.
This process produces films that are significantly harder than similar materials made through conventional fabrication methods. The deposition rate is fairly slow, but the quality of the resulting bond is extremely high.
The Two Primary Categories of CVD
The most critical distinction in CVD processes is how the necessary energy is supplied to drive the chemical reaction. This factor dictates the process temperature and, consequently, which materials can be coated.
Thermal CVD: The High-Temperature Standard
In a traditional thermal CVD process, the reaction chamber is heated to a very high temperature, often above 700°C. This intense heat provides the energy needed for the precursor gases to decompose and react, forming the coating on the substrate's surface.
The primary advantage of this method is the creation of a heat-induced chemical and metallurgical bond. This results in adhesion that is generally superior to other methods.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): The Low-Temperature Alternative
PECVD uses plasma—an ionized gas—to generate highly reactive species within the chamber. This plasma provides the energy for the reaction, allowing the deposition process to occur at significantly lower temperatures, typically around 300°C.
This makes PECVD invaluable for coating substrates that cannot withstand the extreme heat of thermal CVD, such as certain plastics, polymers, or heat-sensitive metal alloys.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a CVD method requires a clear understanding of the give-and-take between process parameters and desired outcomes.
Temperature vs. Substrate Compatibility
The most significant trade-off is temperature. The extreme heat of Thermal CVD provides excellent coating properties but restricts its use to materials that can survive the process without warping, melting, or losing their structural integrity. PECVD's low-temperature nature dramatically expands the range of compatible substrate materials.
Adhesion vs. Application
The high temperatures in Thermal CVD promote a stronger, deeper metallurgical bond between the coating and the substrate. This makes it the preferred method for high-wear applications, such as metal-forming tools, where durability and adhesion are paramount.
Purity and Density
Generally, high-temperature processes like Thermal CVD allow atoms more energy to settle into a dense, highly ordered, and pure crystalline structure. Low-temperature processes like PECVD, while highly effective, can sometimes result in less dense films or the incorporation of impurities.
Specialized CVD Methods
Beyond the two main categories, several other types of CVD are used for specific industrial and research needs.
Low-Pressure CVD (LPCVD)
This is a variant of Thermal CVD conducted at very low pressure. The reduced pressure enhances the uniformity and purity of the coating, making it a common process in manufacturing semiconductors and microelectronics.
Metal-Organic CVD (MOCVD)
MOCVD uses metal-organic compounds as the precursor gases. This technique offers precise control over film composition and thickness, and it is critical for creating complex semiconductor devices like high-performance LEDs.
Laser and Photochemical CVD
These methods use focused energy from a laser or an ultraviolet lamp to initiate the reaction. This allows for highly selective deposition, effectively "drawing" a coating onto a specific area of the substrate without heating the entire part.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
To select the appropriate process, you must first define your primary goal and the limitations of your substrate material.
- If your primary focus is maximum adhesion and hardness on a heat-resistant material: Thermal CVD is the superior choice due to its powerful, high-temperature metallurgical bond.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like a polymer or certain alloys: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the necessary solution because of its low-temperature operation.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing electronics with extreme purity and uniformity: A specialized method like LPCVD or MOCVD is required to achieve the necessary precision.
Ultimately, choosing the right CVD process requires balancing the desired coating properties with the thermal limitations of your substrate material.
Summary Table:
| CVD Method | Primary Energy Source | Typical Temperature | Key Advantage | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD | High Heat | >700°C | Superior Adhesion & Purity | Heat-resistant materials, high-wear tools |
| PECVD | Plasma | ~300°C | Low-Temperature Processing | Polymers, heat-sensitive alloys, electronics |
| LPCVD | High Heat (Low Pressure) | High | High Uniformity & Purity | Semiconductors, microelectronics |
| MOCVD | High Heat (Metal-Organic) | High | Precise Composition Control | LEDs, complex semiconductor devices |
Need Help Selecting the Right CVD Coating Process?
Choosing between Thermal CVD, PECVD, and other specialized methods is critical to your project's success. The wrong choice can lead to substrate damage or inadequate coating performance.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you navigate these critical decisions. We provide the equipment and technical support to ensure you achieve the perfect coating for your specific material and application requirements.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your project and discover how our solutions can enhance your research and development outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Lab and Diamond Growth
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- CVD Diamond Optical Windows for Lab Applications
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
People Also Ask
- What is the temperature of PECVD deposition? Achieve High-Quality Films at Low Temperatures
- What is the plasma CVD process? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the uses of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin-Film Deposition
- What is plasma activated chemical vapor deposition? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















