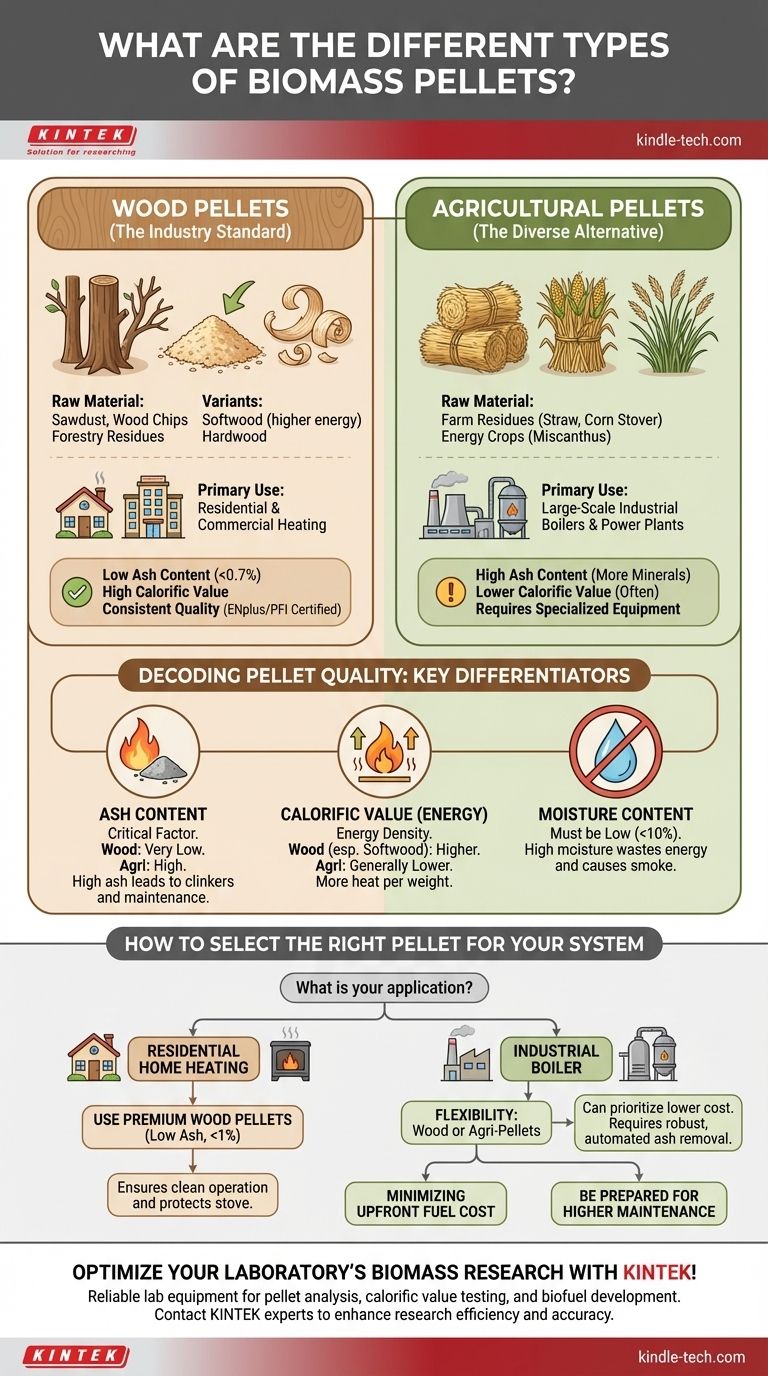
Fundamentally, biomass pellets fall into two main categories based on their raw material source. These are wood pellets, derived from forestry products like sawdust and wood chips, and agricultural pellets (or agri-pellets), made from farm residues such as straw, corn stover, or dedicated energy crops. While both are forms of densified biomass, their distinct properties dictate their appropriate use.
The critical factor in choosing a biomass pellet is not simply its source material, but matching its specific properties—primarily ash content and calorific value—to the sensitivity and design of your combustion equipment.

The Two Primary Categories of Biomass Pellets
Understanding the origin of a pellet is the first step. The raw material directly influences its burning characteristics, ash output, and ultimately, its suitability for a given application.
Wood Pellets: The Industry Standard
Wood pellets are the most common type, especially in residential and commercial heating. They are manufactured by compressing clean sawdust, wood shavings, or forestry residues.
Within this category, you will find distinctions based on the wood source, such as softwood (e.g., pine, fir) and hardwood (e.g., oak, maple). Softwood pellets generally have a higher resin content, which leads to a slightly higher energy value and better compaction during production.
Agricultural Pellets: The Diverse Alternative
Agricultural pellets utilize a wide range of non-wood biomass. This includes crop residues like straw and corn stover, or dedicated energy crops like miscanthus (switchgrass).
These pellets are typically used in large-scale industrial boilers and power plants. The equipment in these facilities is specifically engineered to handle the unique properties of agri-pellets, which differ significantly from wood pellets.
Decoding Pellet Quality: Key Differentiators
The source material is just the starting point. The true performance of a pellet is defined by a few key technical specifications. These metrics are what separate a premium fuel from a low-grade alternative.
Ash Content
Ash content is arguably the most critical factor. It refers to the amount of incombustible mineral residue left after the pellet is burned.
Wood pellets, particularly those made from debarked logs and clean sawdust, have very low ash content (often below 0.7%). In contrast, agri-pellets have a much higher ash content because plants absorb more minerals (like silica and potassium) from the soil.
A high ash content can lead to slagging and the formation of hard deposits called clinkers in the burner, requiring frequent and intensive maintenance.
Calorific Value (Energy Content)
This metric measures the amount of energy released when the pellet is burned, often expressed in BTU per pound or megajoules per kilogram. A higher calorific value means you get more heat from the same amount of fuel.
Softwood pellets typically have a slightly higher calorific value than hardwood pellets. Both, however, generally offer more energy density than many types of agri-pellets.
Moisture Content
For efficient combustion, moisture content must be low, ideally under 10%. High moisture wastes energy by converting water to steam and can lead to incomplete combustion and excessive smoke. Reputable pellet manufacturers carefully control for moisture.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Selecting the right pellet involves balancing cost, performance, and equipment requirements. An incorrect choice can lead to inefficiency, high maintenance costs, and even equipment damage.
Cost vs. Quality
Agri-pellets or lower-grade wood pellets (made with bark or other contaminants) are often cheaper to produce and purchase. However, the lower upfront cost is frequently offset by higher maintenance demands due to ash-related issues.
Premium wood pellets cost more but provide a cleaner, more efficient burn with minimal residue, protecting your equipment and reducing your maintenance workload.
Equipment Compatibility
This is the most important trade-off. Standard residential pellet stoves are not designed to handle high-ash fuels. Using agri-pellets or low-grade wood pellets in such a stove will quickly lead to clinkers, blockages, and potential system failure.
Industrial boilers, on the other hand, are built with more robust materials and often include features like automated ash removal systems, making them fully capable of utilizing higher-ash agricultural pellets.
Sourcing and Certification
The reliability of your fuel supply is also a factor. Wood pellets are widely available, and certifications like ENplus or PFI (Pellet Fuels Institute) provide a guarantee of quality regarding ash content, moisture, and energy value. The supply chain for specific types of agri-pellets may be more localized or less consistent.
How to Select the Right Pellet for Your System
Your choice must be driven by your specific application and equipment.
- If your primary focus is residential home heating: You must use premium-grade wood pellets with a certified low ash content (typically under 1%). This ensures clean operation and protects your stove from damage.
- If you are operating a large-scale industrial boiler: You have the flexibility to use a wider range of fuels, including lower-grade wood pellets and various agri-pellets, allowing you to prioritize the lowest-cost fuel source.
- If your main driver is minimizing upfront fuel cost: Be prepared for the consequences. This path is only viable if you have industrial-grade equipment and are willing to accept significantly higher maintenance requirements.
Ultimately, understanding these core differences empowers you to select a fuel that optimizes performance, cost, and the long-term health of your equipment.
Summary Table:
| Pellet Type | Primary Raw Material | Typical Ash Content | Primary Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Wood Pellets | Sawdust, Wood Chips | Low (< 1%) | Residential/Commercial Heating |
| Agricultural Pellets | Straw, Corn Stover | High | Industrial Boilers/Power Plants |
Optimize your laboratory's biomass research with the right equipment from KINTEK!
Whether you are analyzing pellet composition, testing calorific value, or developing new biofuel formulations, having reliable lab equipment is crucial. KINTEK specializes in supplying high-quality laboratory apparatus and consumables to support your work in biomass and renewable energy.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research efficiency and accuracy.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- FS Electrochemical Hydrogen Fuel Cells for Diverse Applications
- Customizable Fuel Cell Stack Components for Diverse Applications
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
- Twin Screw Extruder Plastic Granulation Machine
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
People Also Ask
- What structural advantages do PEM electrolyzers offer? Compact, High-Density Hydrogen Production Solutions
- What role does a double-chamber electrochemical permeation cell play in studying hydrogen diffusion in 9% Cr steel?
- What are the technical advantages of using ceramic materials as membranes in MFC stacks? Boost Scalability and Durability
- What are the dimensions for thin-layer spectroelectrochemical cells? Optimize Your Lab's Optical Path Length
- What are the procedures for handling a proton exchange membrane after use? Ensure Longevity and Performance




